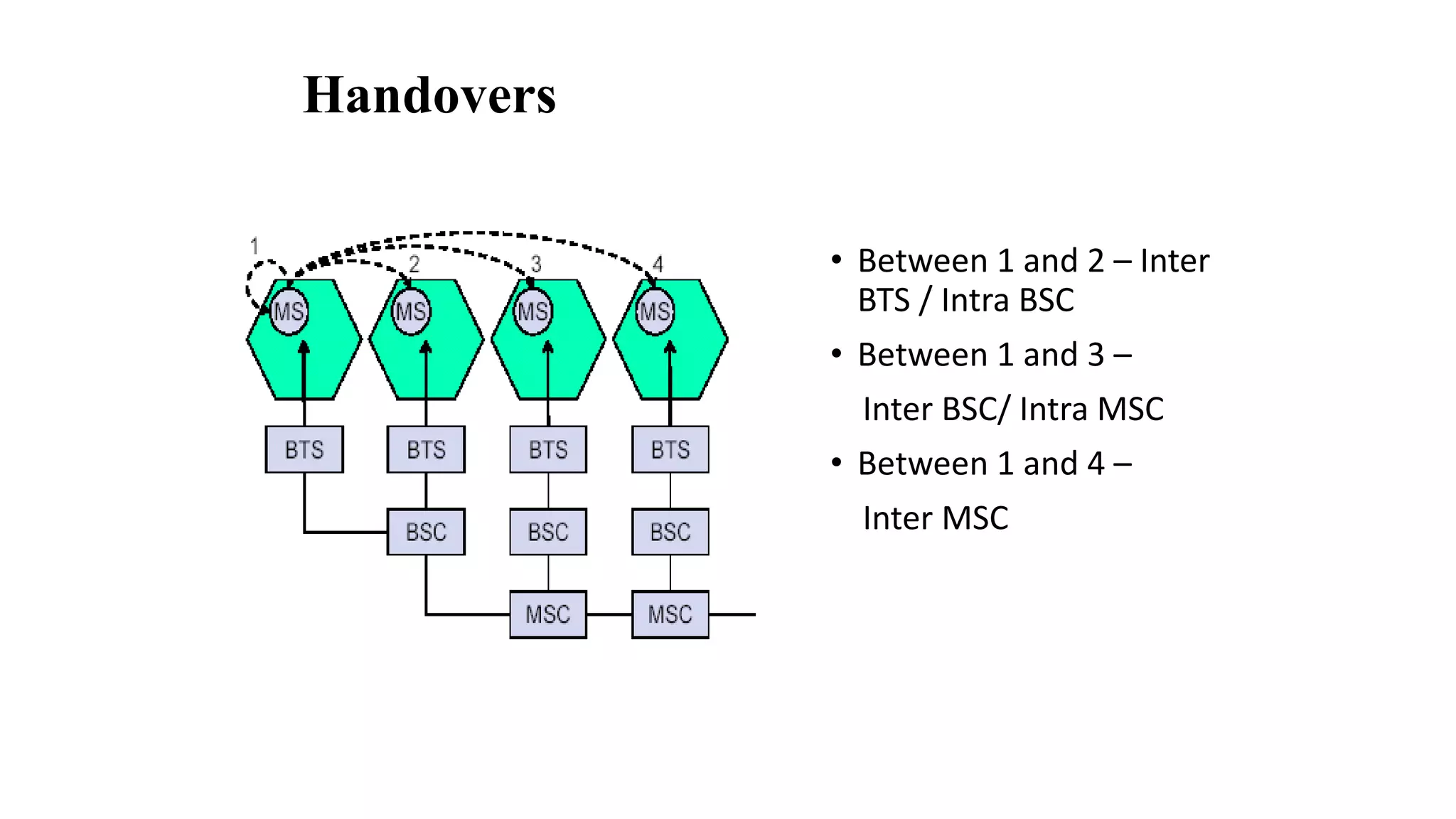
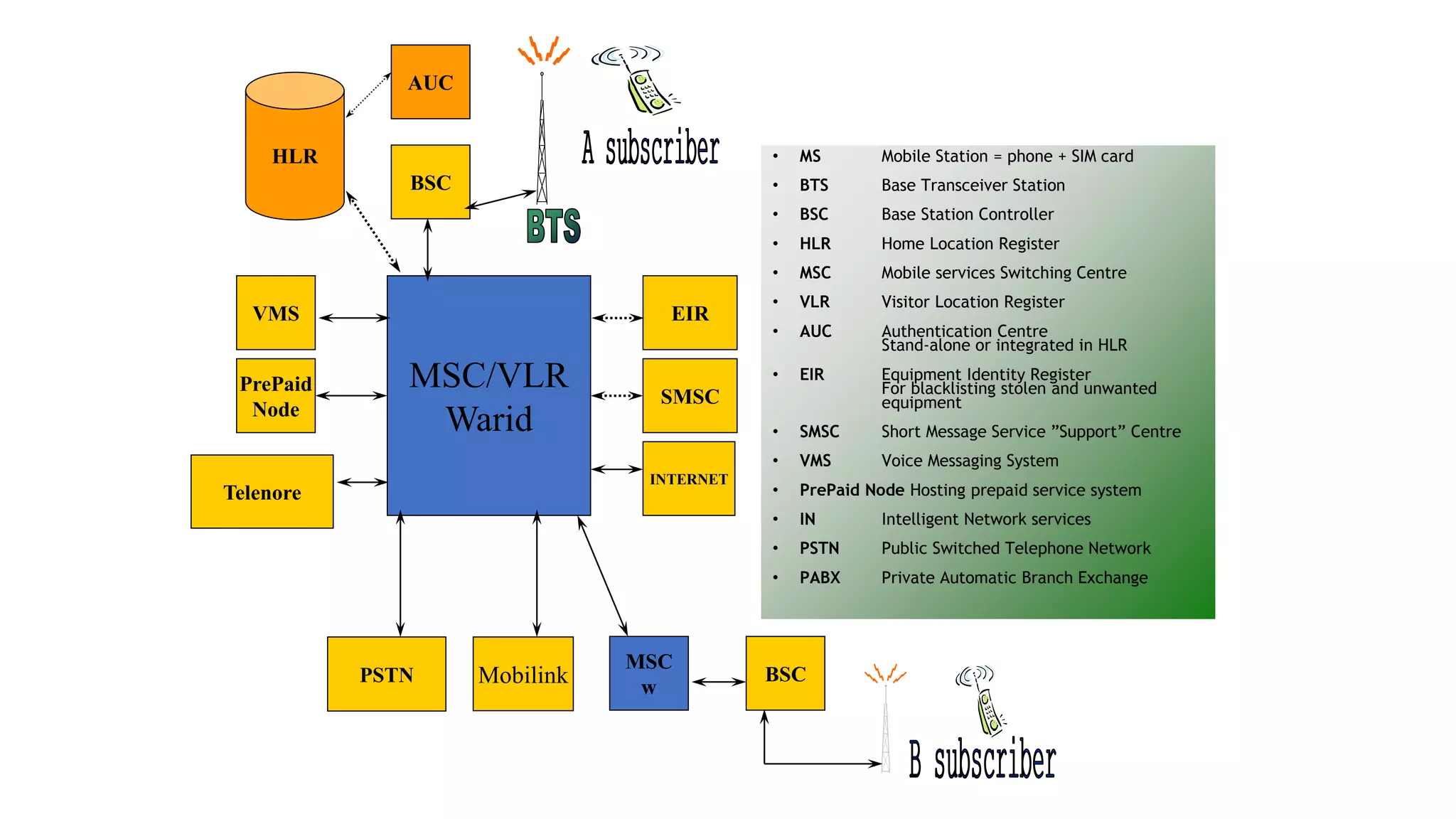
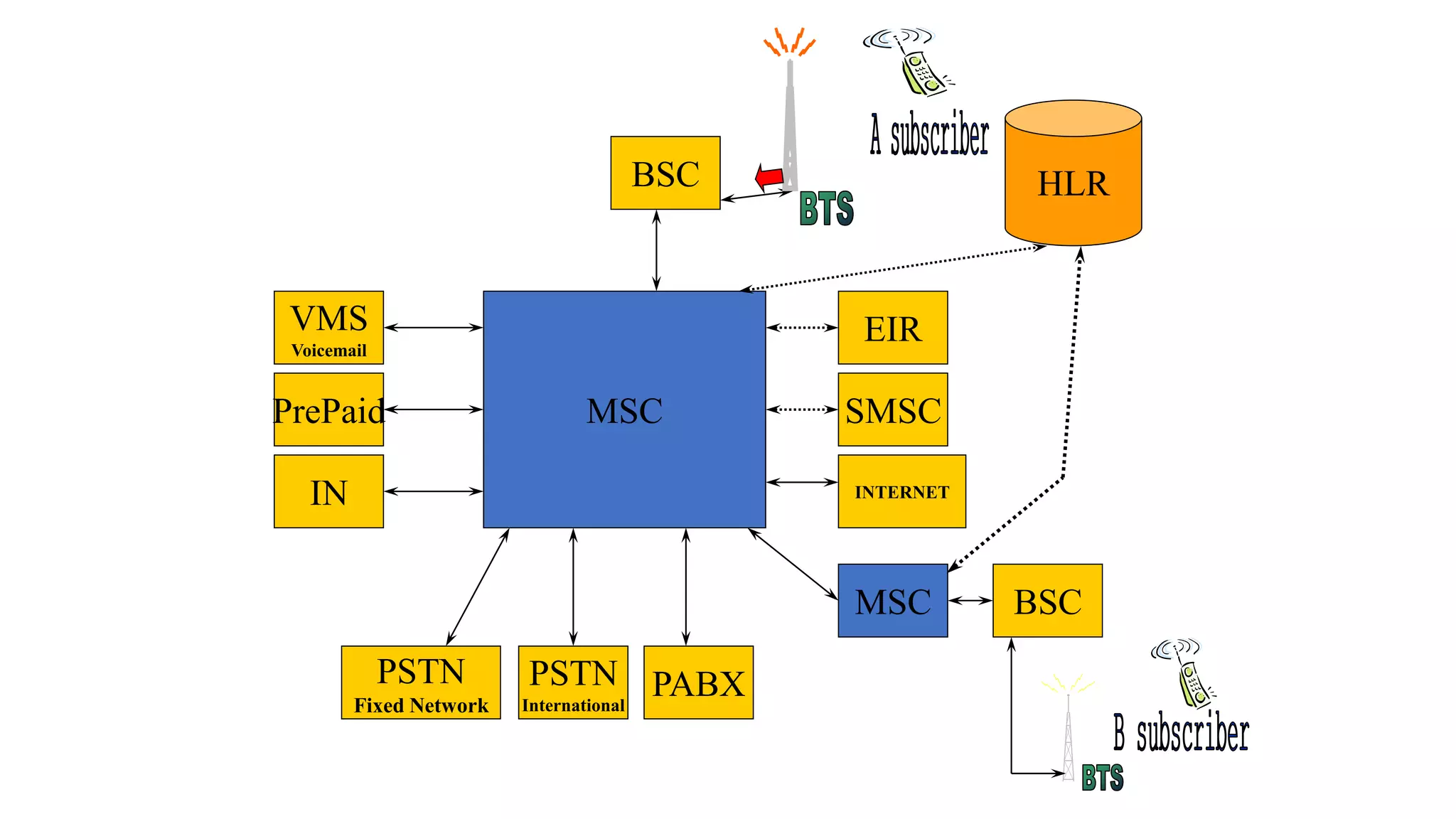
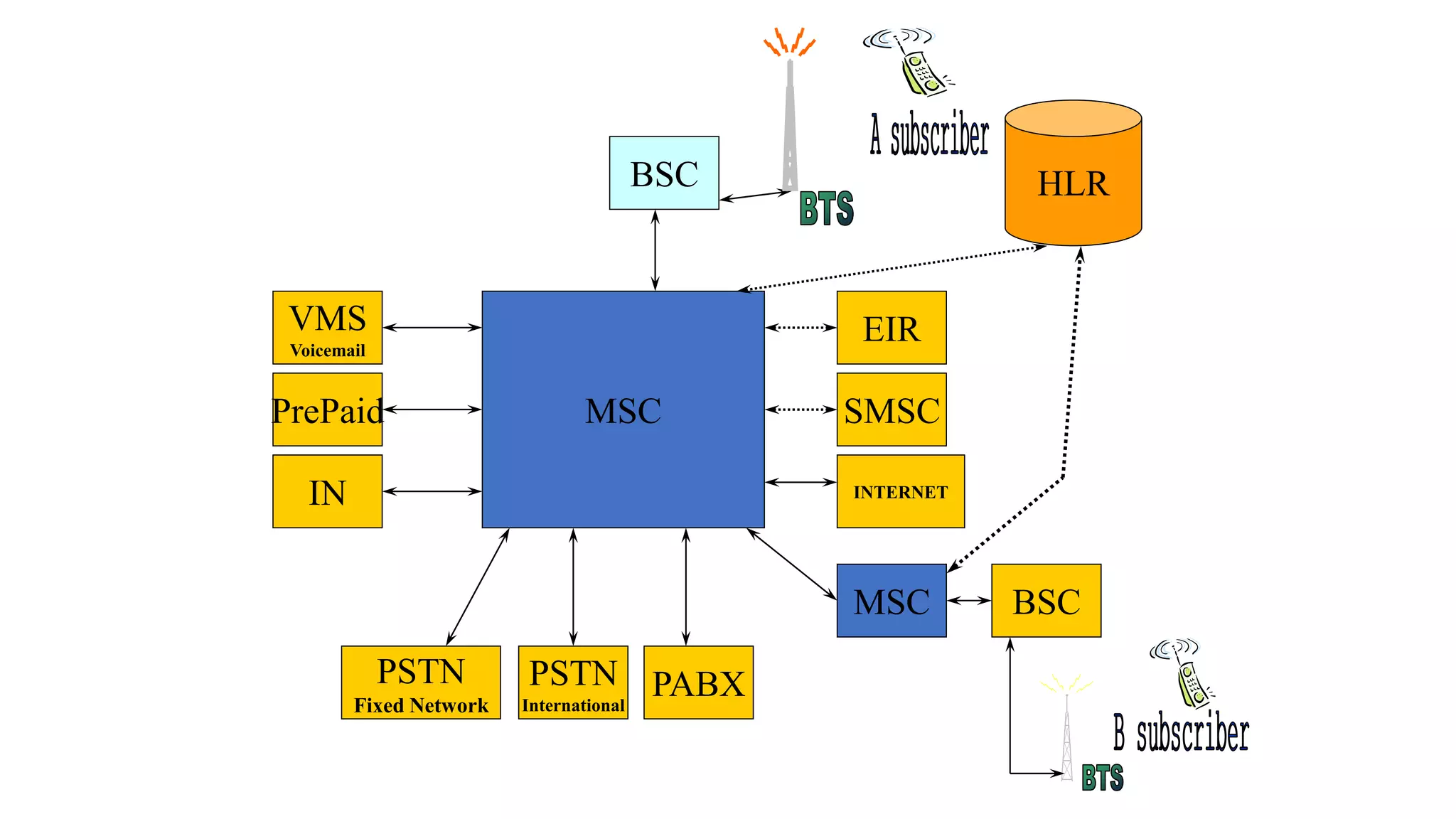
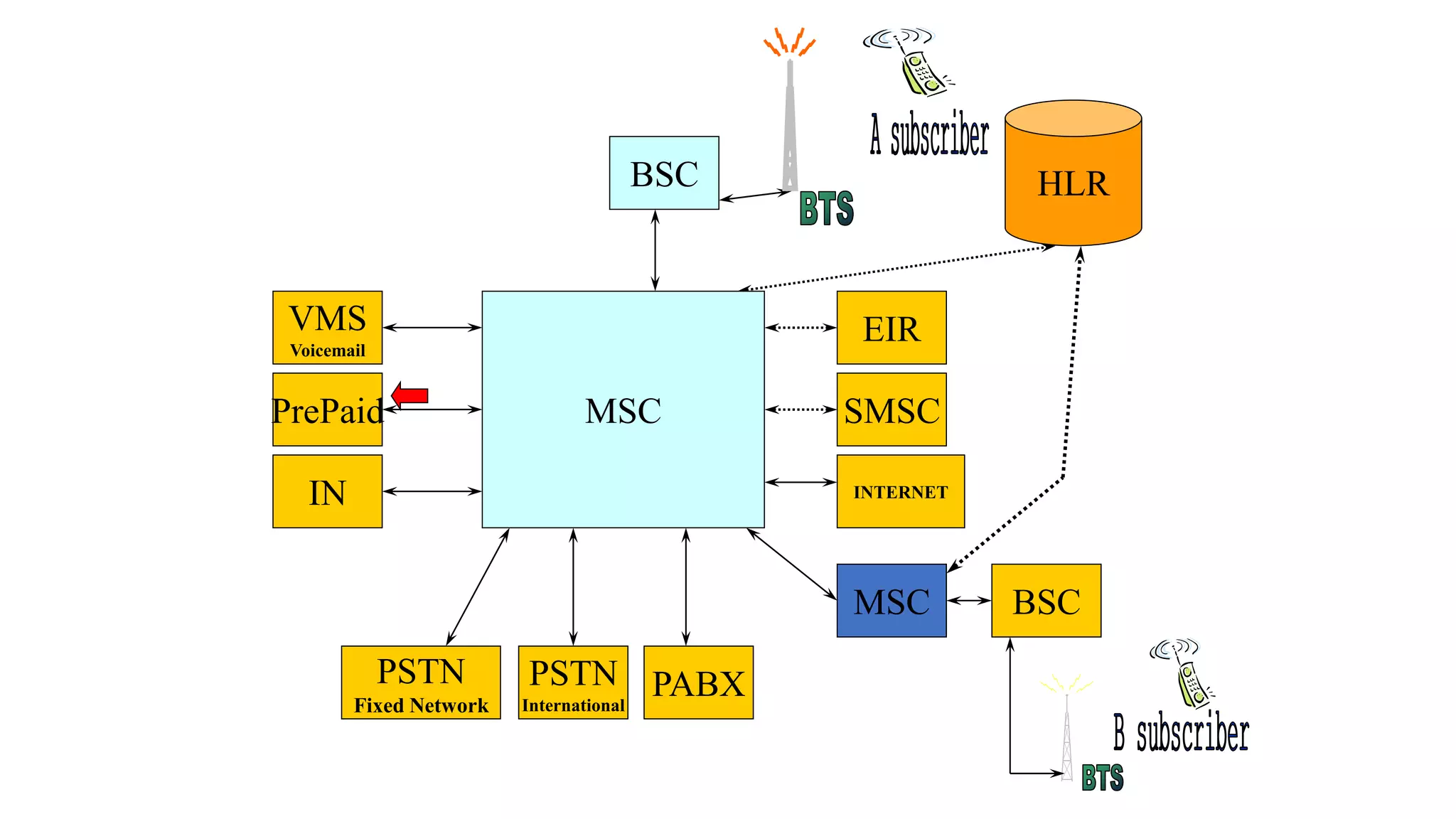
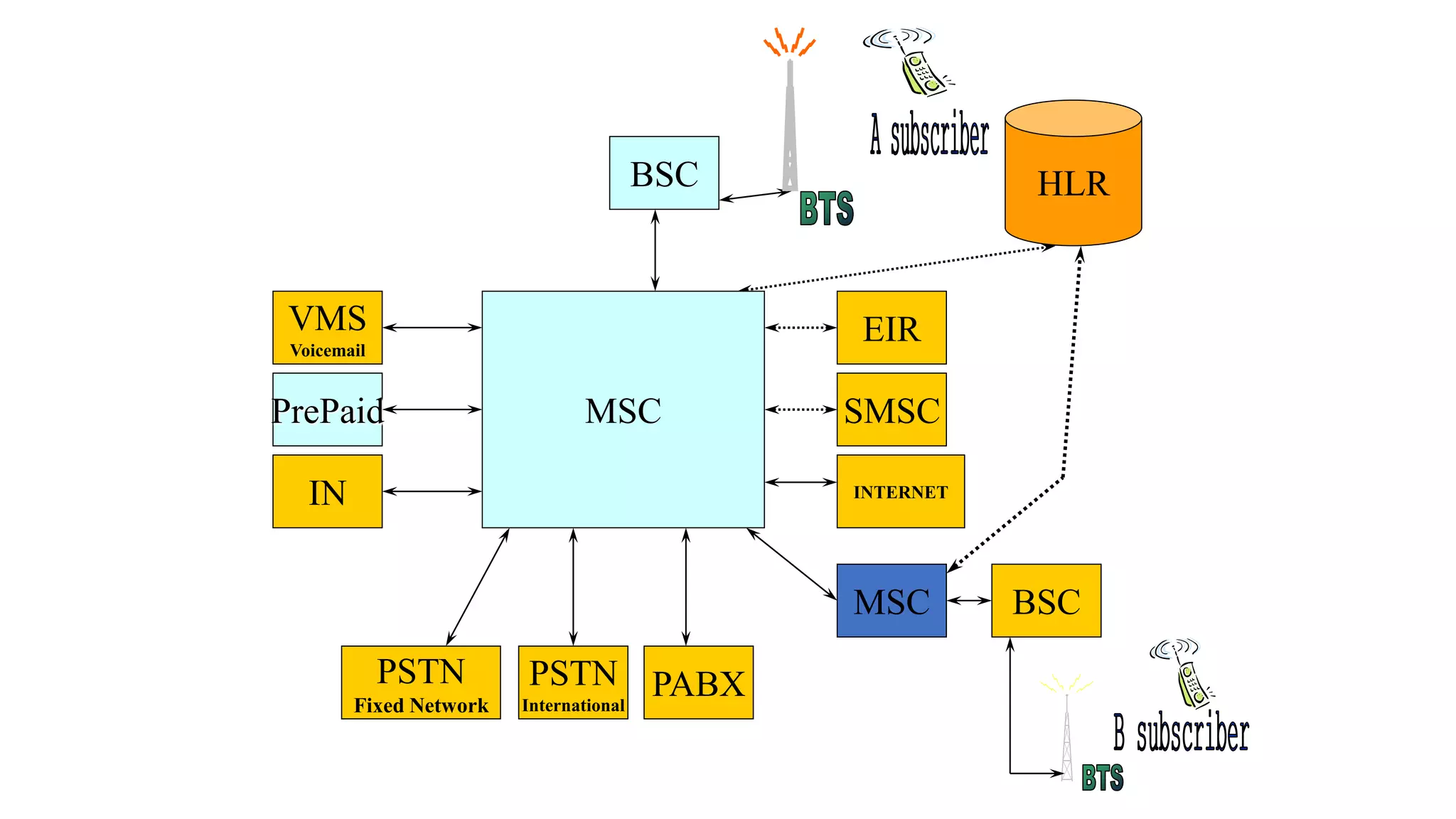
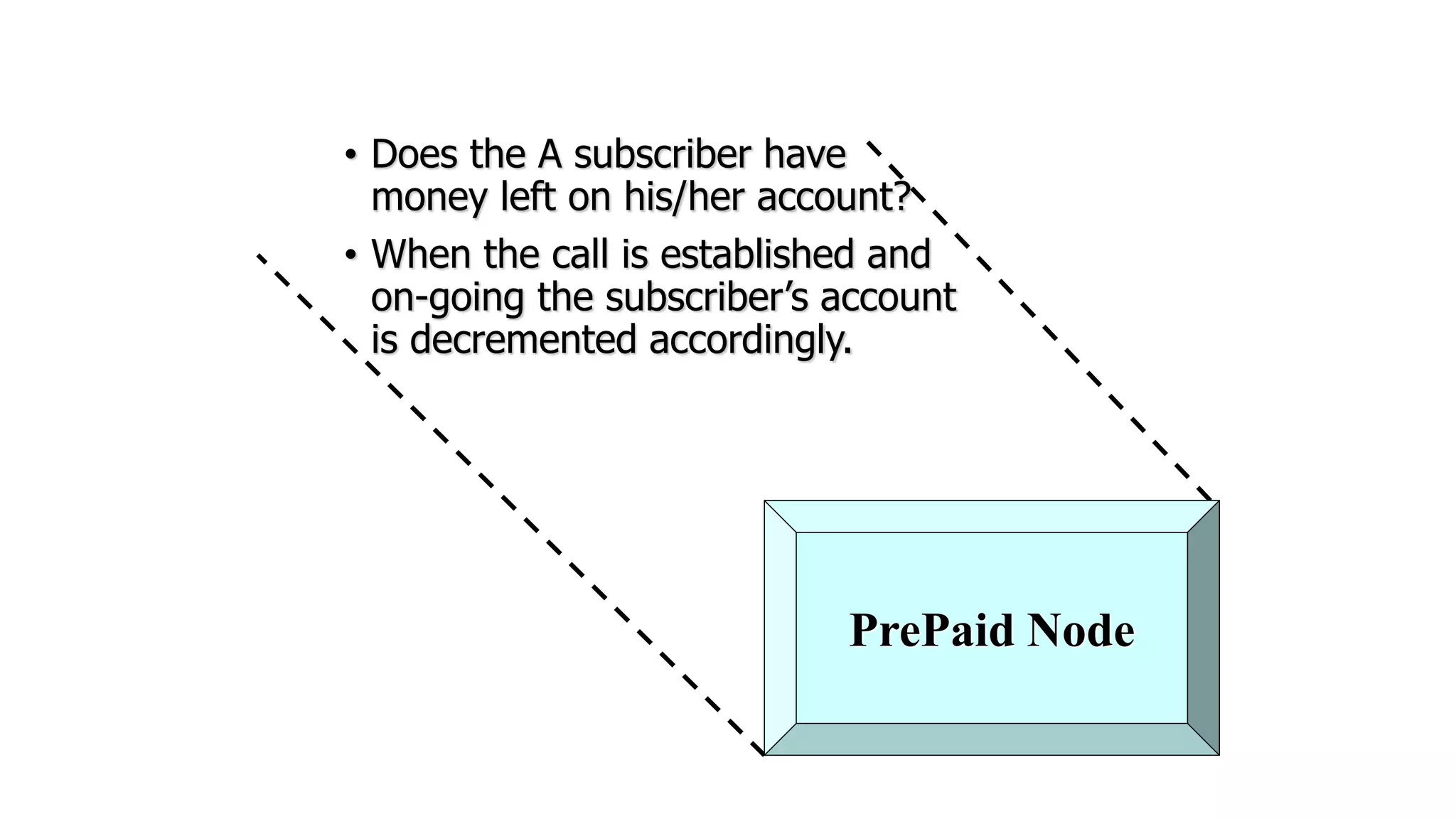
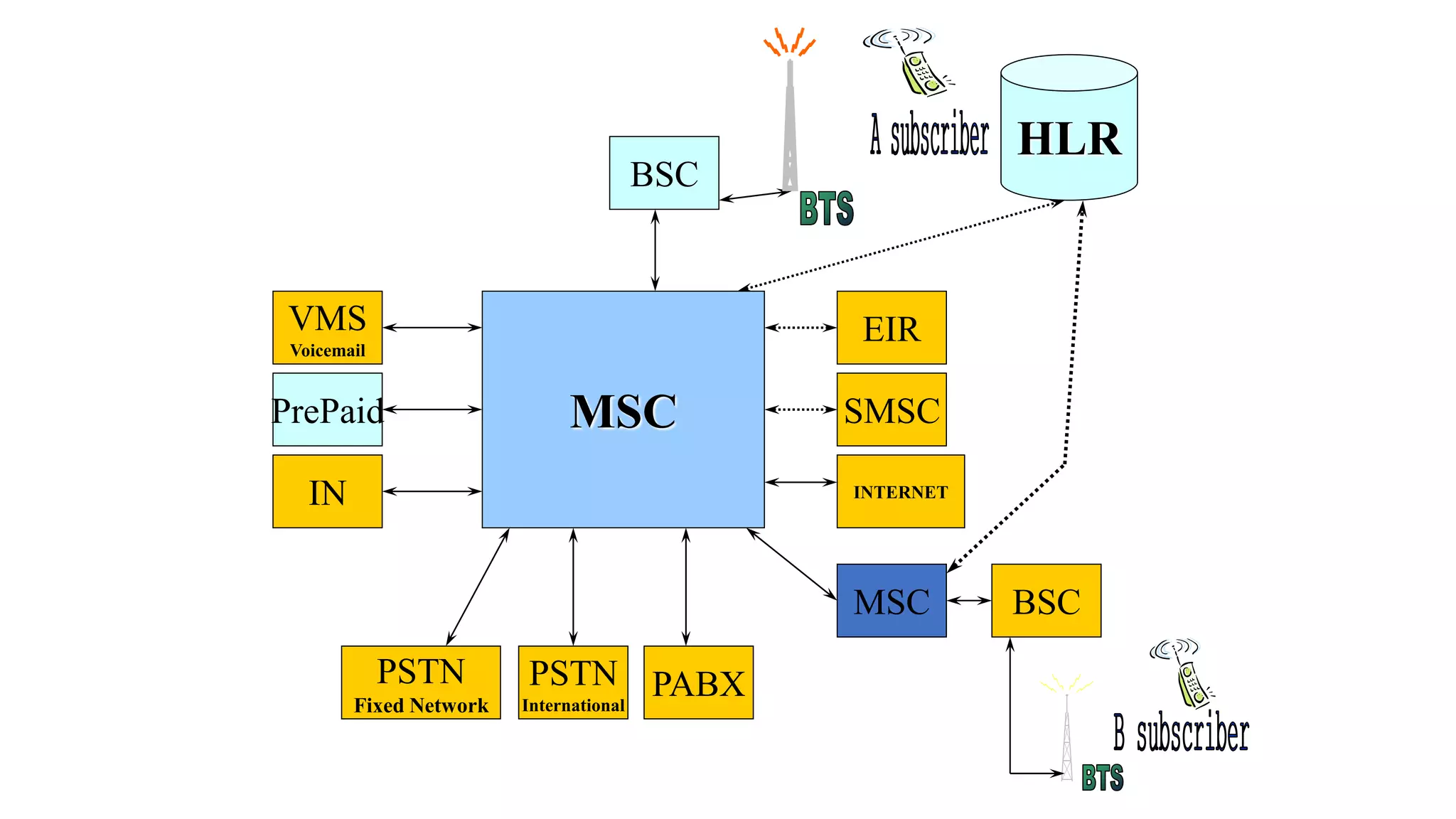
The document discusses cellular network basics and generations, including:
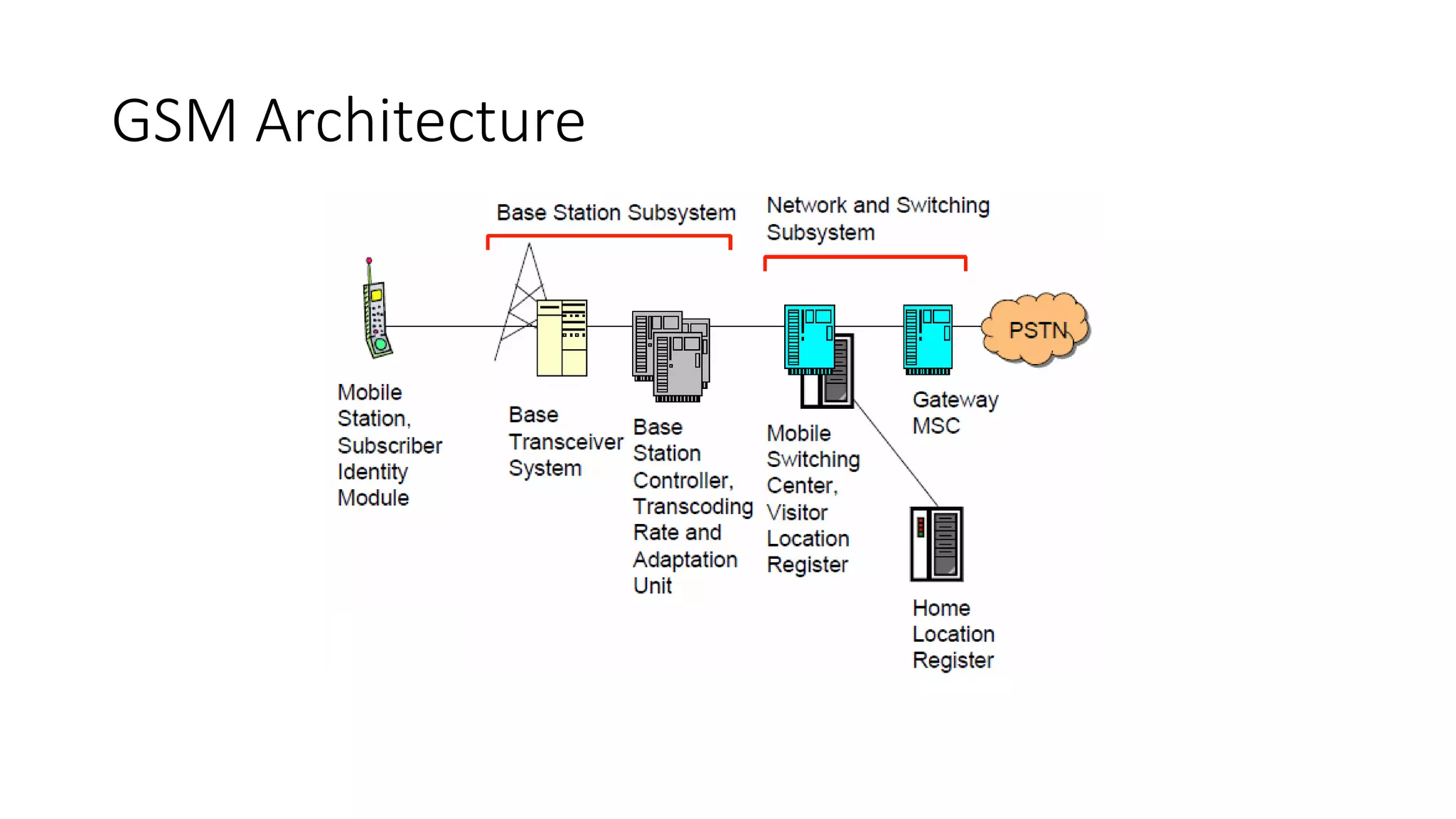
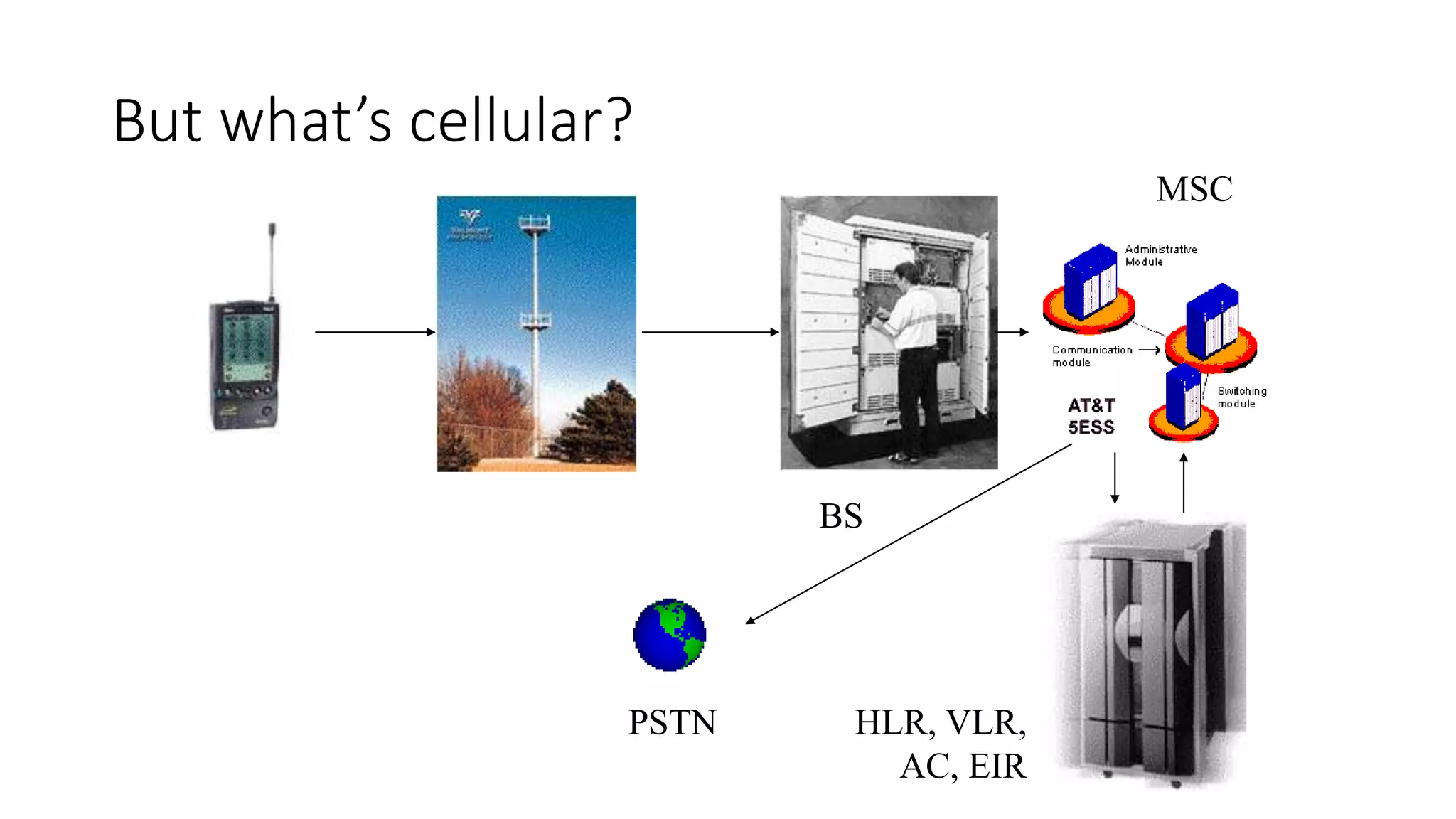
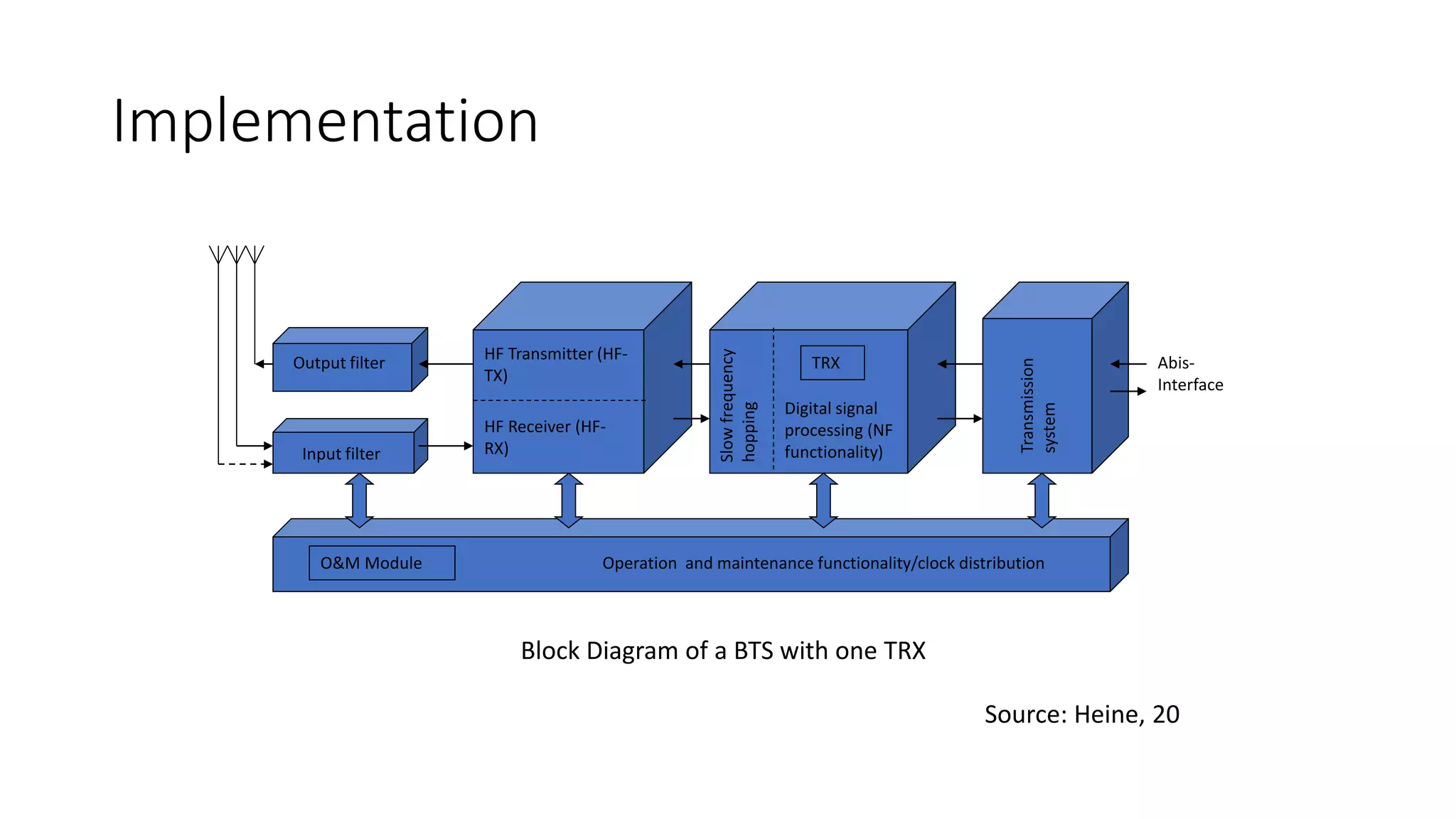
1) Cellular networks use radio waves to allow cell phones to operate within certain frequency bands and connect to nearby base stations.
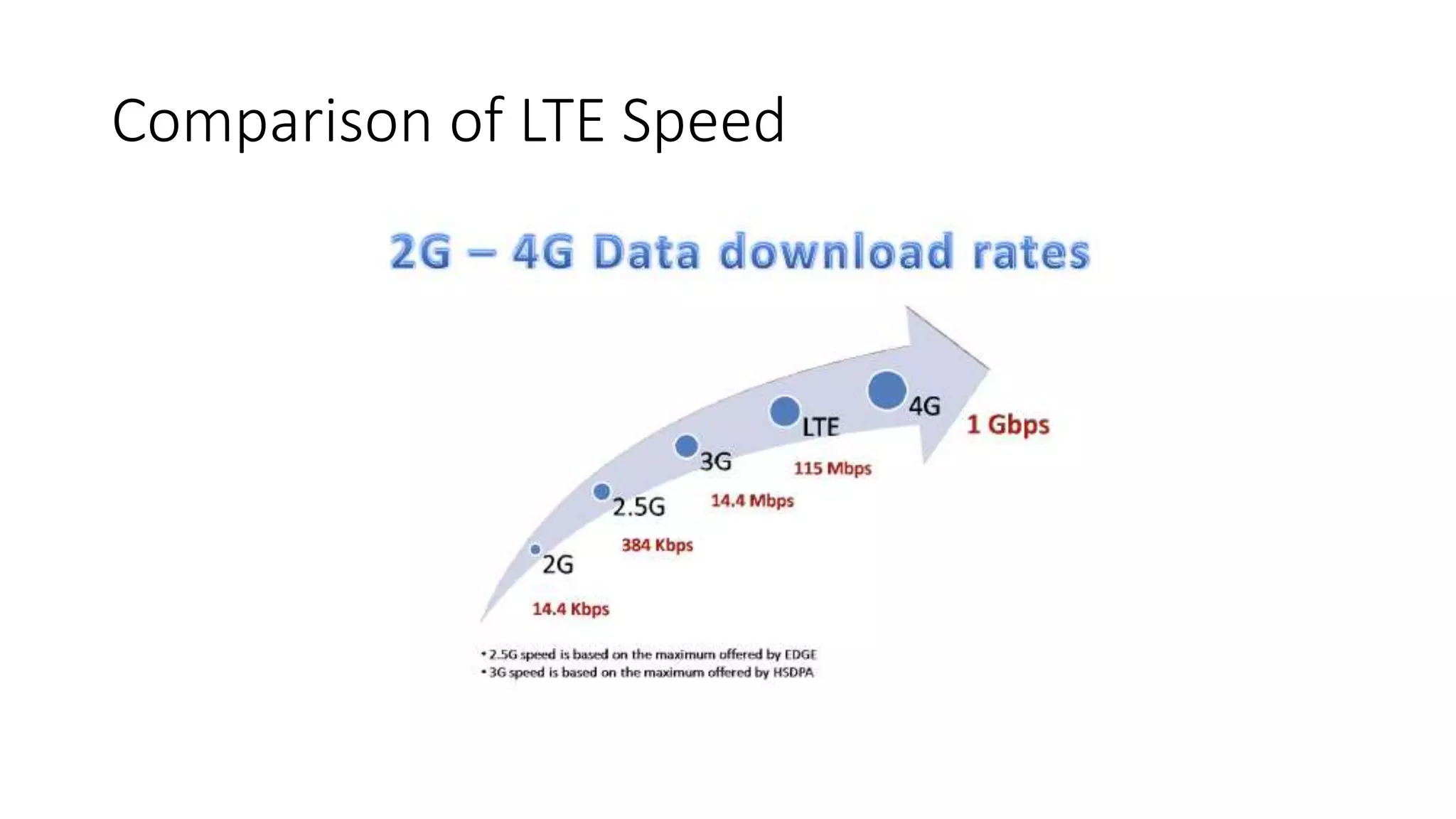
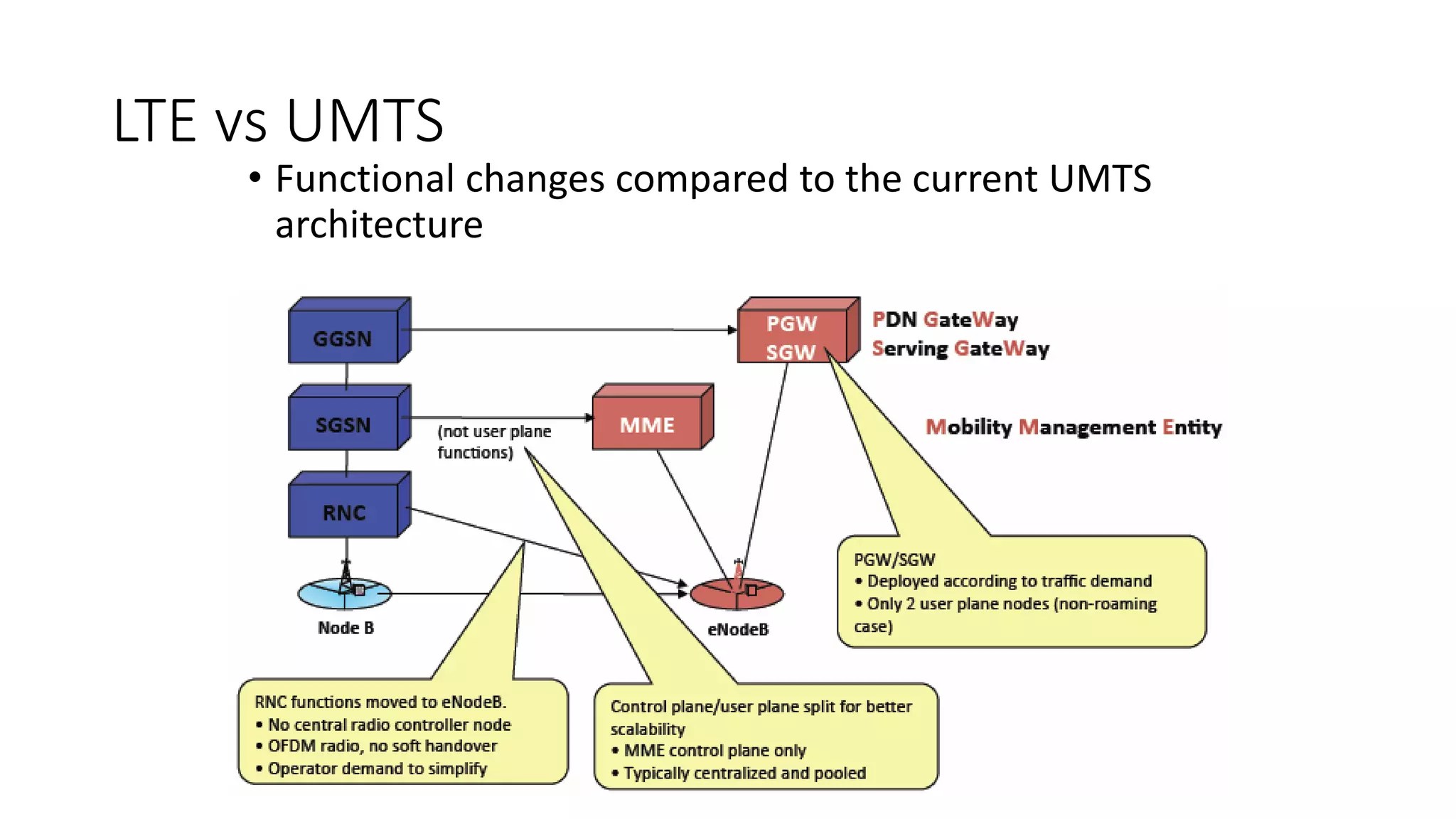
2) Cellular networks have evolved through generations from early analog mobile phones to current digital networks that support high-speed data and multimedia services.
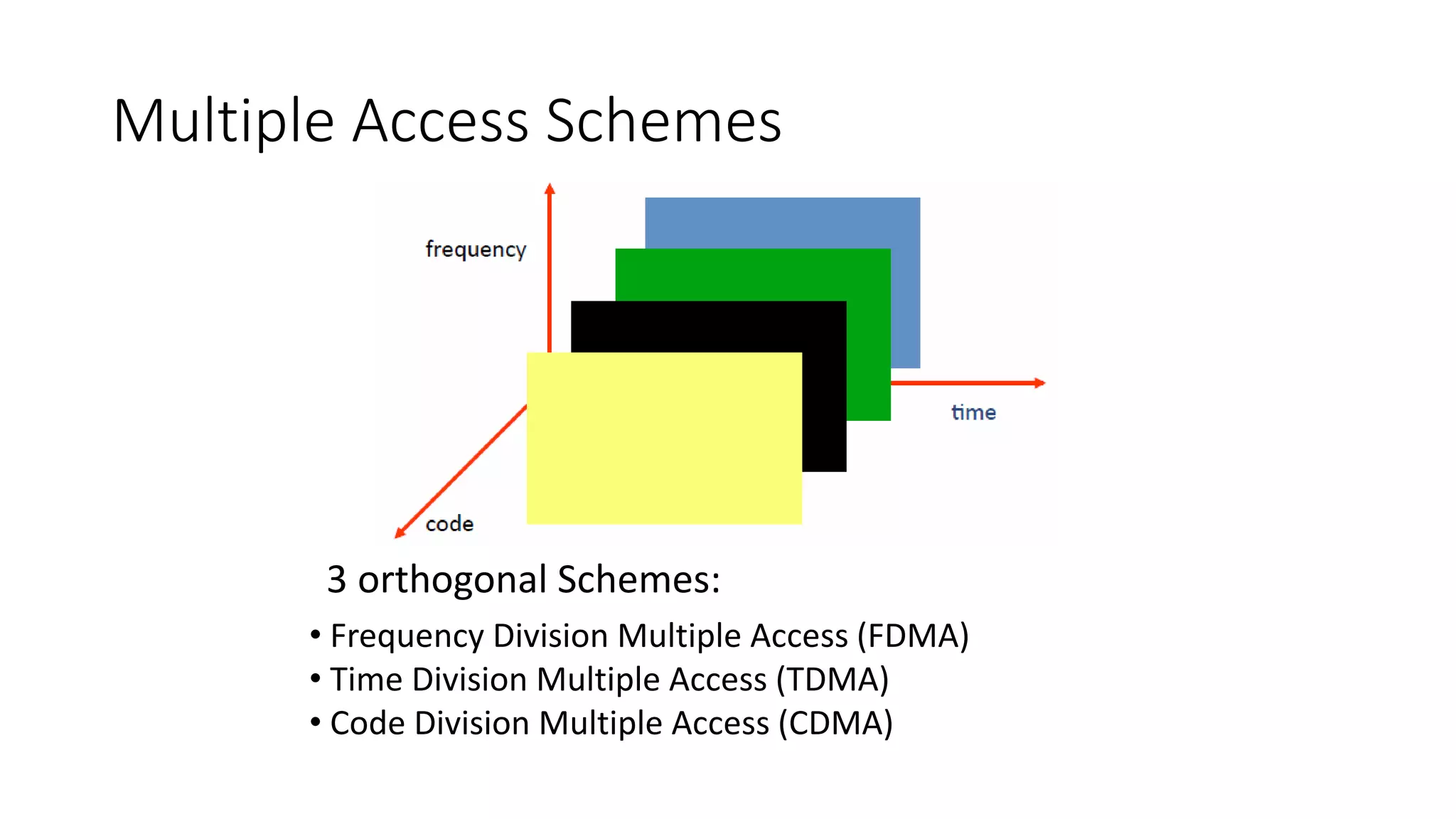
3) Cellular networks face the problem of allowing multiple mobile users to access the network simultaneously, which they address through multiple access schemes like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA that divide available airlink resources.