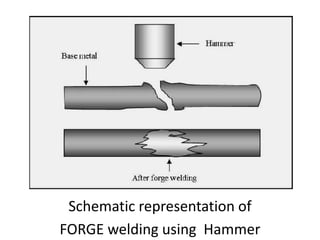
This presentation provides an overview of forge welding, including its principles, classification, process parameters, temperature requirements, tools needed, forgeable metals, common hand tools, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Forge welding is a solid-state welding process that joins two pieces of metal by heating them above 1000 degrees Celsius and hammering them together. It can be done via hammer welding, roll welding, or die welding and is used in industries like aerospace, shipbuilding, and manufacturing.