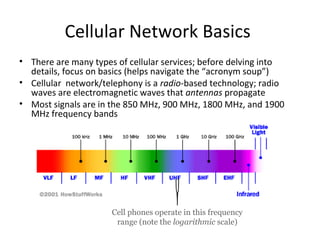
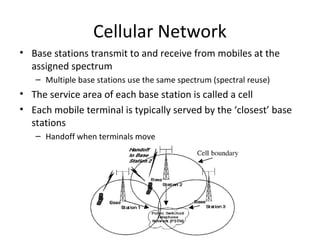
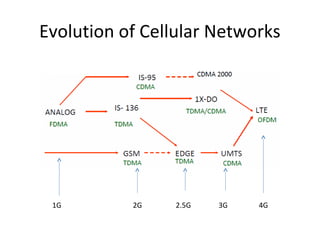
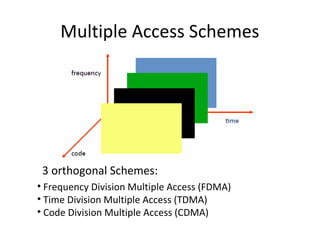
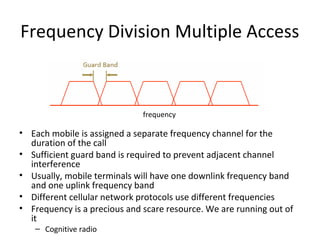
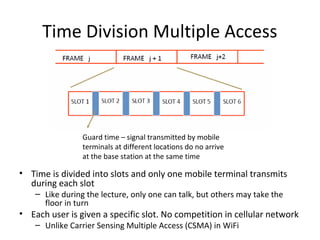
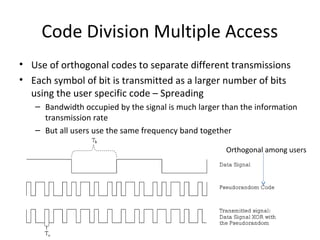
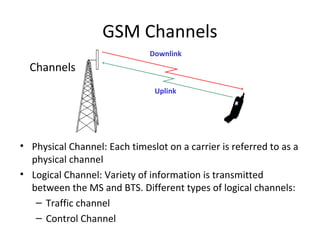
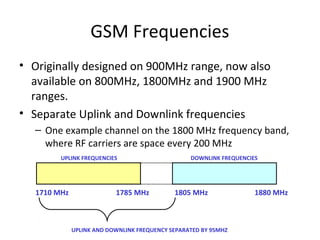
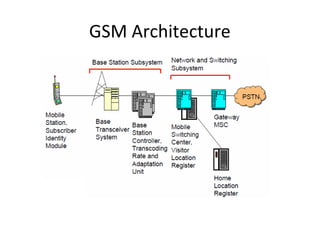
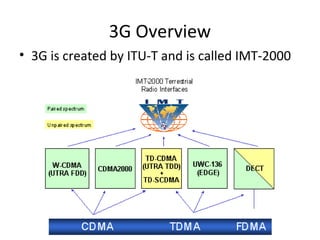
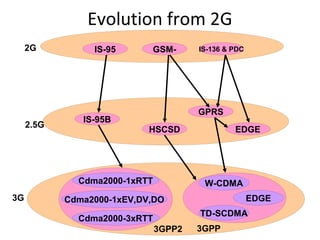
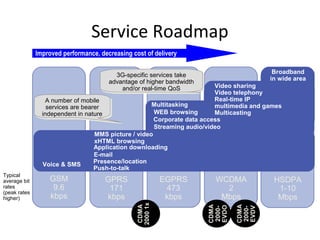
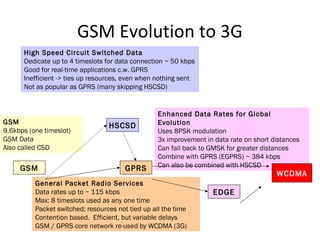
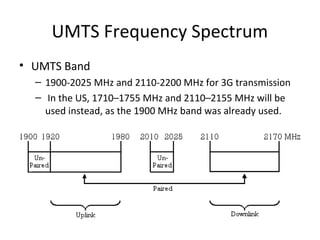
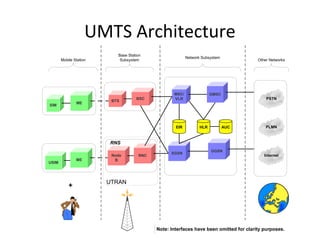
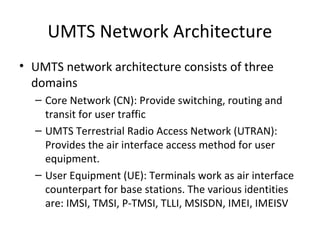
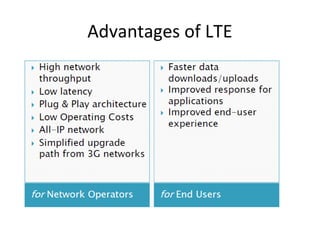
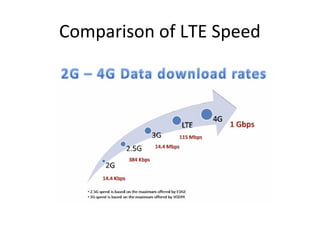
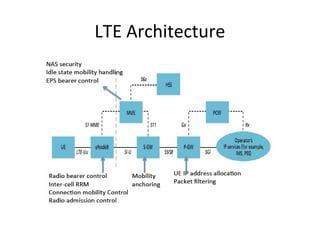
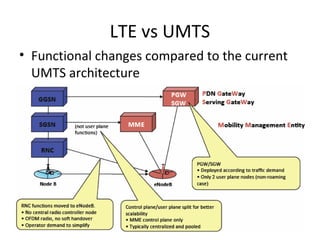
The document discusses cellular network basics and the evolution of cellular network generations from 0G to 4G. It covers key aspects of 2G cellular networks including GSM standards, channels, frequencies, architecture involving mobile stations, base station subsystems, switching subsystems, and location and handoff procedures. It also provides an overview of 3G networks and the transition from 2G technologies like GSM to 3G standards like UMTS, discussing services and performance improvements with each generation.