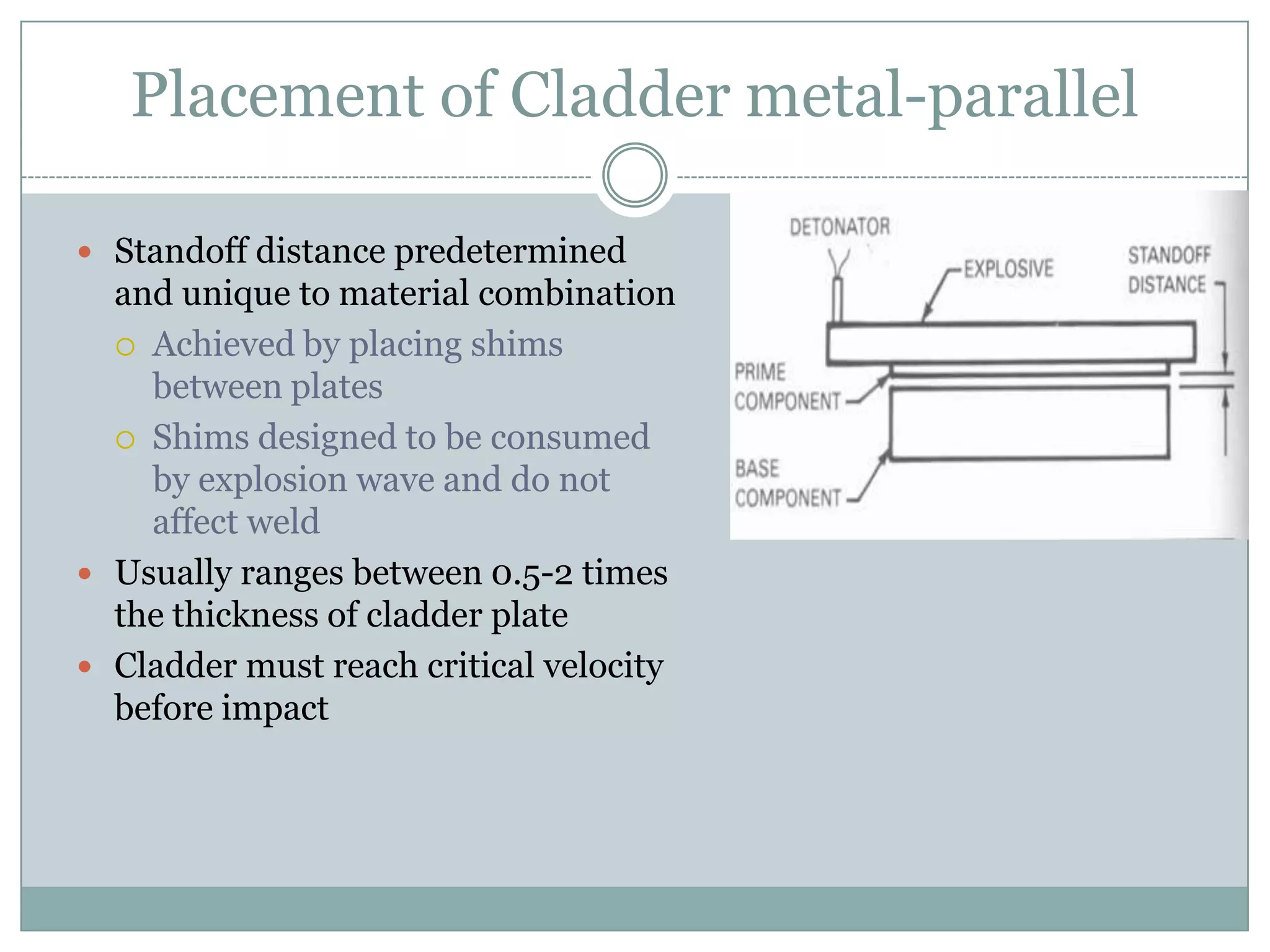
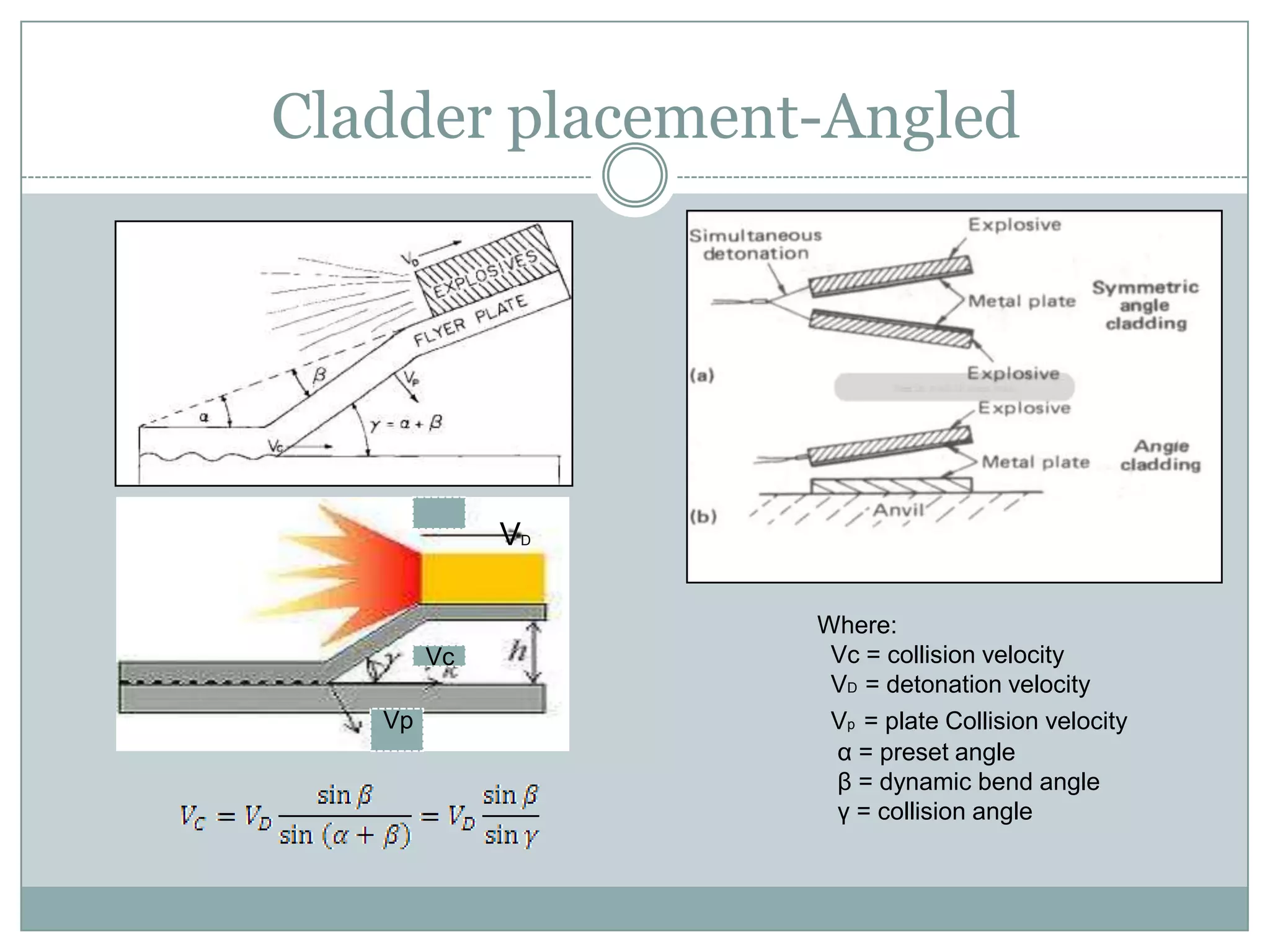
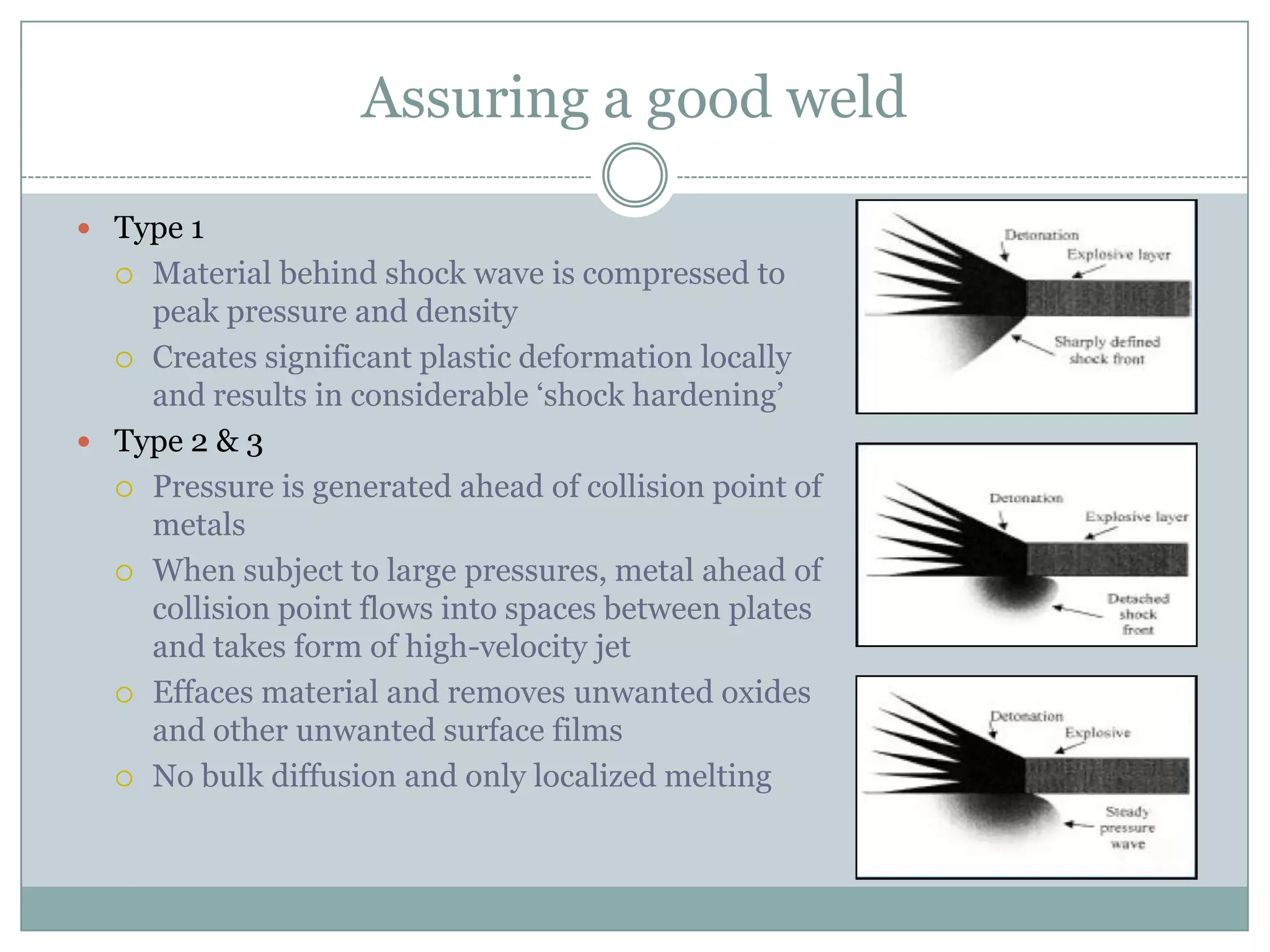
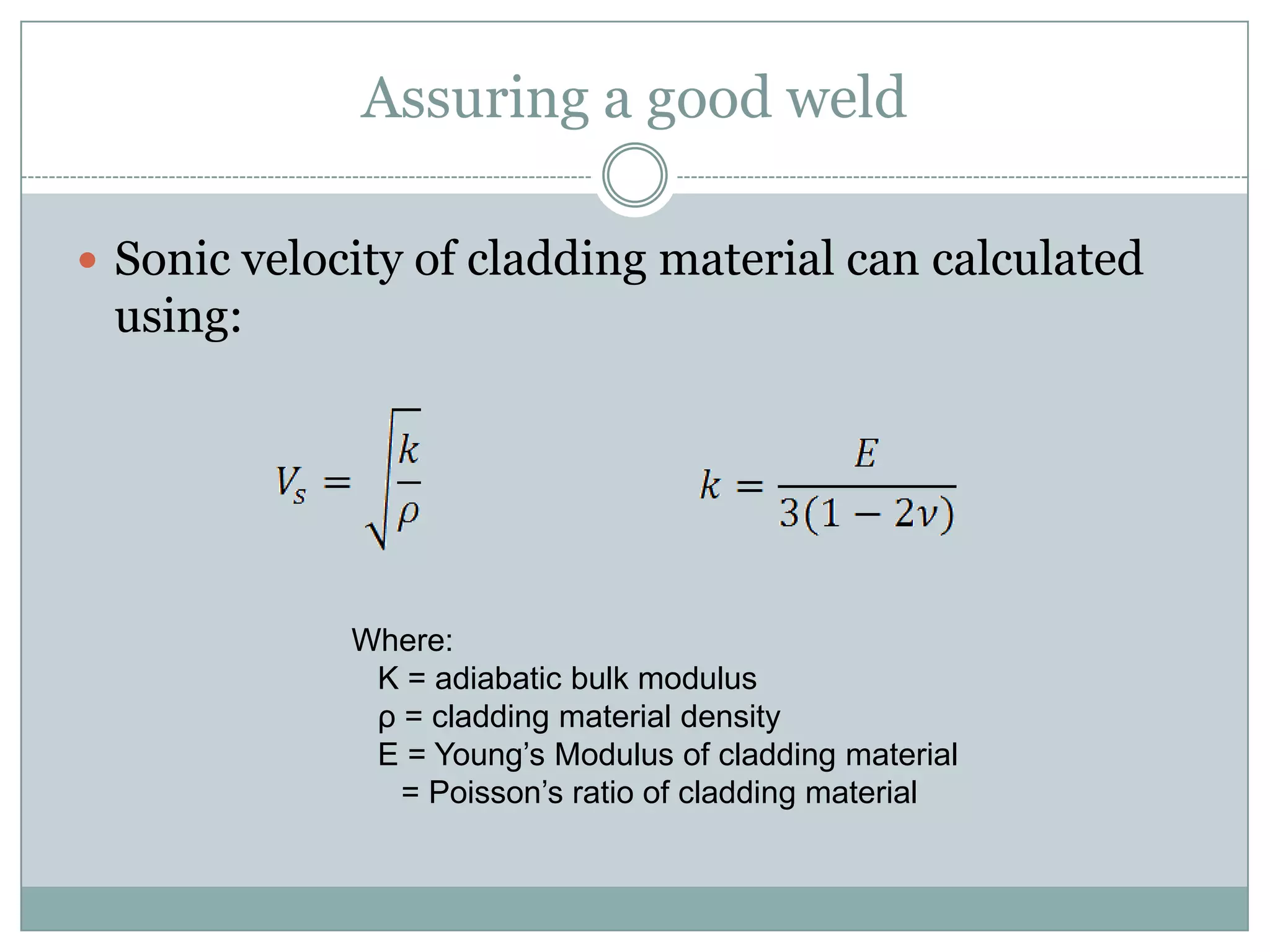
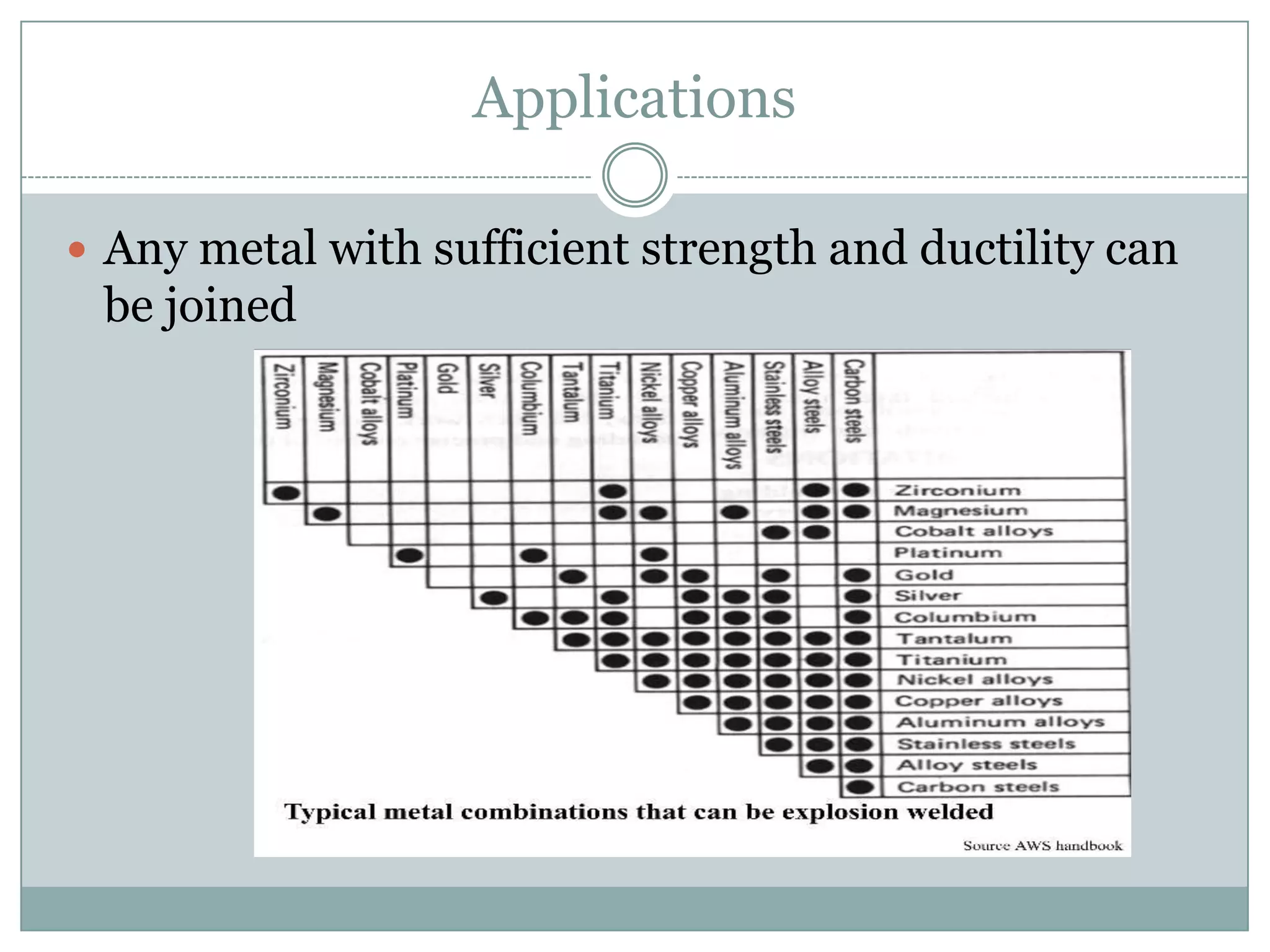
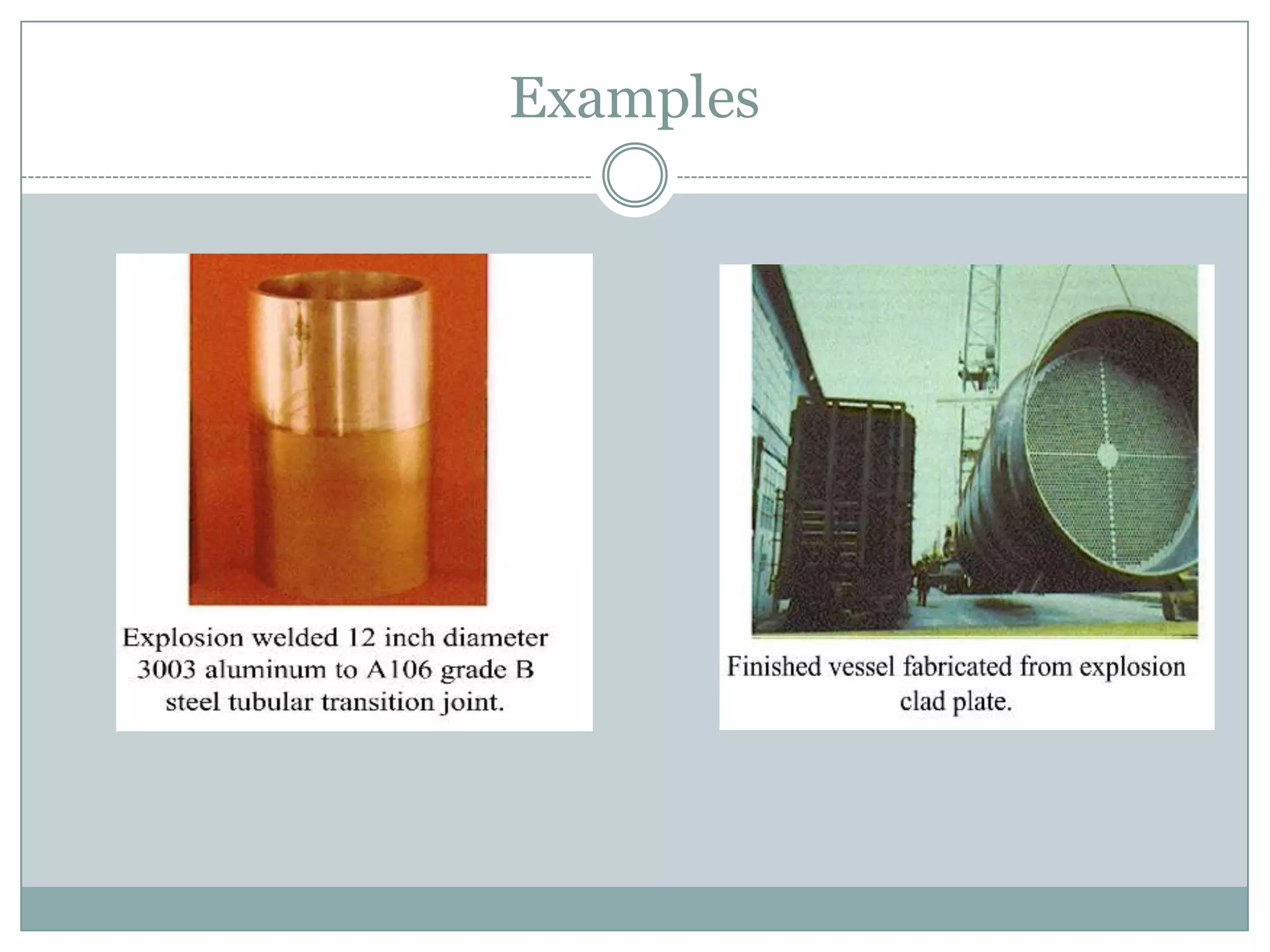
Explosion welding is a solid-state process that enables the high-velocity bonding of dissimilar metals through controlled detonation, avoiding significant heat-affected zones. The bonding process depends on factors like the standoff distance, collision velocities, and explosive types, ensuring intimate contact between the metals for effective welding. Applications span various industries, including chemical processing, shipbuilding, and power generation, and the technique has historical significance dating back to the early 1960s.