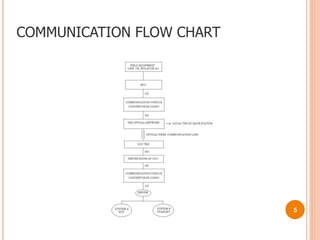
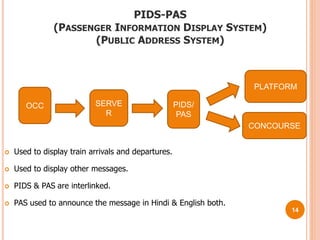
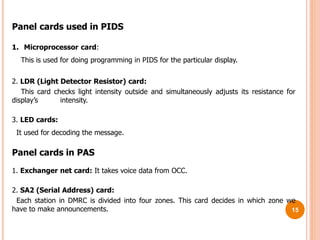
This document provides an overview of the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation's (DMRC) Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system. It describes the key components of the SCADA system including remote terminal units (RTUs) used to monitor and control field devices, different input/output cards in the RTUs for digital, analog and control signals, the SCADA software for monitoring and reporting, and applications of the SCADA system for functions like power distribution, passenger information displays, and automatic fare collection gates.