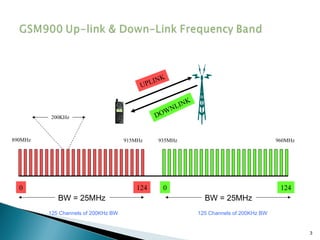
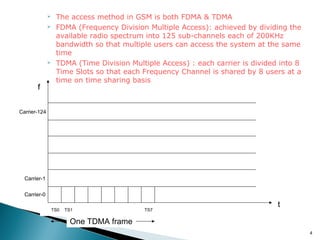
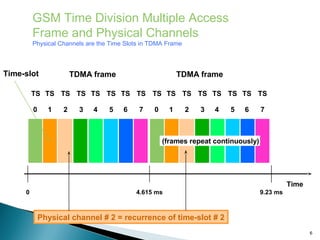
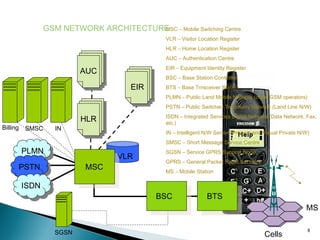
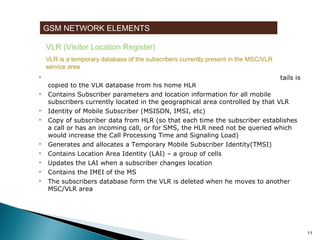
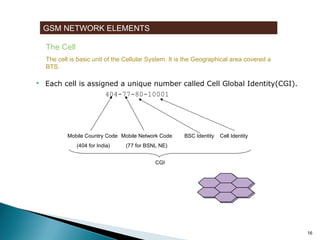
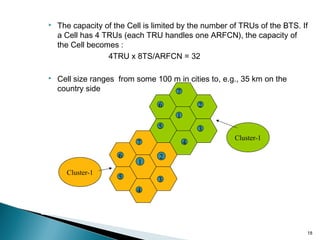
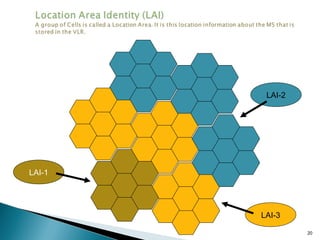
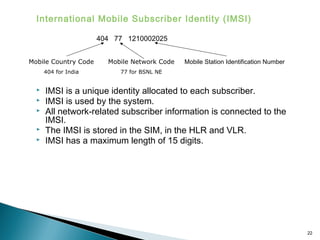
GSM is a standard for digital cellular networks that allows subscribers to use their phones globally. It uses FDMA to divide the spectrum into channels and TDMA to divide each channel into timeslots. The network consists of MSCs, HLRs, VLRs, BSCs, BTSs and cells. The MSC handles calls and interfaces with other networks. HLRs store subscriber data and VLRs temporarily store data for subscribers in the local area. BSCs control BTSs which transmit signals to mobile devices within cells. Key identifiers include IMSI, IMEI, MSISDN and MSRN.