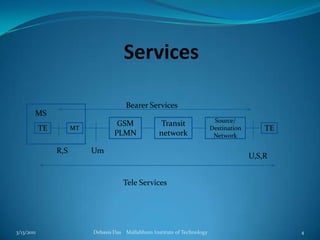
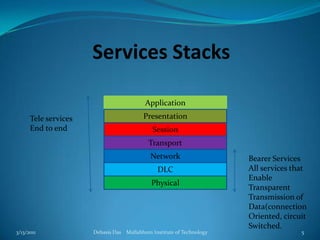
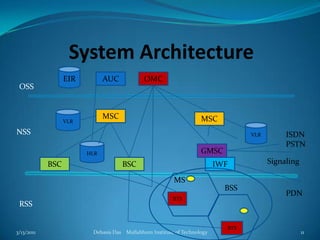
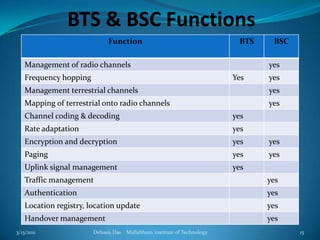
This document provides an overview of the GSM mobile communication system. It describes the different frequency bands used by GSM (900, 1800, 1900 MHz), as well as the GSM rail system. It discusses the various mobile services including bearer services, teleservices, and supplementary services. The document outlines the key components of the GSM system including the radio subsystem (containing the mobile station, base station subsystem and base transceiver stations), the network and switching subsystem (containing the MSC, HLR, VLR), and the operation subsystem (containing the OMC, AuC and EIR). It provides details on the functions and roles of these various components in enabling GSM mobile communication.