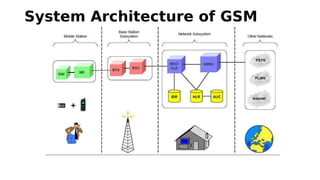
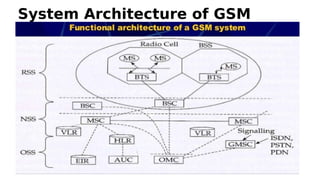
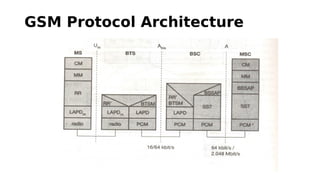
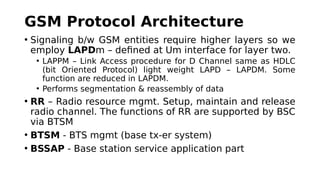
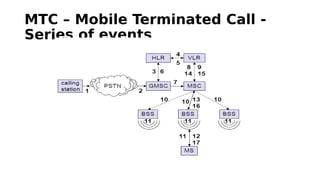
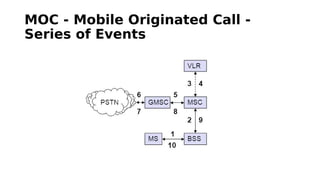
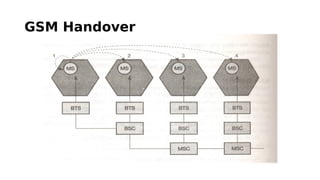
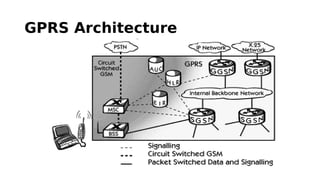
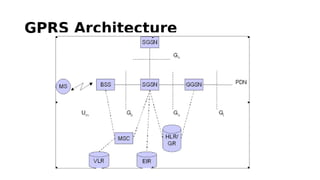
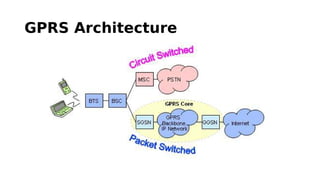
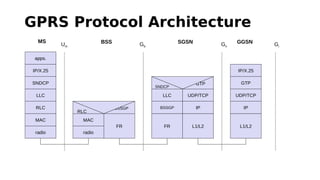
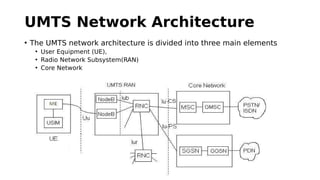
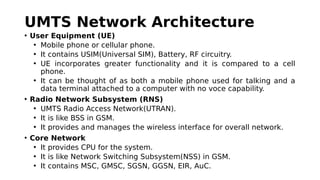
GSM is a 2G mobile communication system that provides voice and data services. It uses TDMA and FDMA to allow multiple users to access the network simultaneously. The key components of a GSM network are the radio subsystem including the BTS, BSC and MS; the network and switching subsystem including the MSC, HLR, VLR; and the operation subsystem including the OMC, AuC and EIR. GSM provides services like telephony, SMS, and data transmission using bearer channels while ensuring security, anonymity and authentication of users.