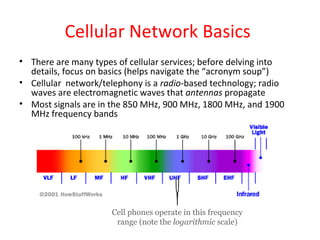
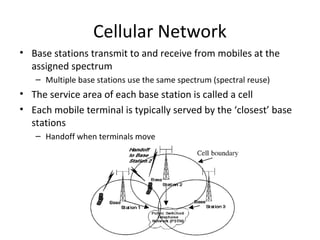
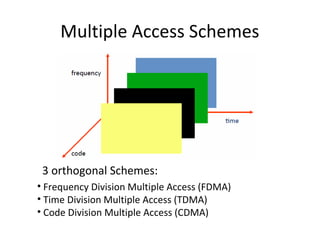
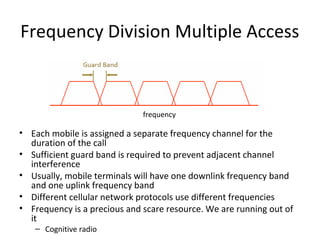
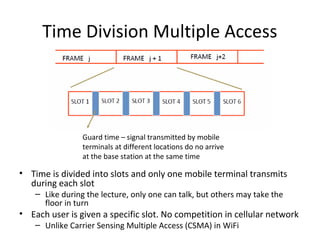
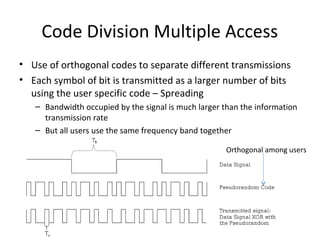
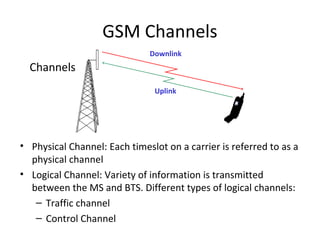
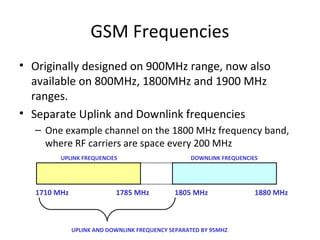
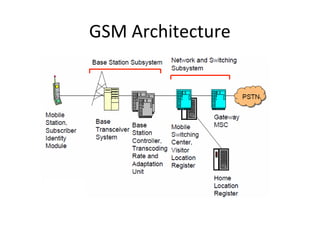
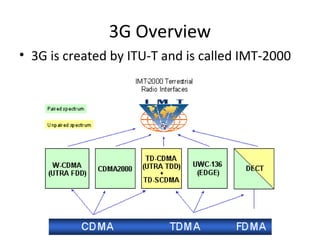
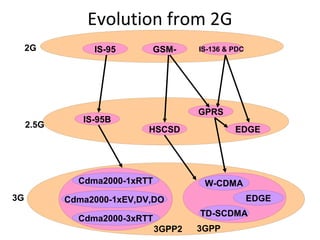
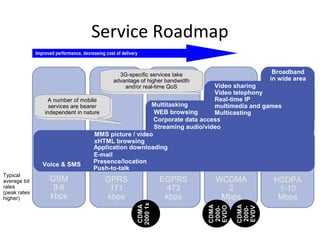
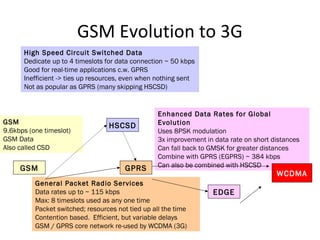
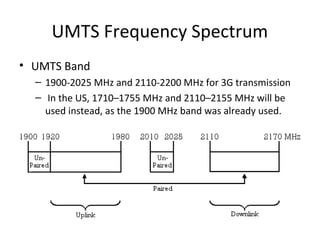
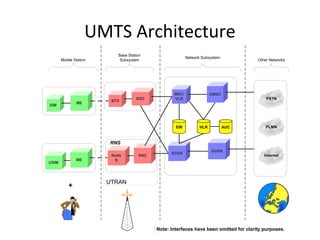
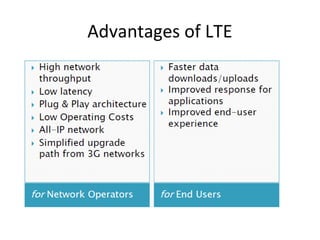
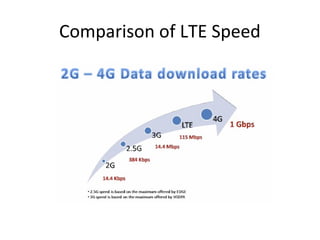
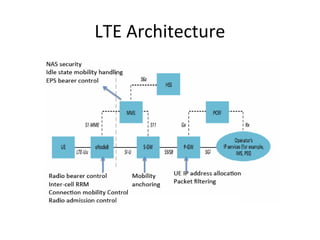
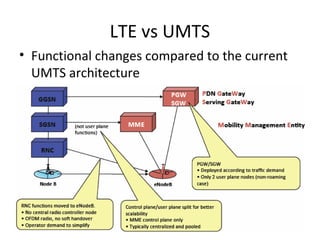
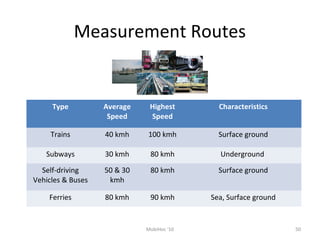
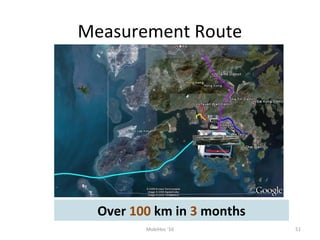
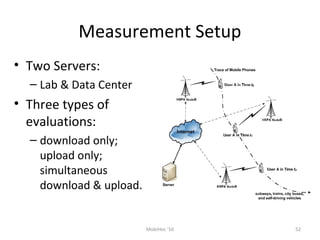
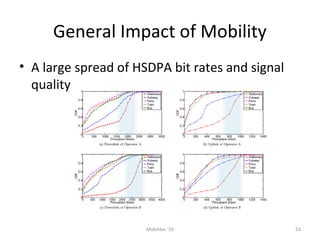
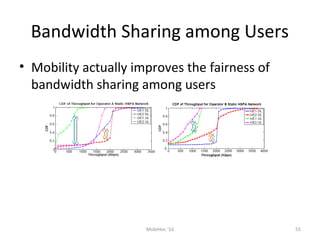
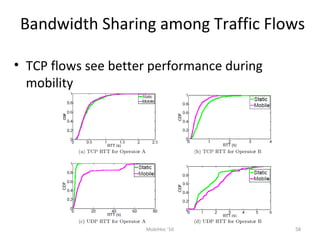
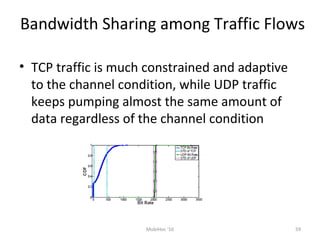
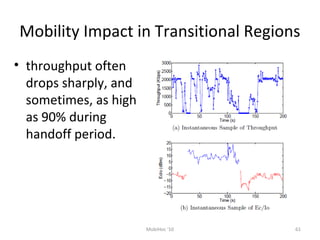
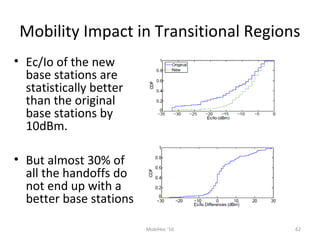
Mobile networks use radio frequencies to allow cellular devices to connect to a network of base stations. Base stations transmit and receive signals in frequency bands between 850-1900 MHz. As devices move between base station coverage areas, the network performs handoffs to transfer the connection seamlessly. Higher generations of cellular networks like 3G and 4G provide improved data speeds but still must handle user mobility effectively.