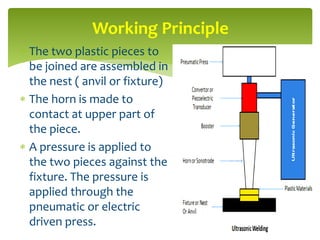
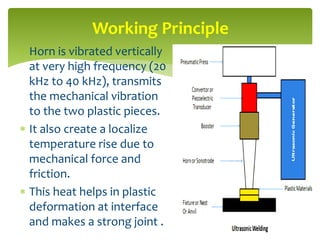
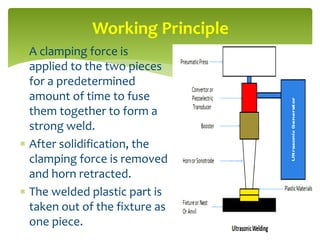
Ultrasonic welding is an industrial process that uses high-frequency acoustic vibrations to locally weld workpieces under pressure. The process involves clamping plastic pieces in a fixture below an ultrasonically vibrating horn. Pressure and vibrations from the horn cause localized heating and plastic deformation at the interface, forming a strong weld. It is a fast, automated process that produces clean, precise welds without thermal damage, used for applications in automotive, medical, and other industries.