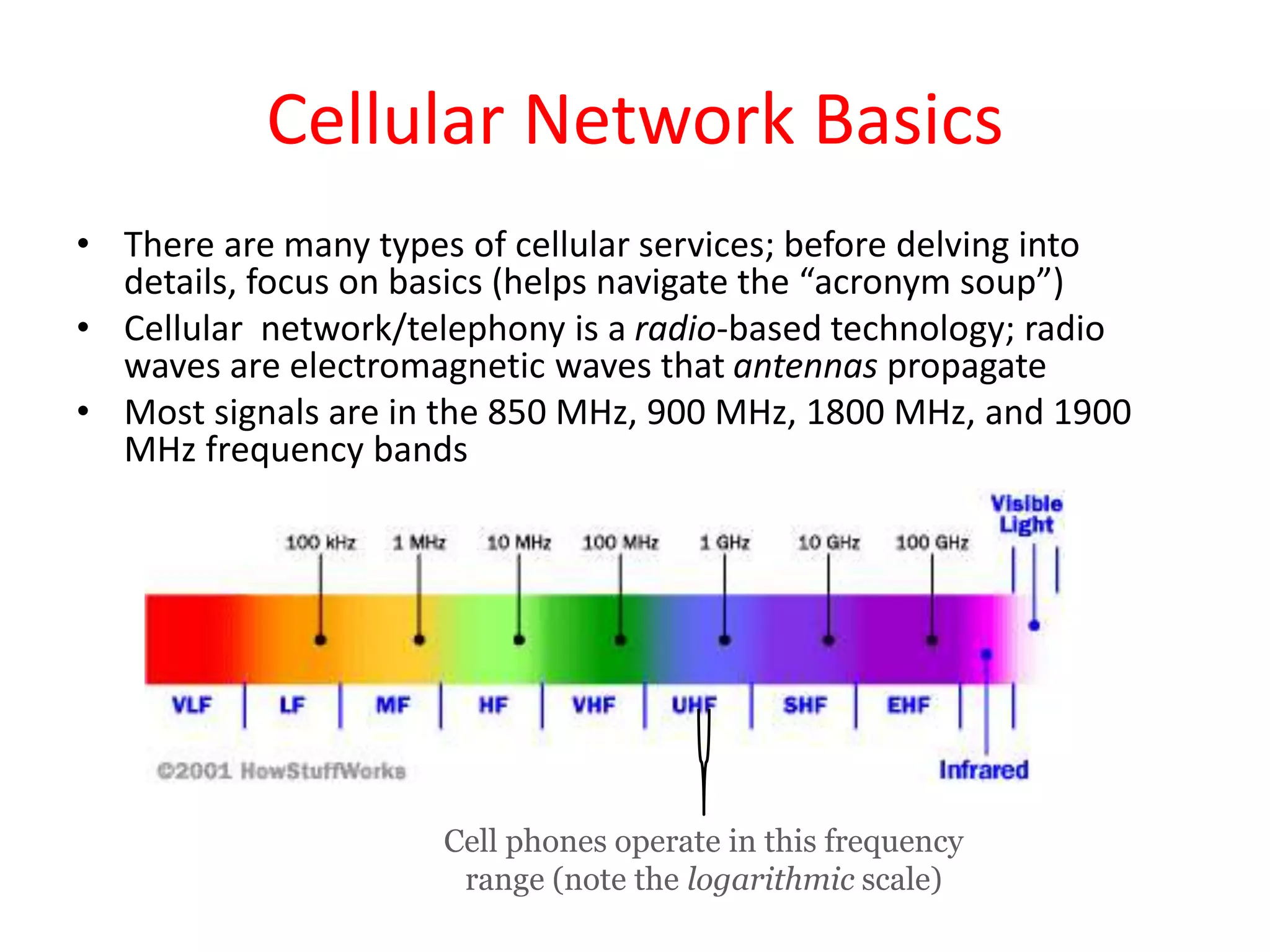
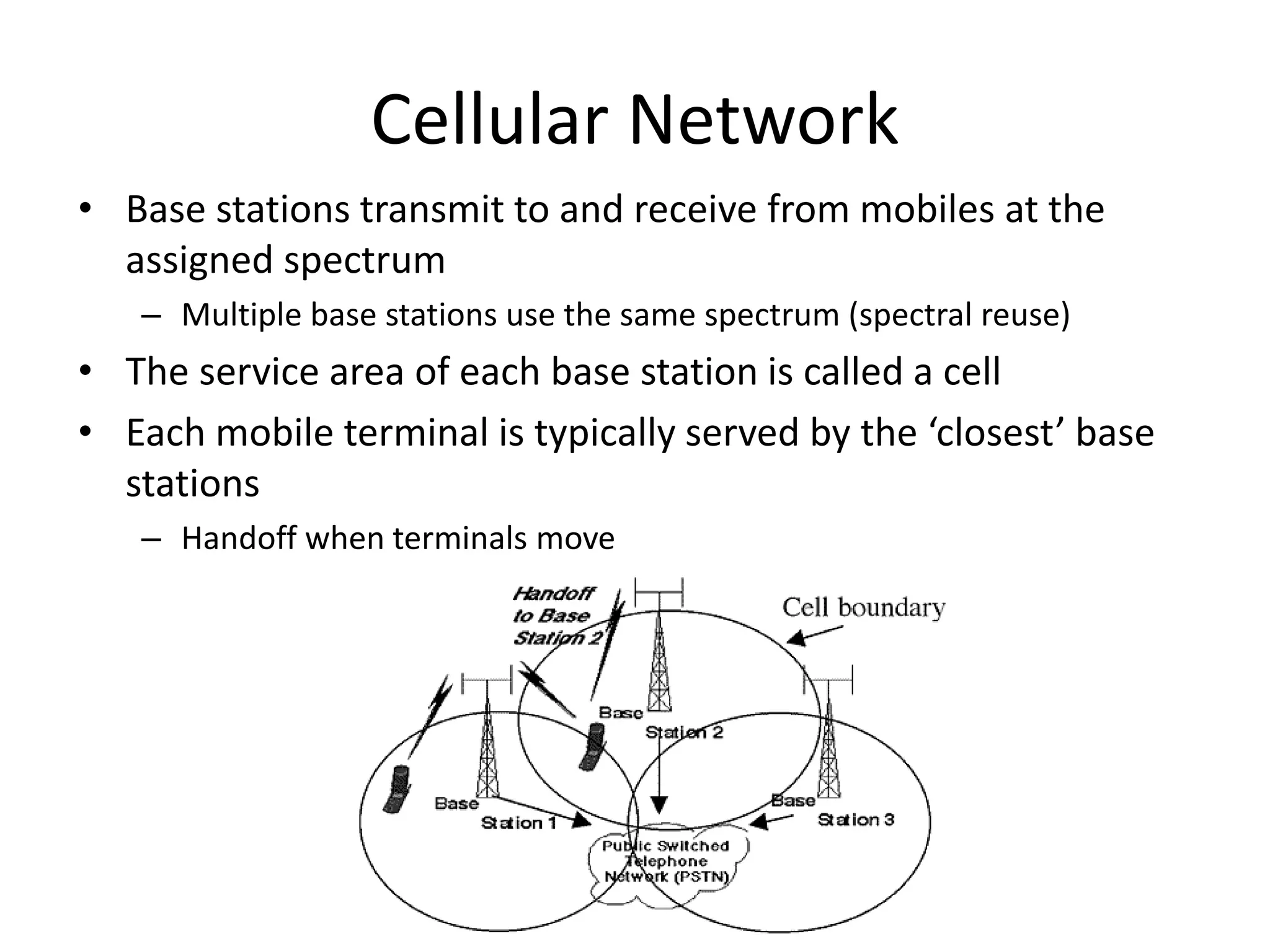
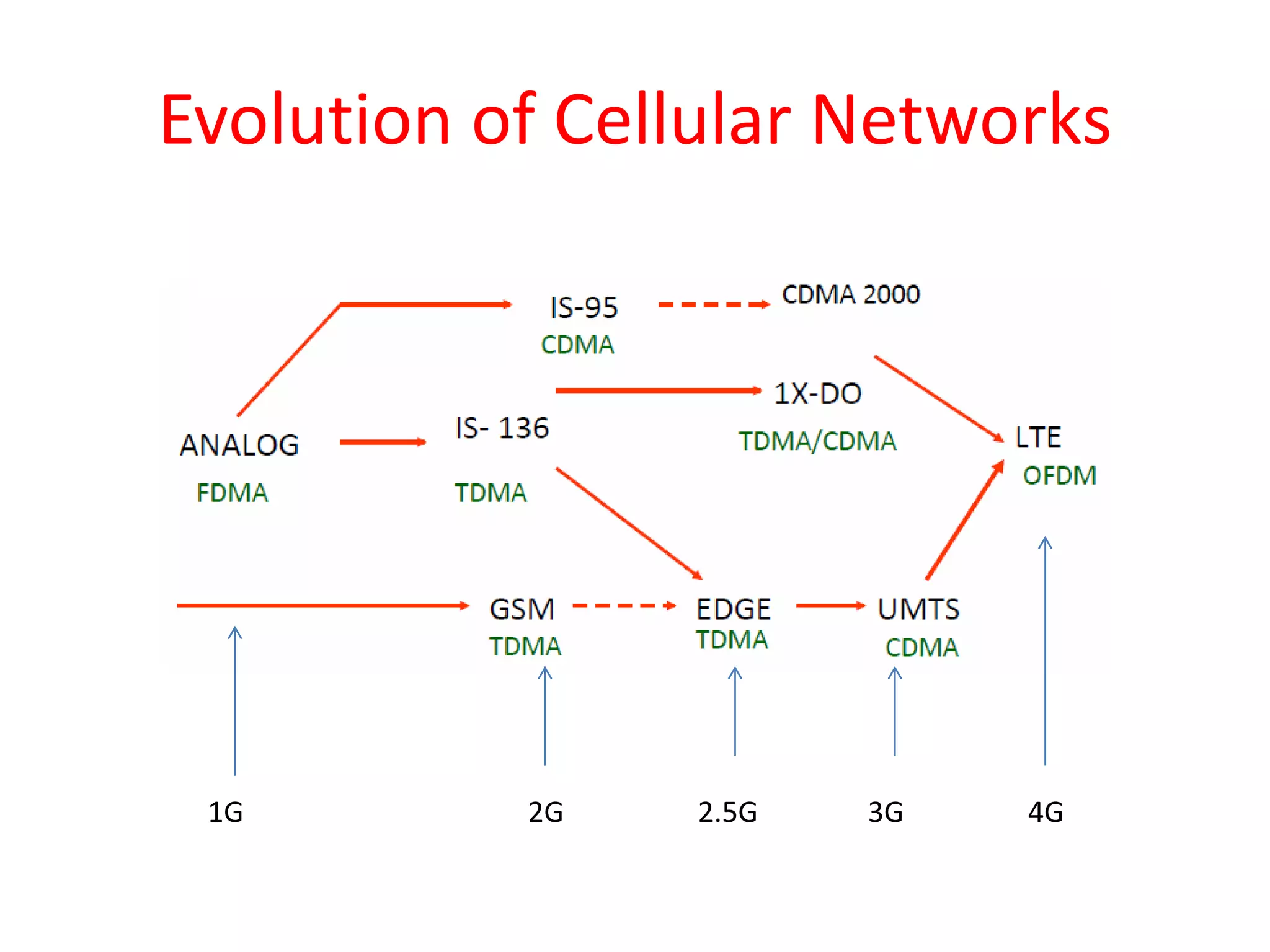
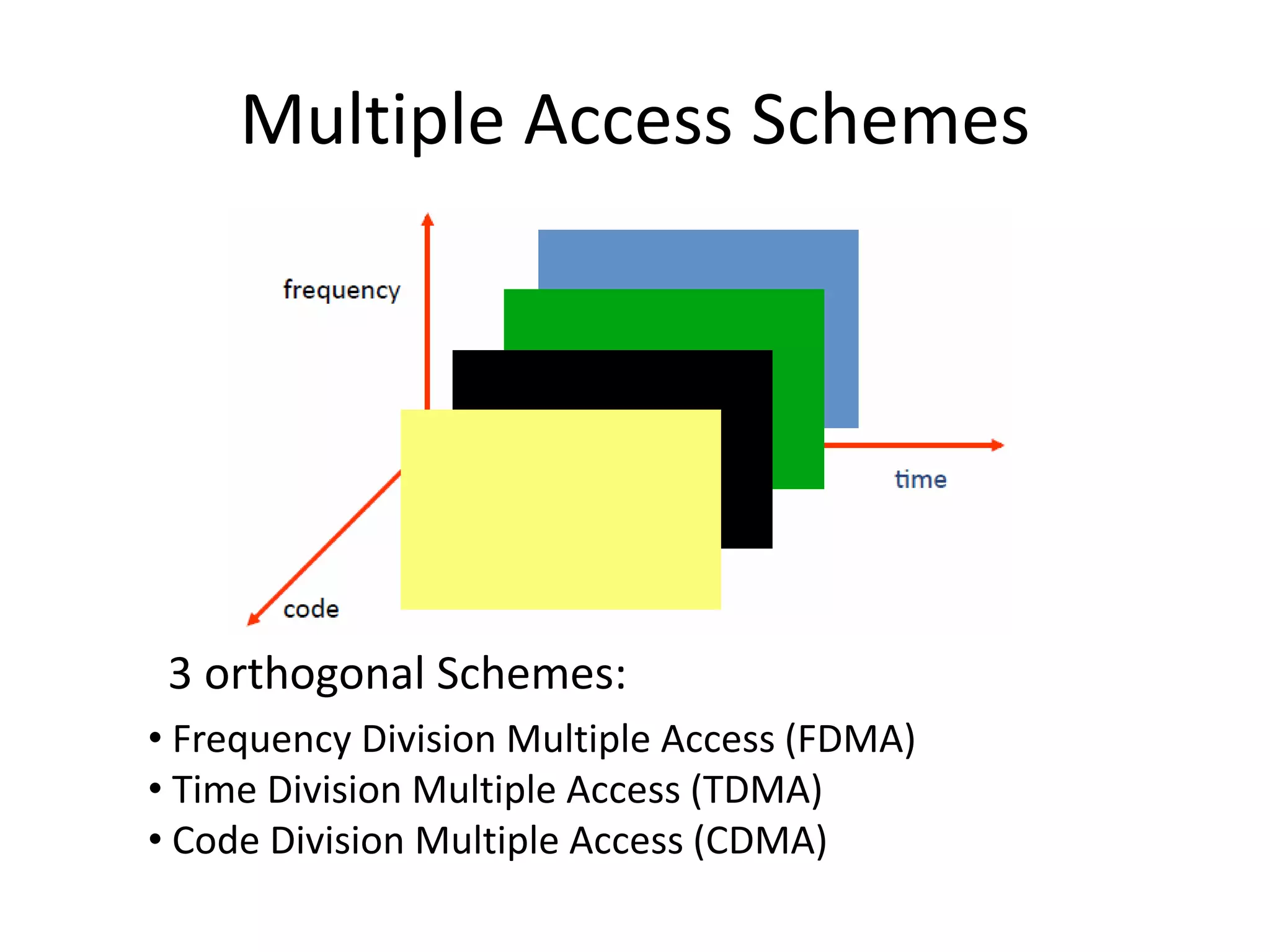
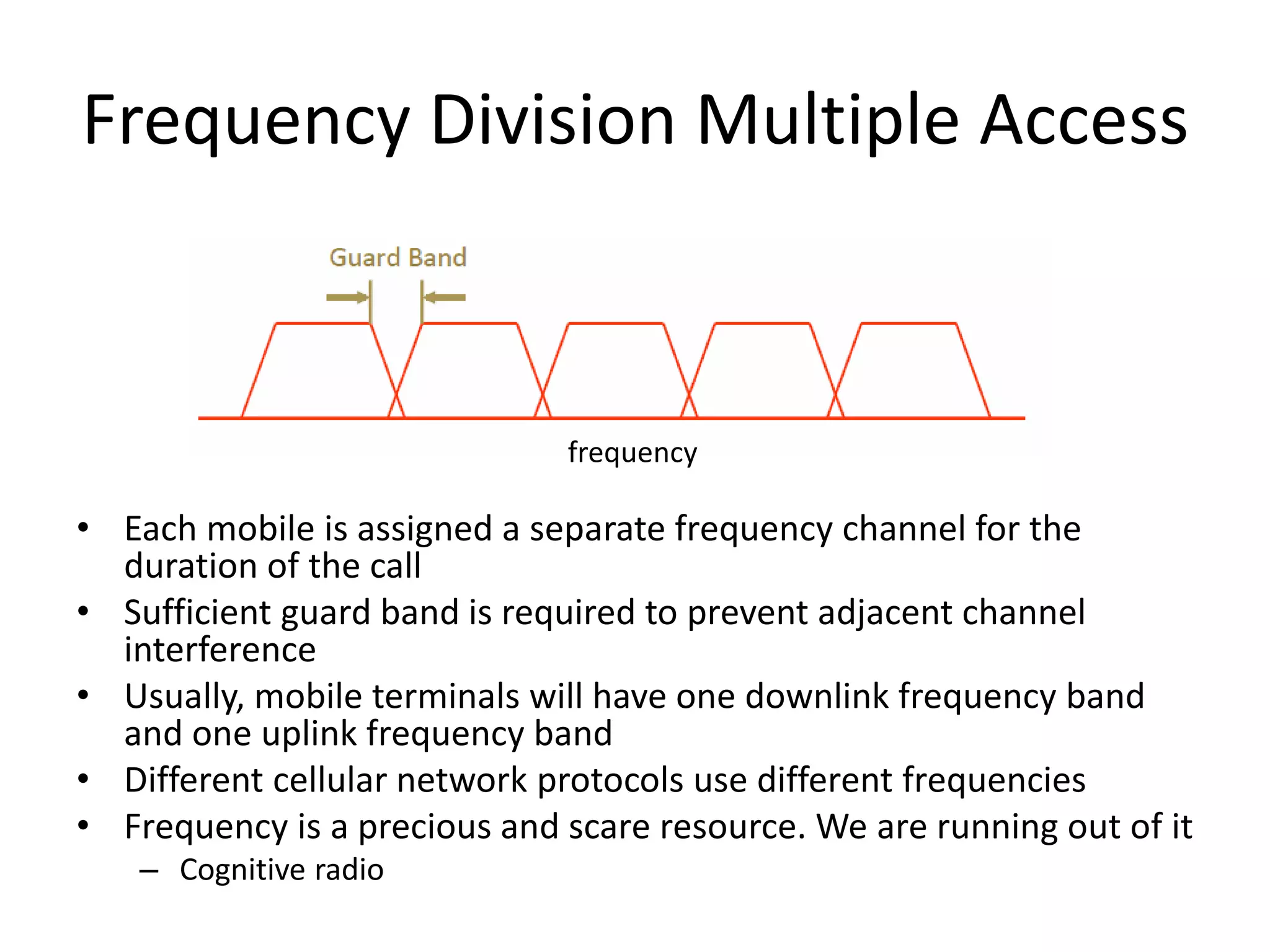
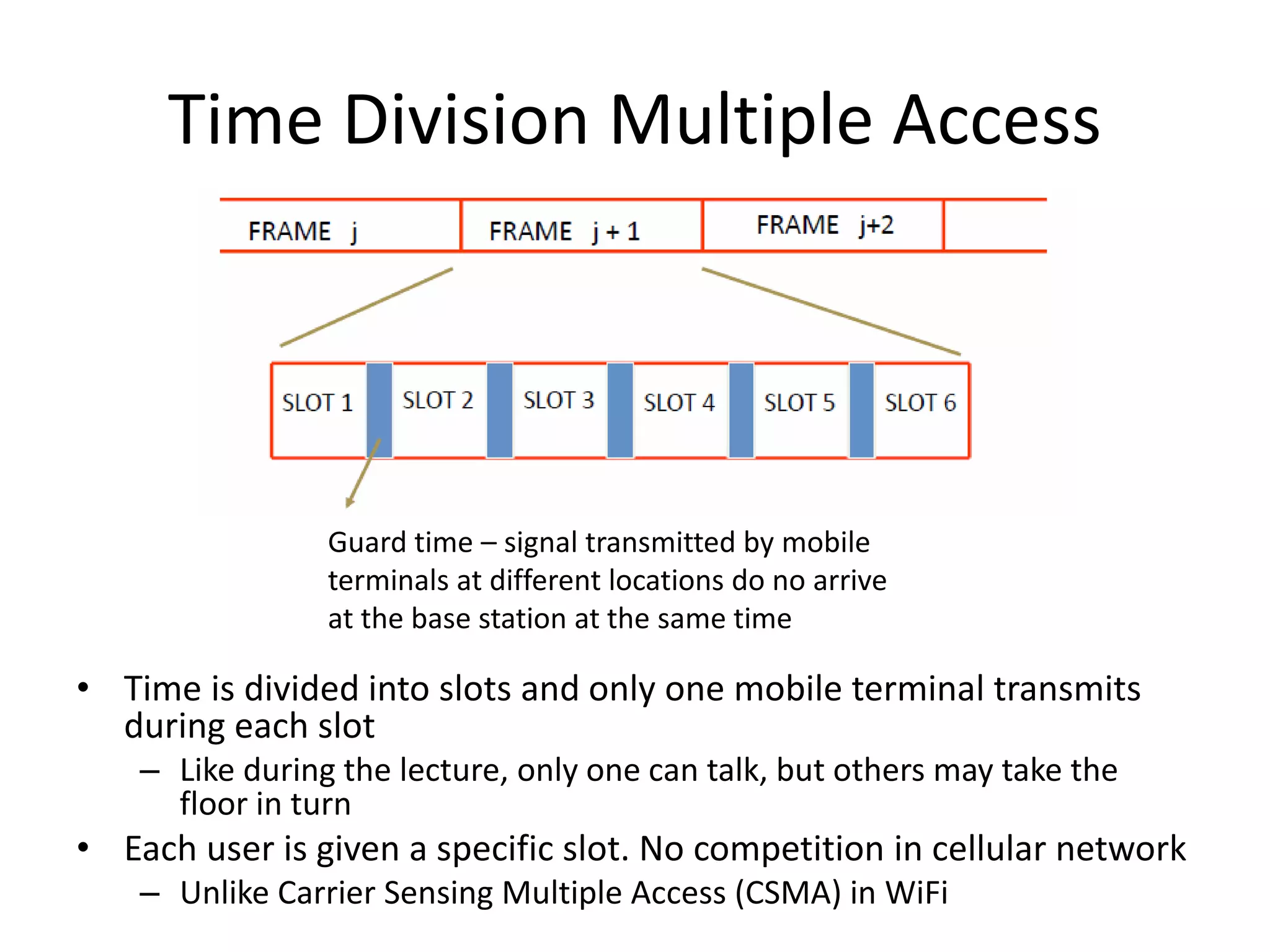
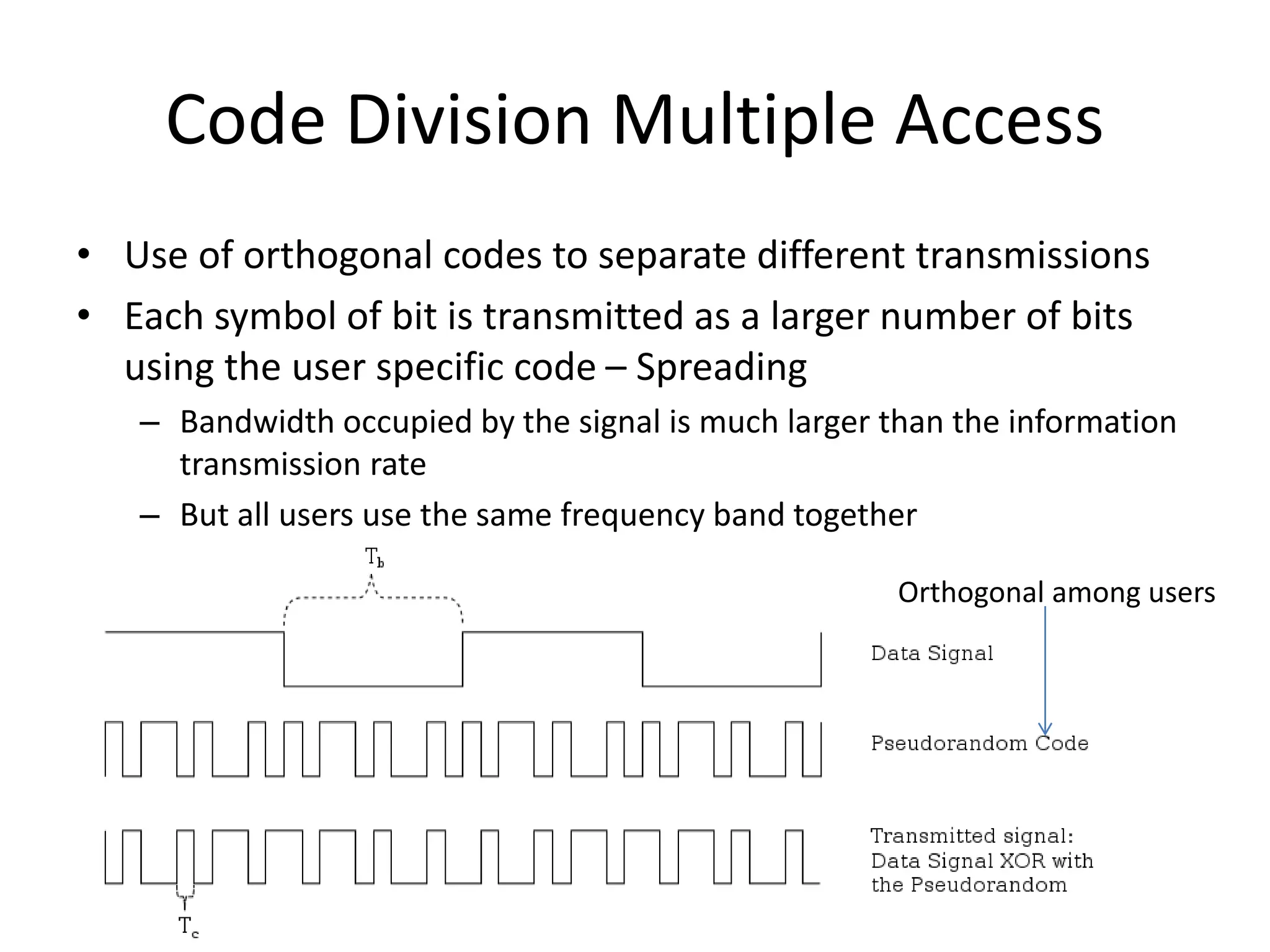
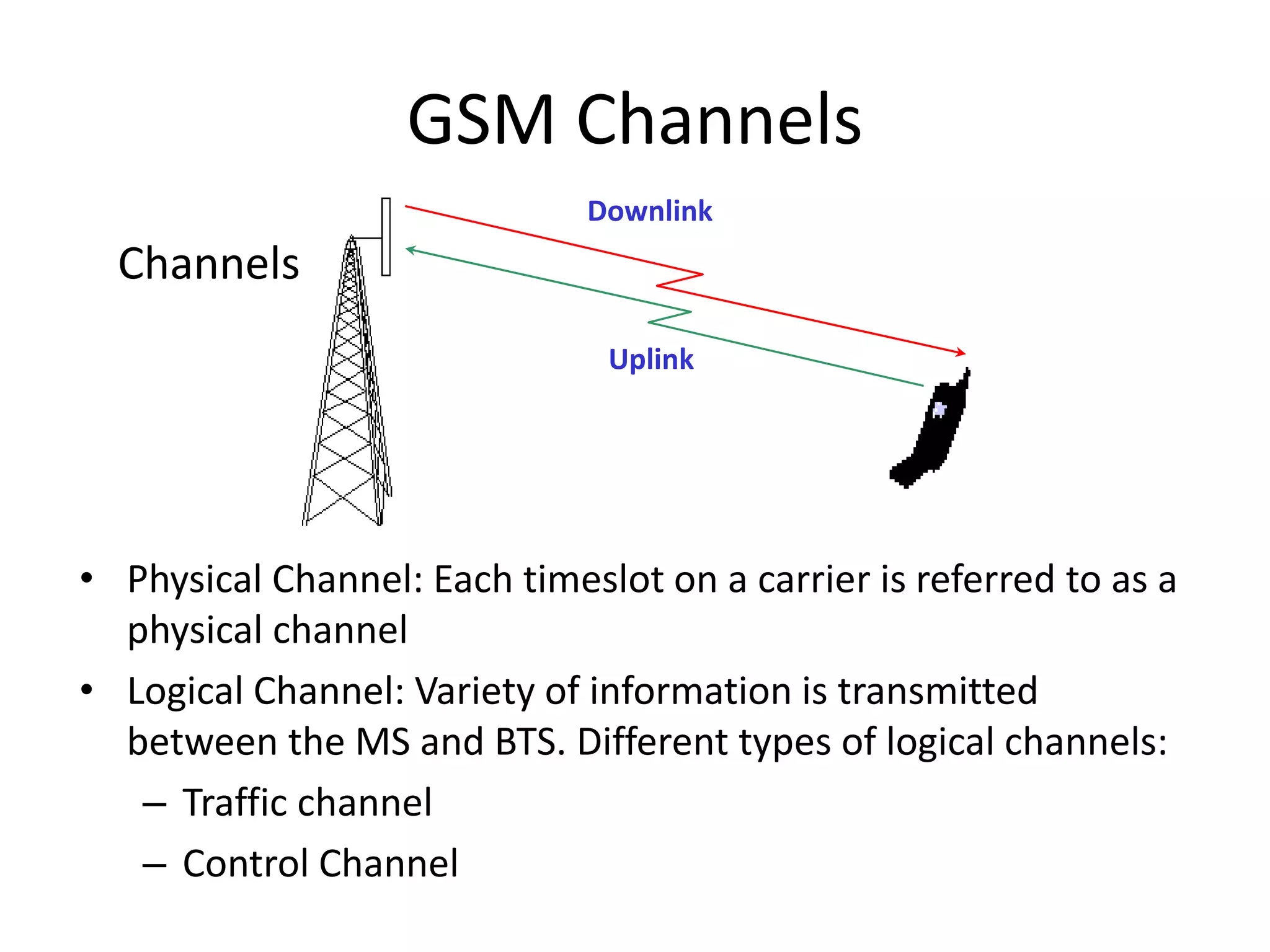
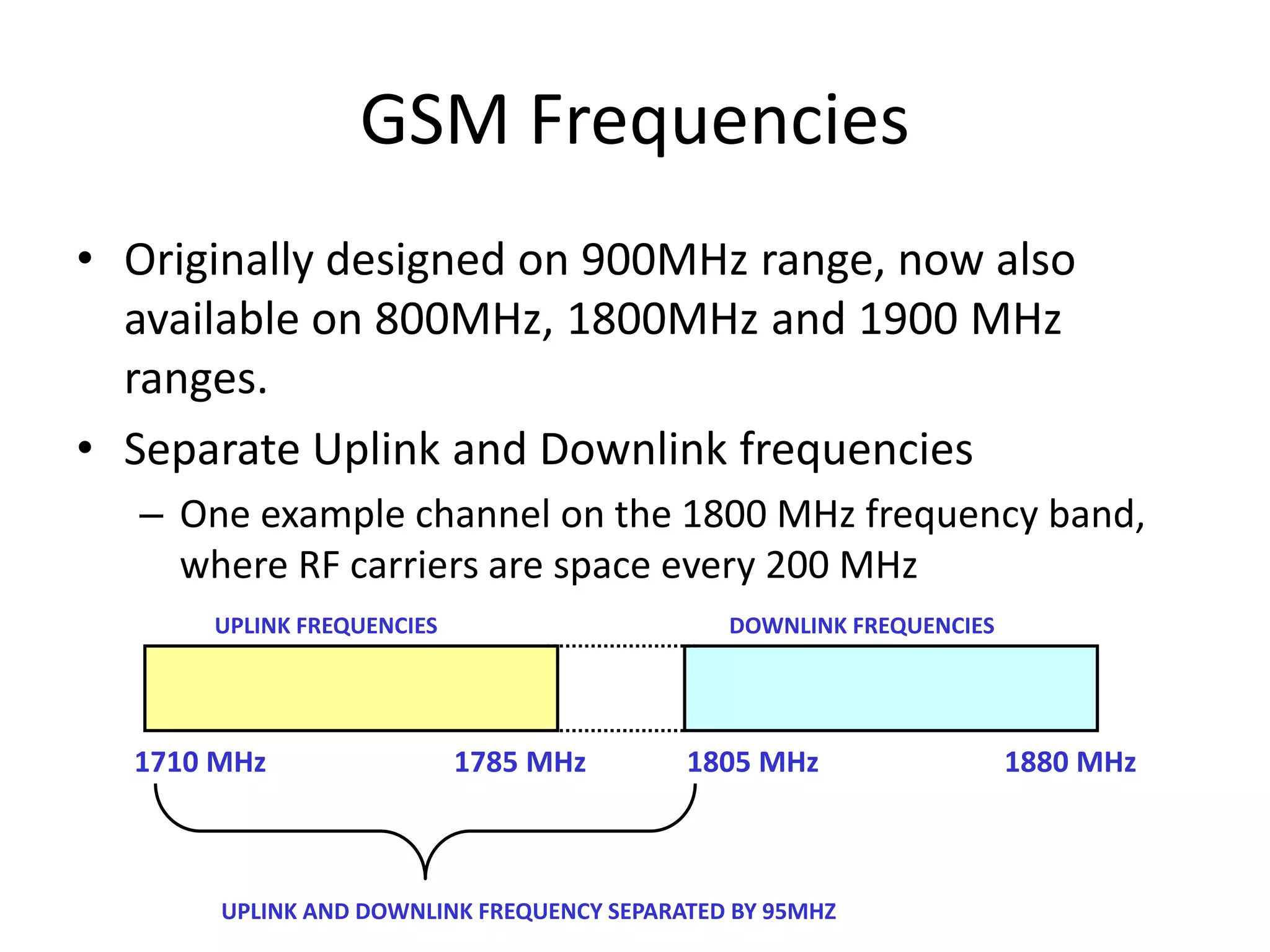
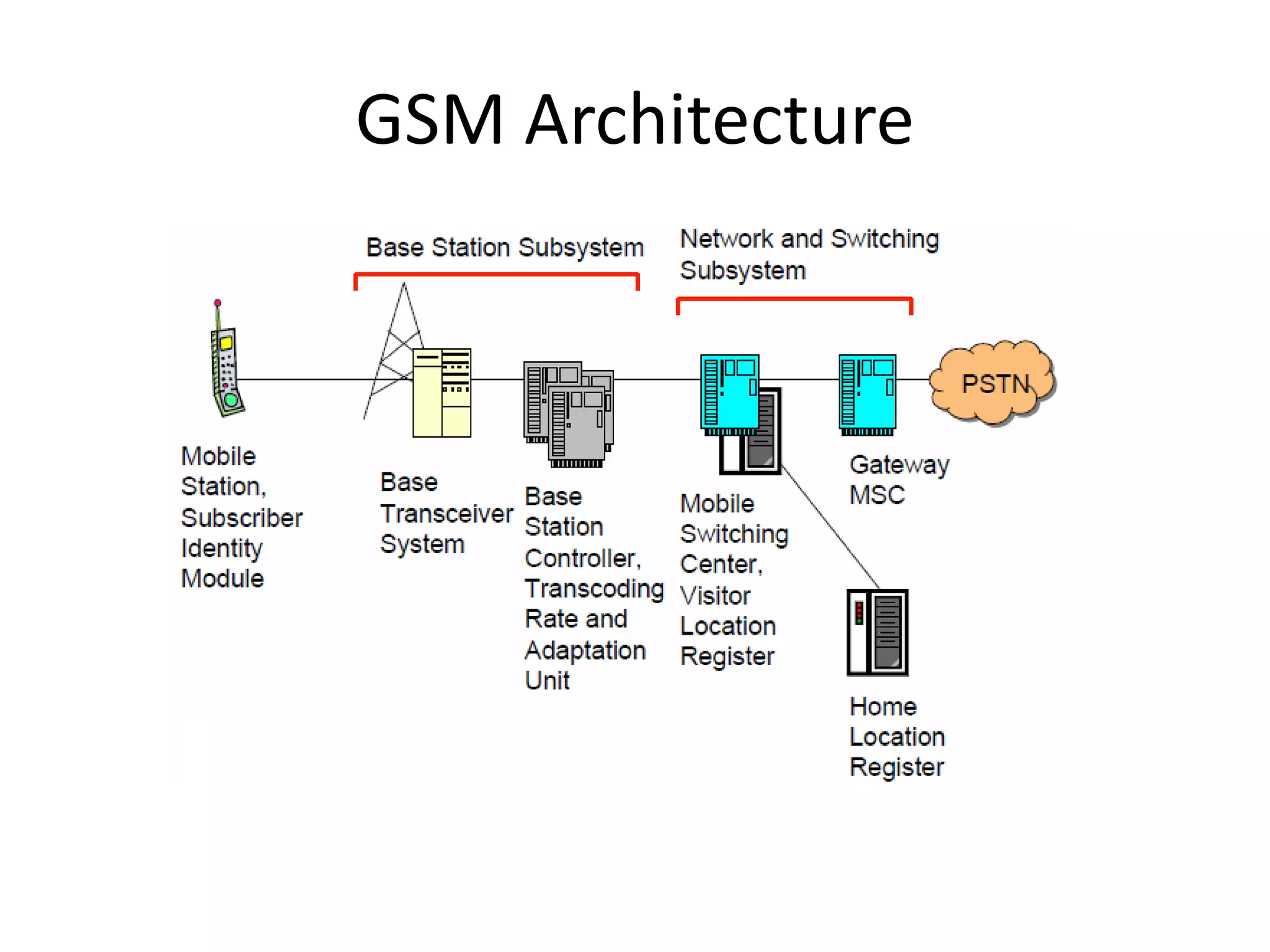
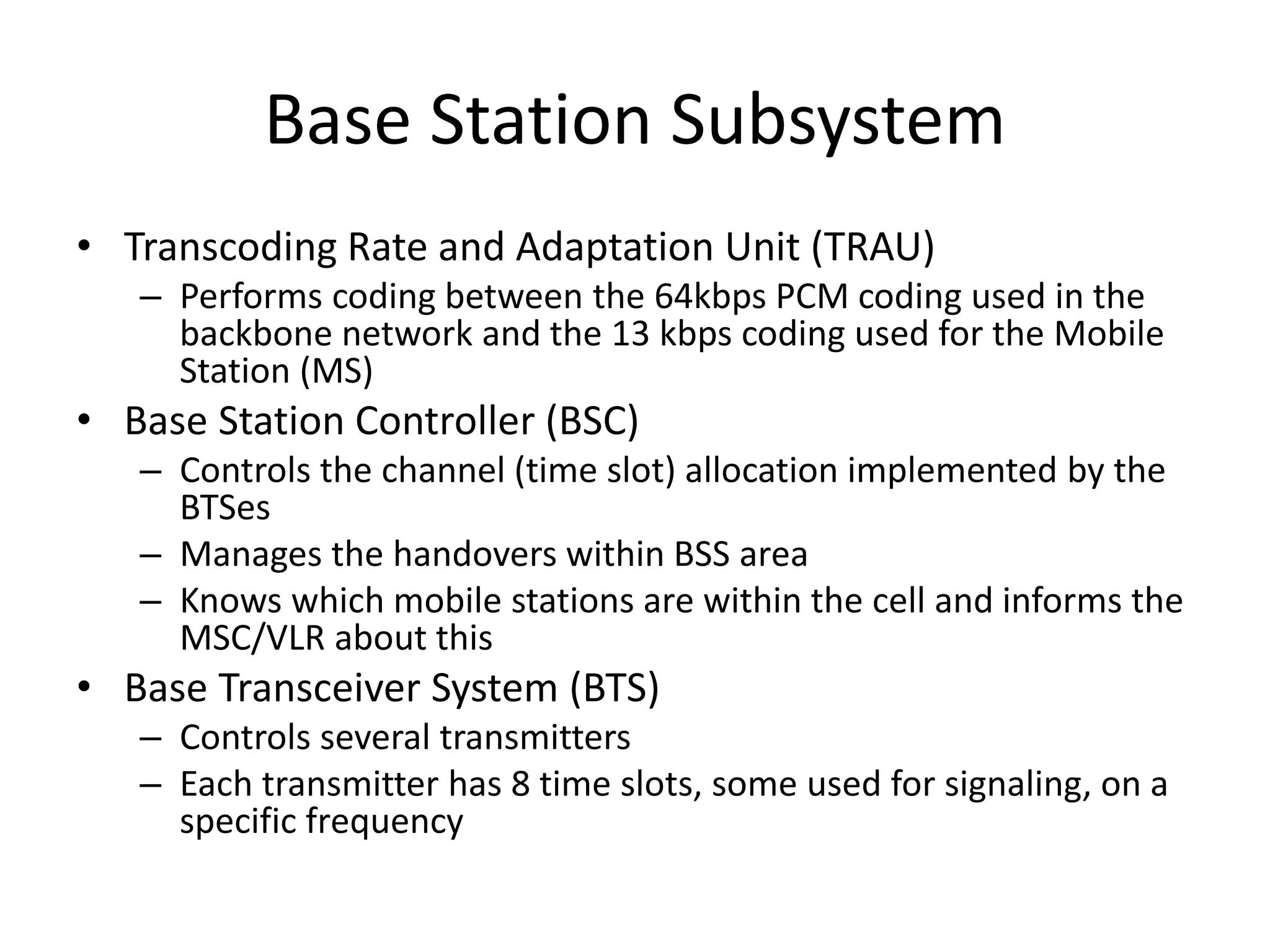
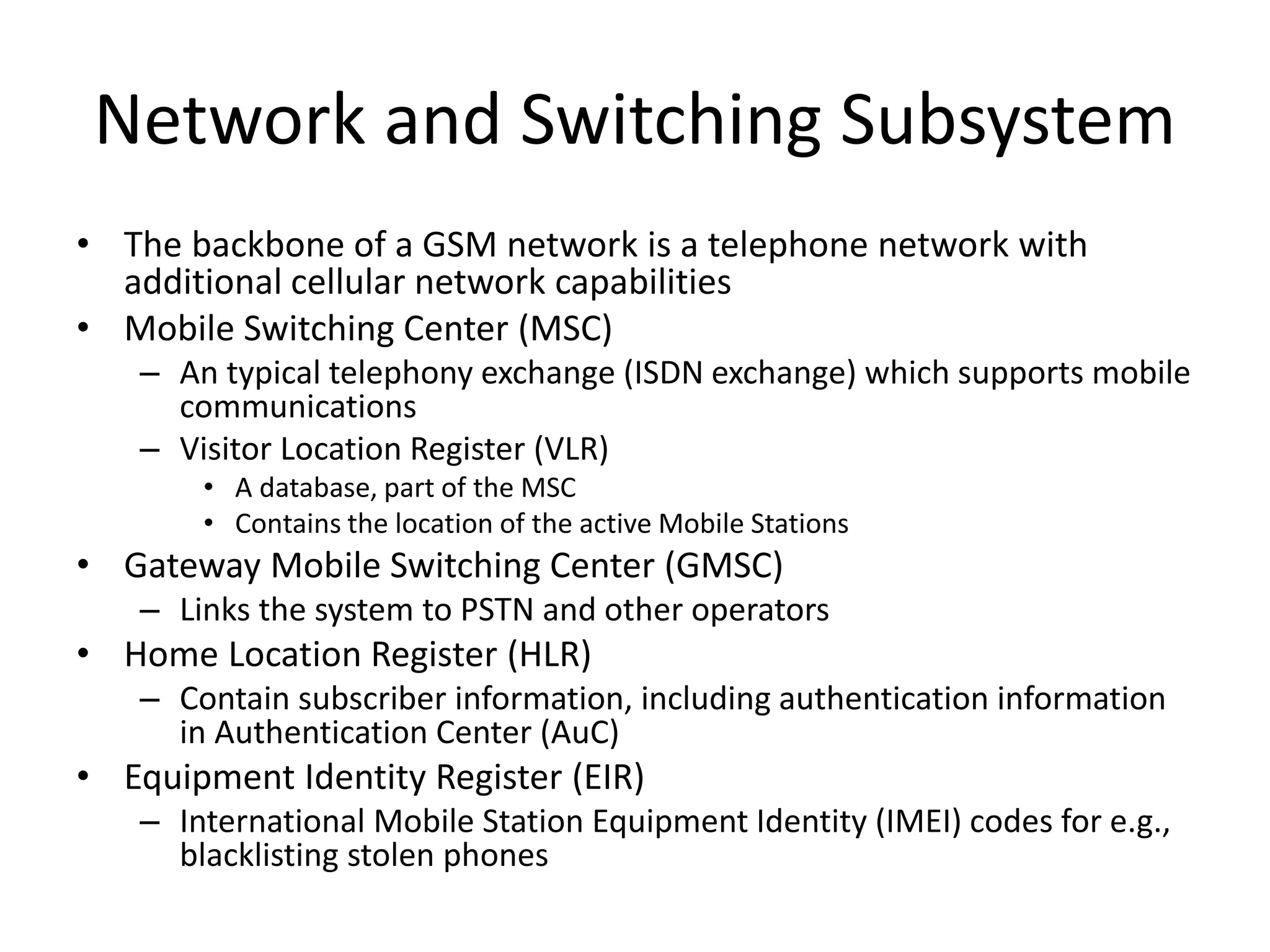
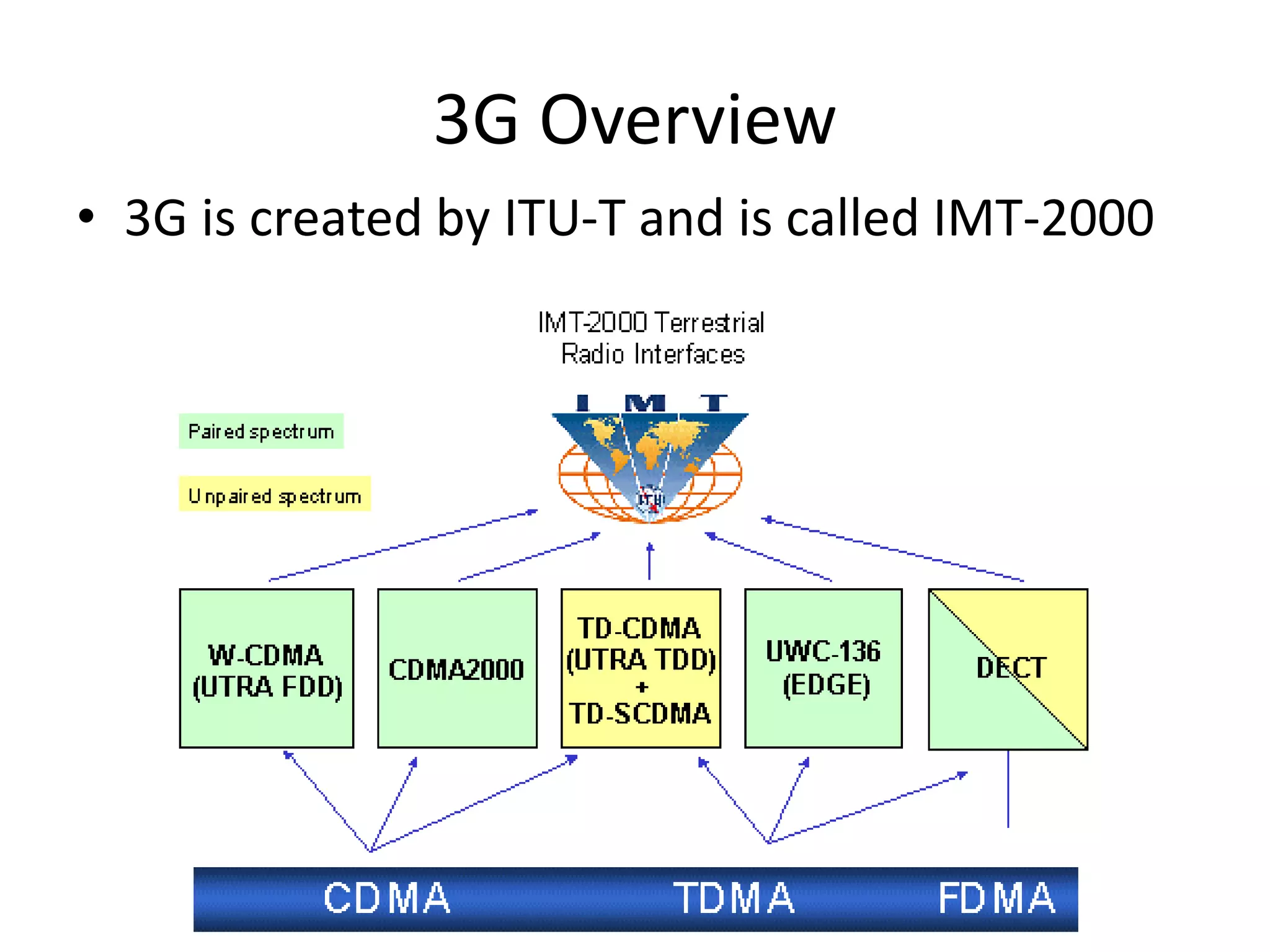
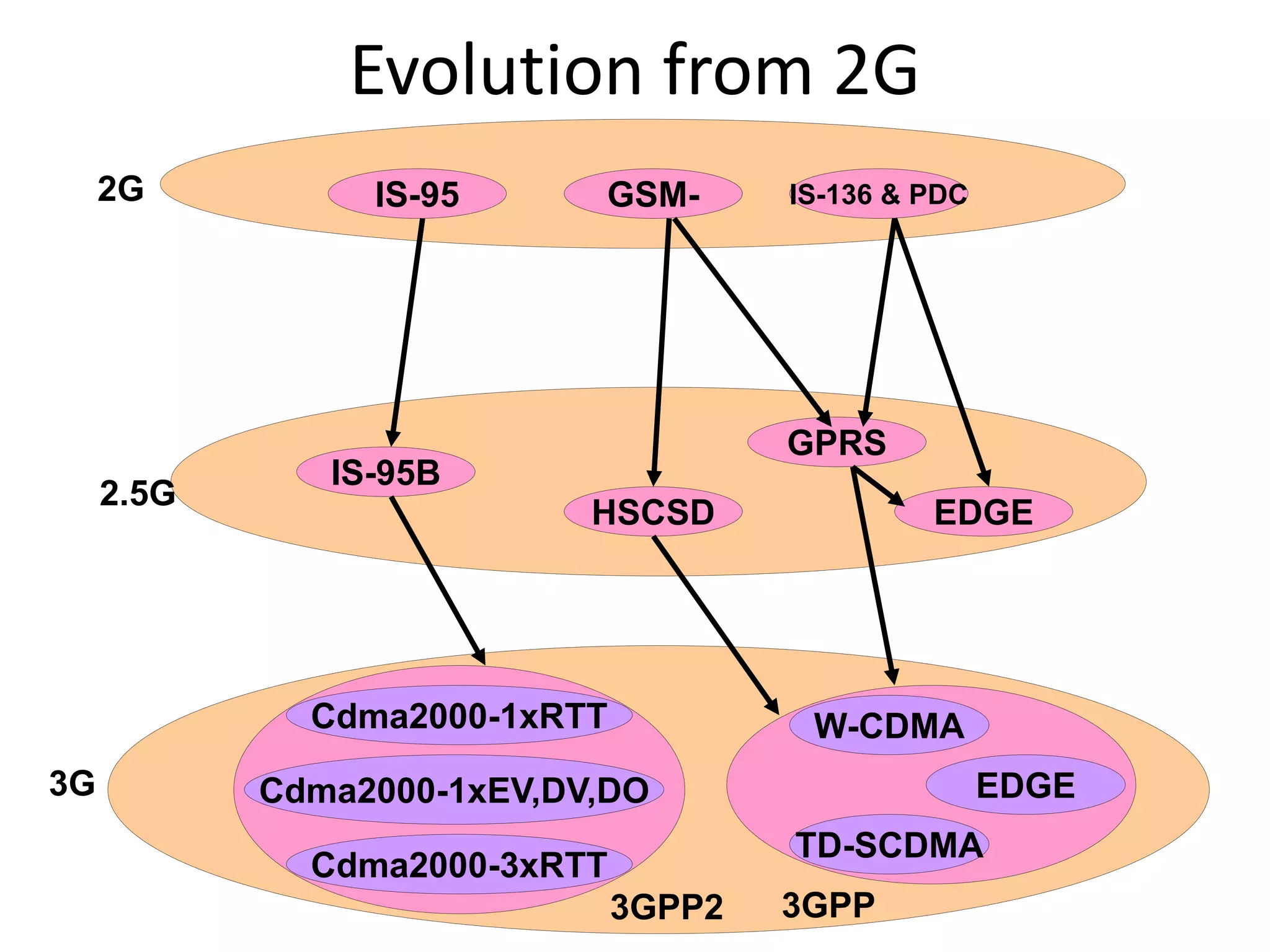
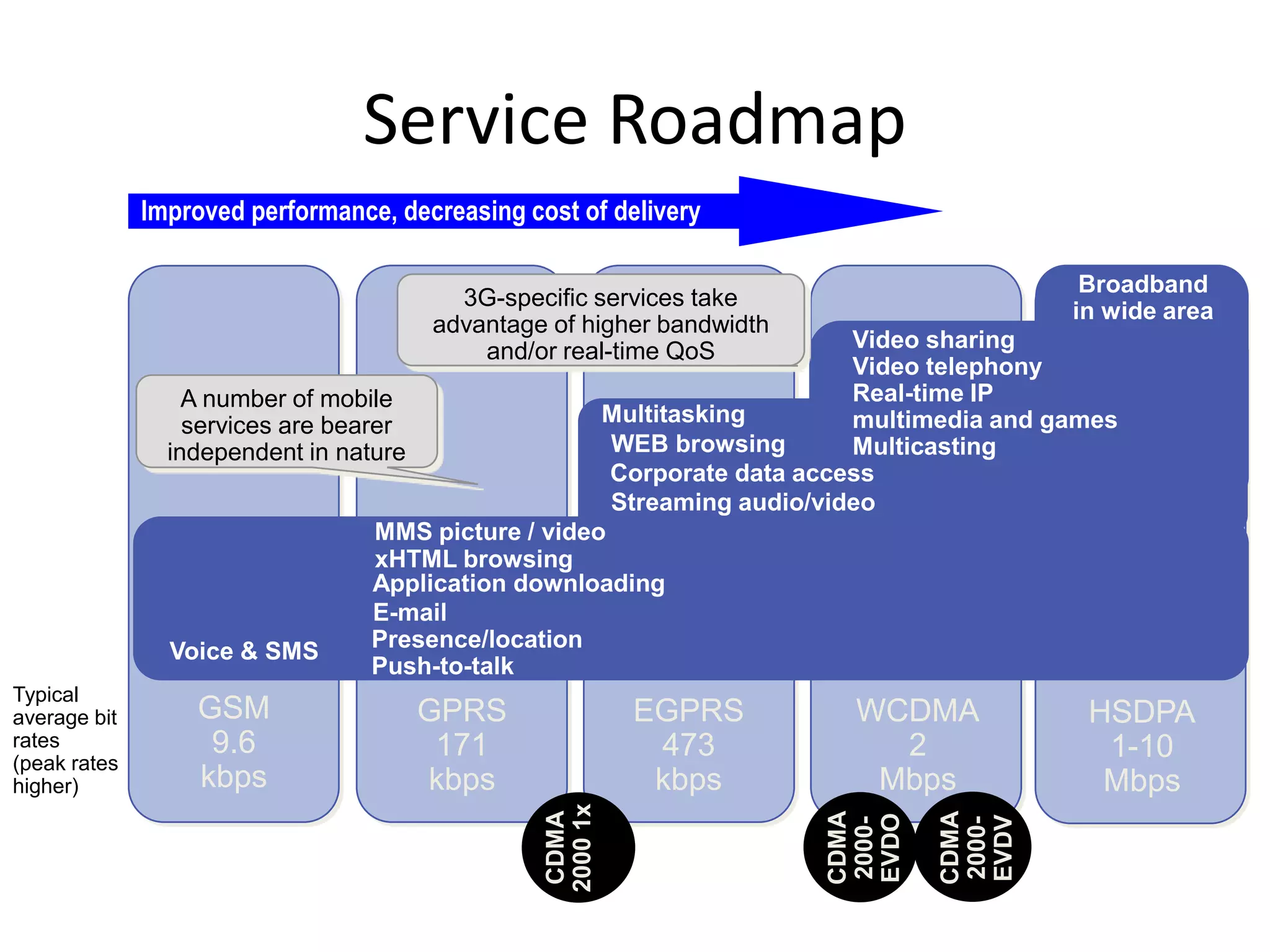
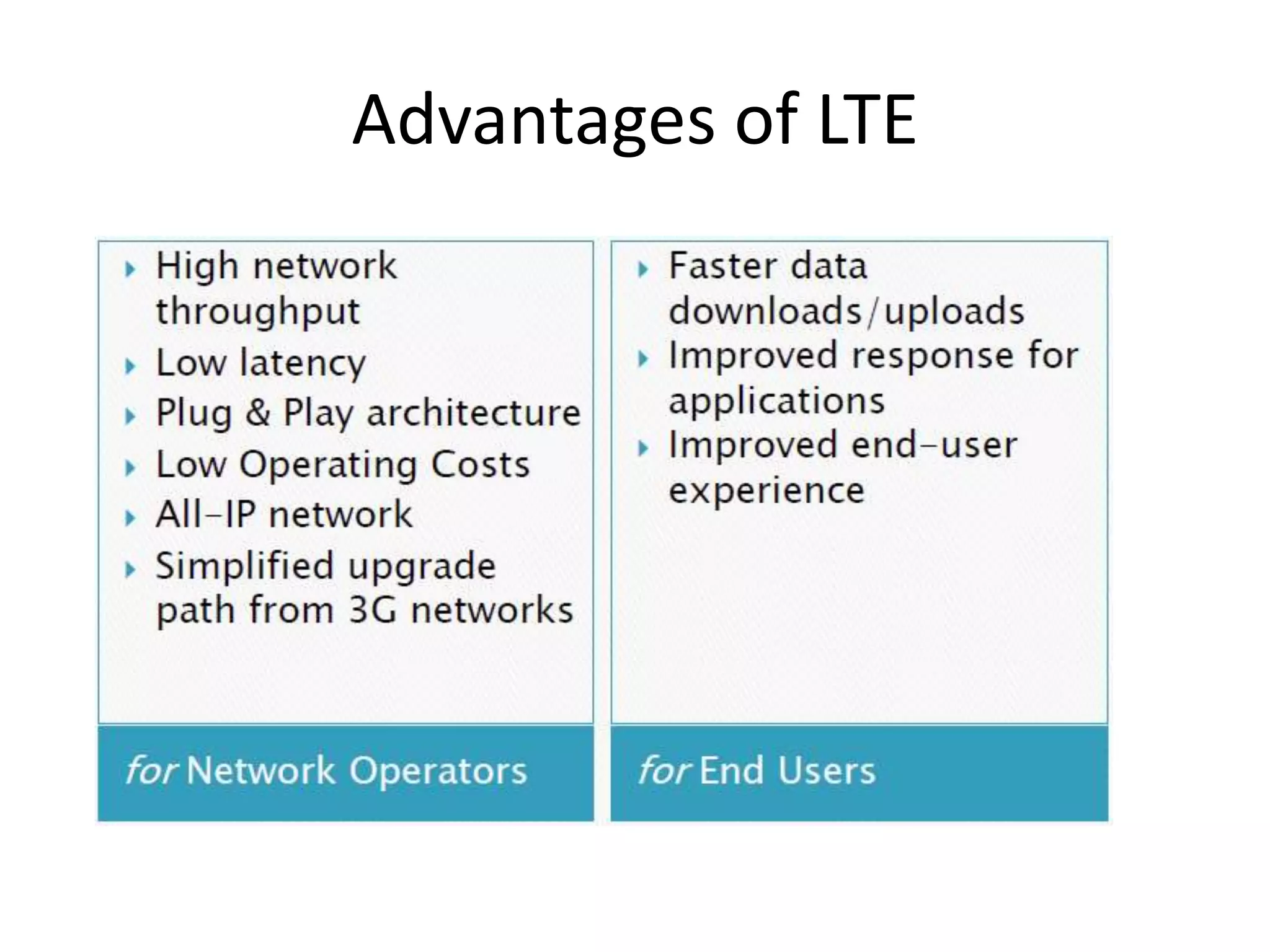
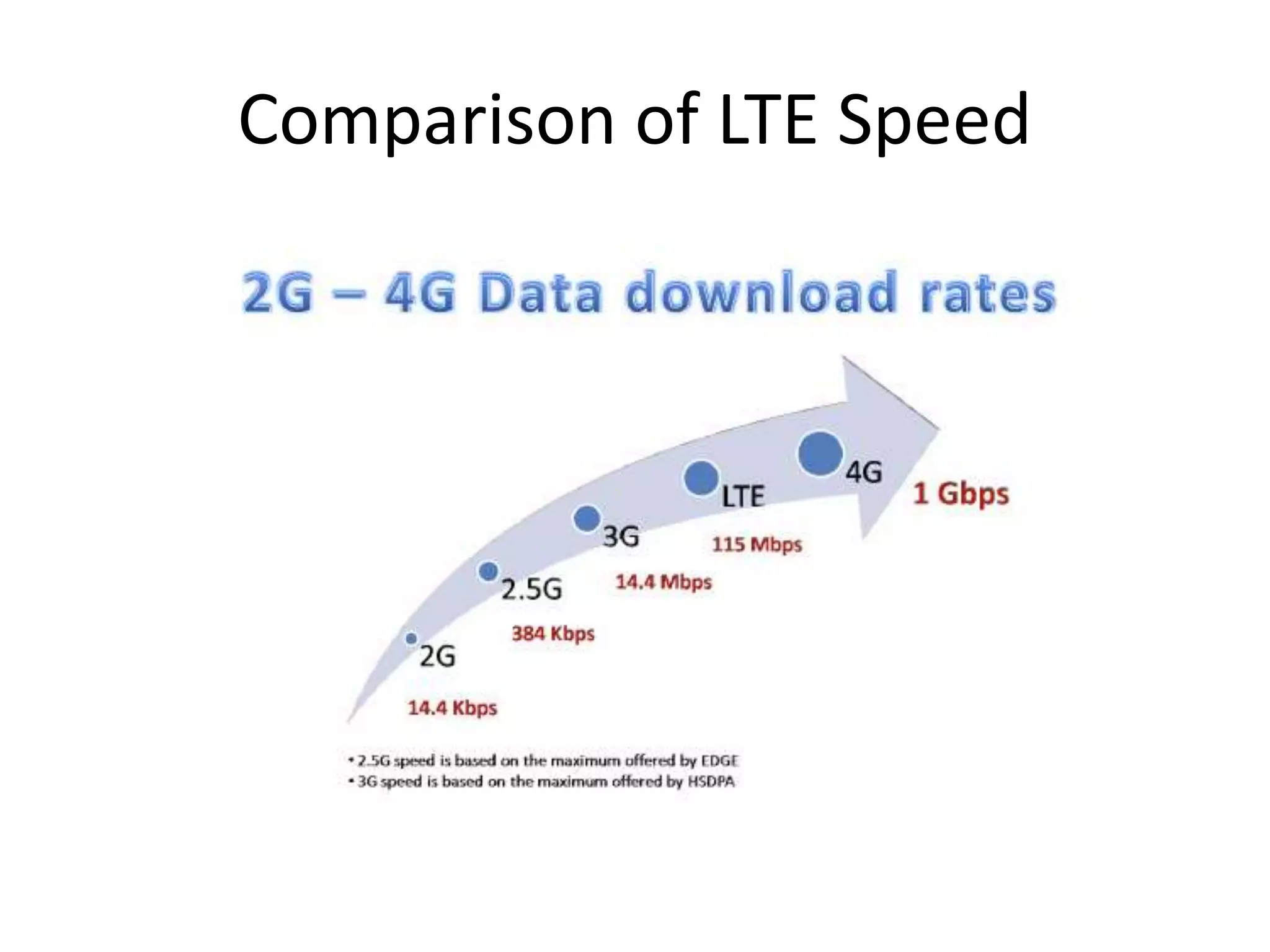
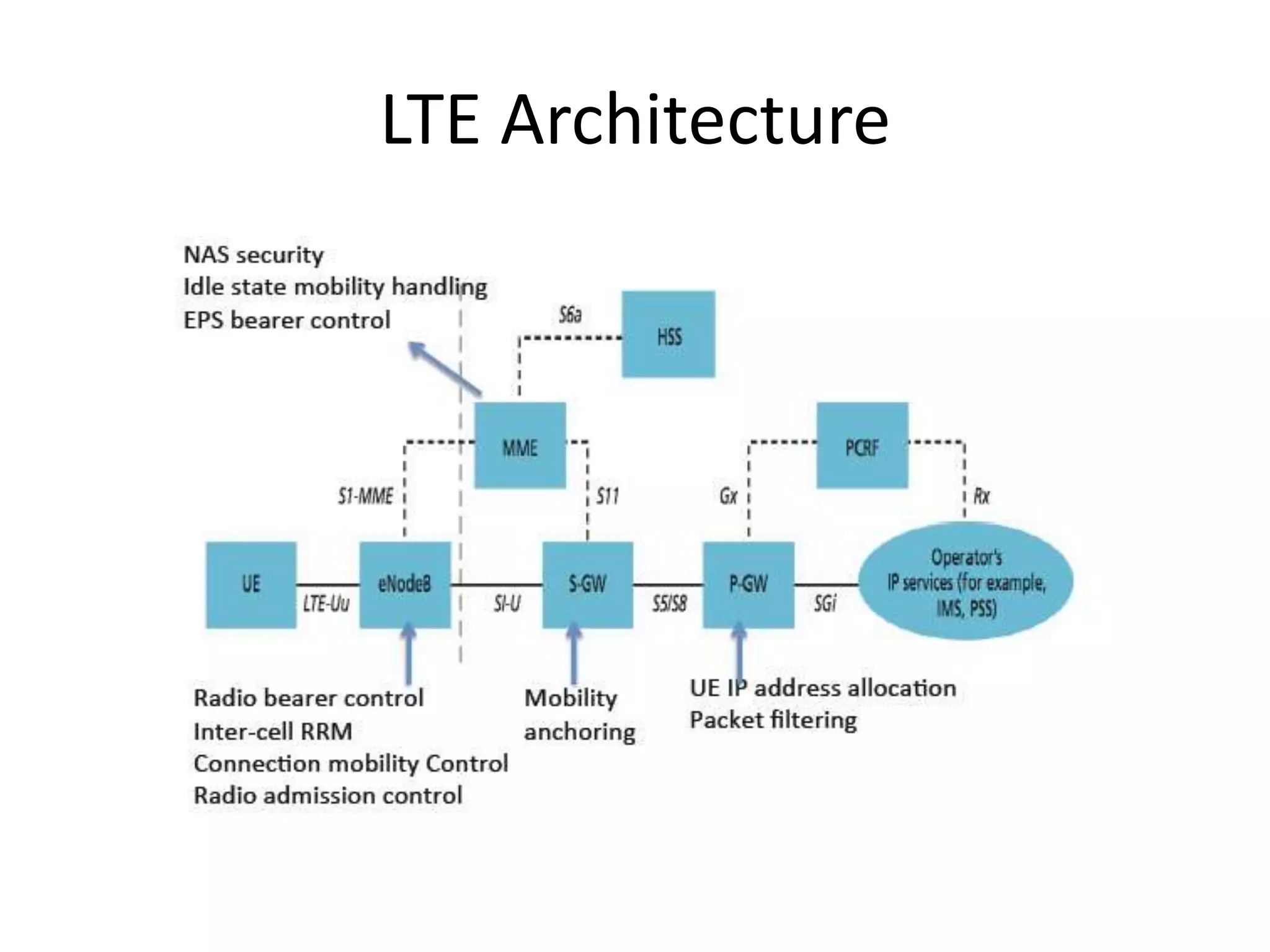
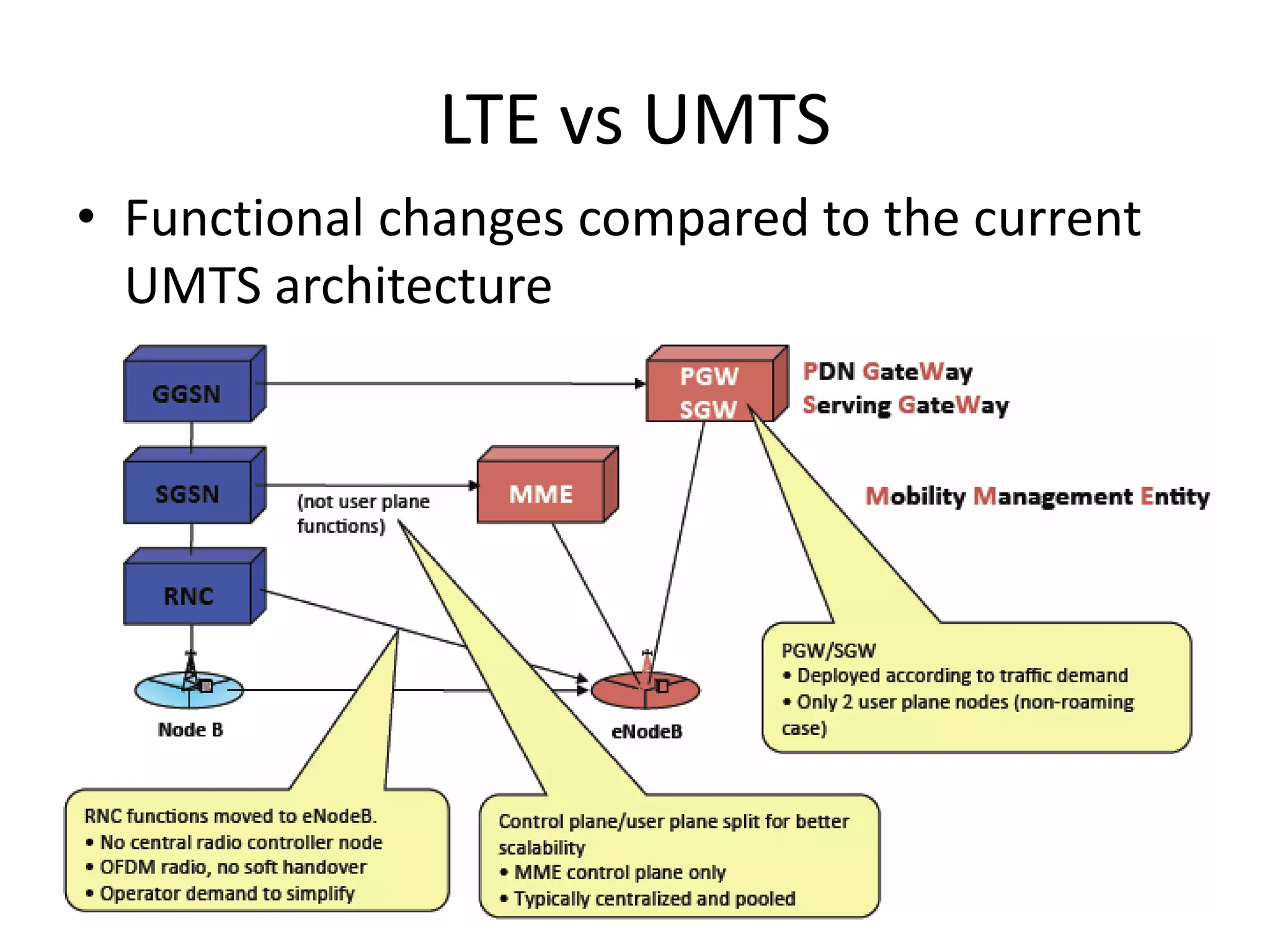
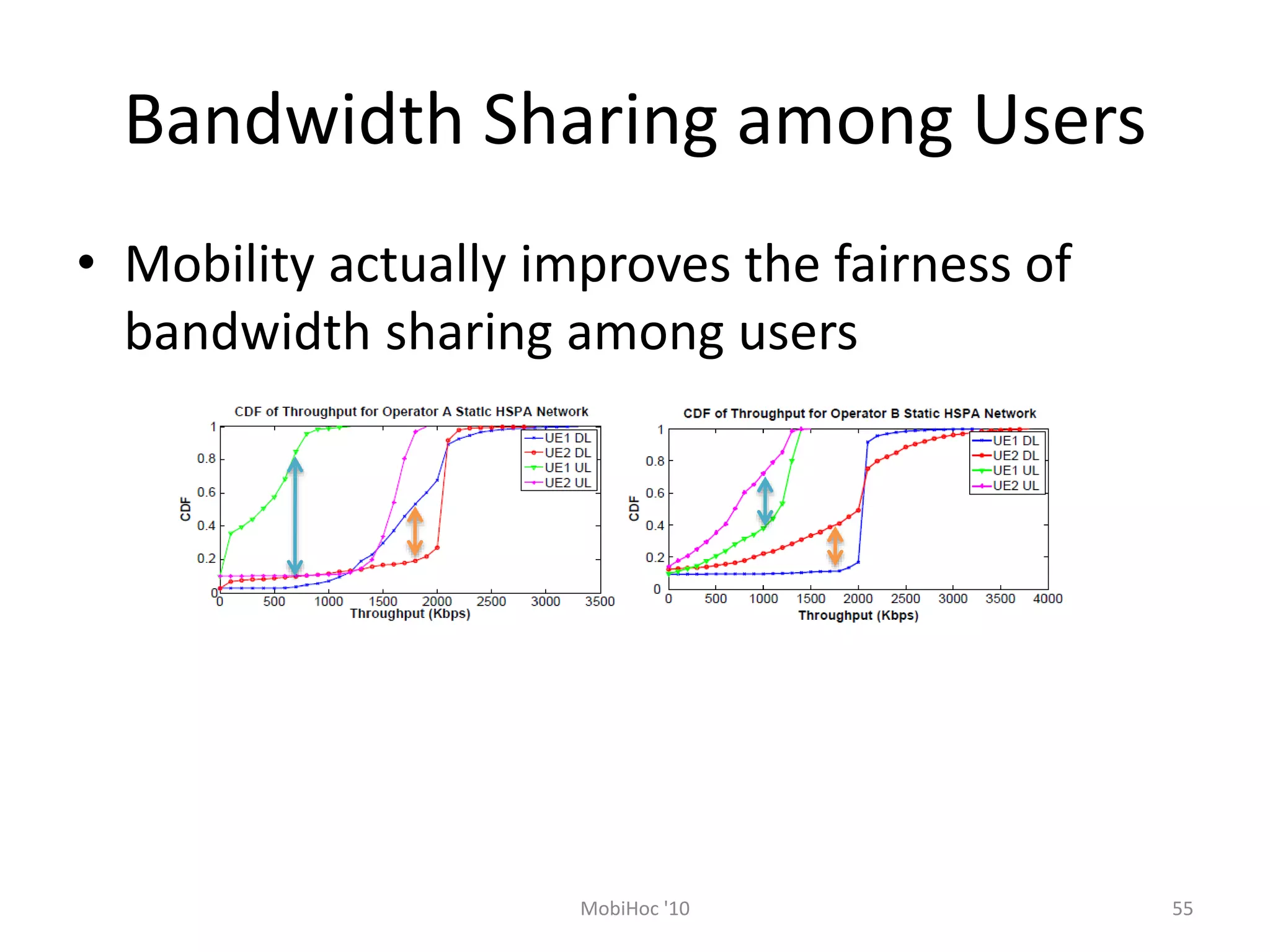
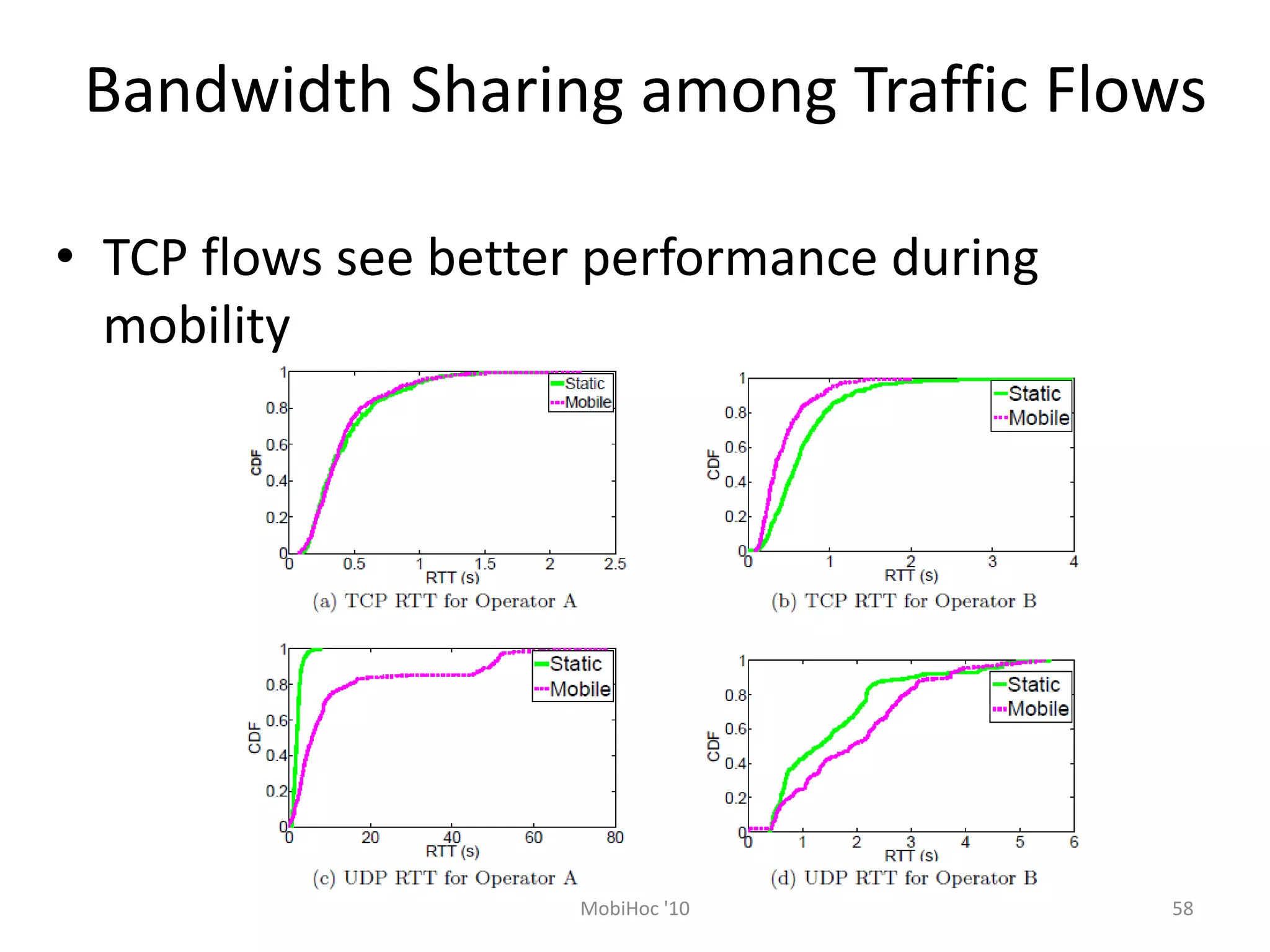
Mobile phones operate using cellular networks that transmit radio signals in frequency bands between 850-1900 MHz. A cellular network consists of base stations that transmit to and receive from mobile devices. Each base station covers a geographic cell area. As devices move between cells, handoffs of the connection occur. Cellular networks have evolved through generations starting with analog 1G networks to current digital 4G networks that provide high-speed internet access. Multiple access schemes like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA are used to allow multiple devices to access the network simultaneously. Popular cellular standards include GSM, CDMA, and LTE which define network architecture, protocols, and services.