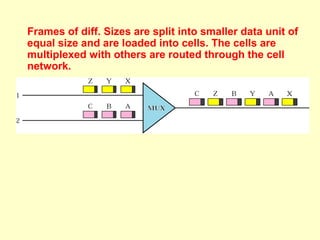
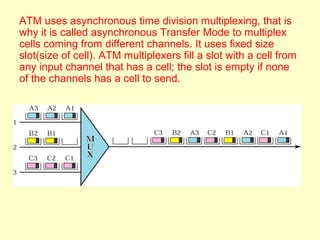
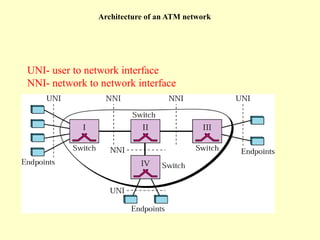
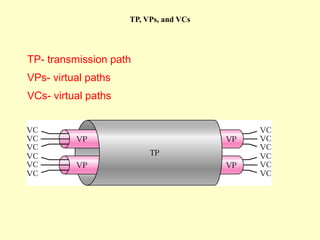
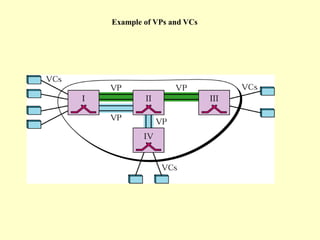
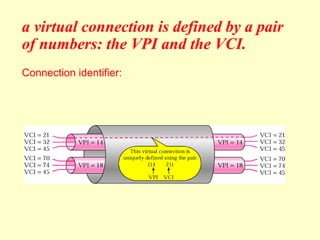
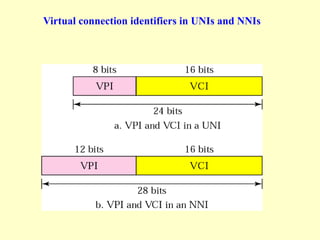
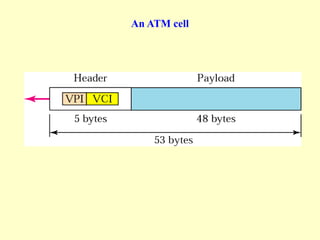
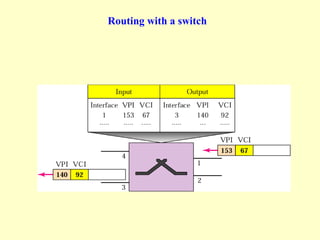
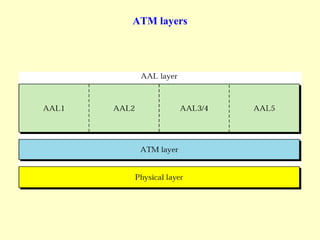
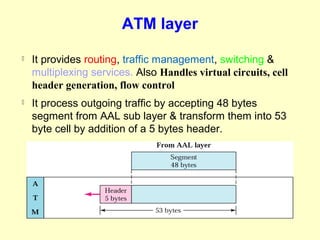
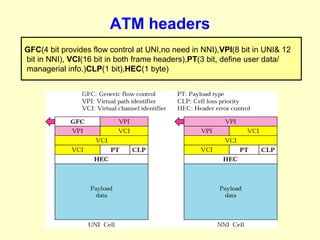
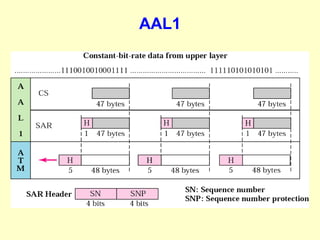
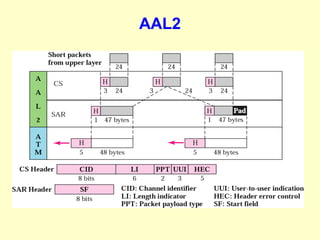
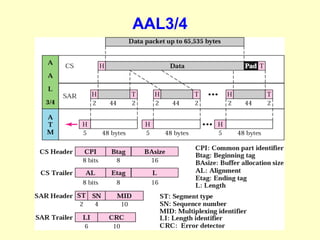
ATM is a cell switching and multiplexing technology designed to unify telecommunication network infrastructures. It uses fixed length cells to transport data and signaling information. ATM networks support connections with different quality of service (QoS) levels for various media like voice, video, and data. ATM allows for predictable delivery of real-time media through constant bit rate connections while also supporting bursty data traffic.

















![QoS in ATM
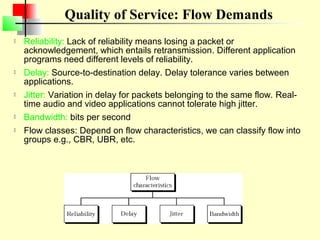
CBR: Designed for real-time audio or video services
VBR: Variable-bit-rate
– VBR-RT [Real-time]
» For real time services
» Uses compression techniques to create a variable bit rate.
– VBR-NRT [Non-real-time]
» Uses compression but for non real time.
ABR: Available bit rate
– Delivers cells at a minimum rate.
– If more network capacity is available, this minimum rate can be exceeded.
– Suitable for applications that are bursty.
UBR: Unspecified bit rate; Best effort delivery that does not guarantee
anything.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atm-130105114512-phpapp01/85/Atm-Asynchronous-Transfer-mode-34-320.jpg)