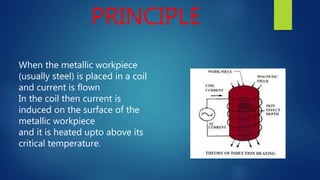
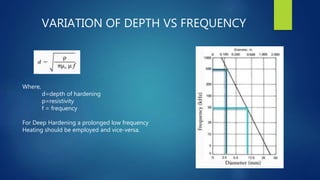
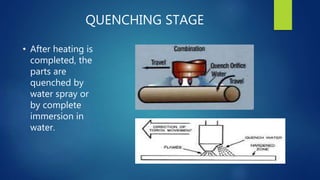
This document summarizes induction hardening and flame hardening surface hardening techniques. It explains that surface hardening increases the hardness of a component's outer surface while leaving the core soft. Induction hardening uses an induction coil to heat a component's surface above the critical temperature, then quenches it to form martensite for hardness. Flame hardening uses an oxy-acetylene flame to selectively harden specific surface areas, then quenches. Both provide wear resistance and control over hardness depth. Induction hardening offers more control and less distortion while flame hardening is economical for large or complex parts.