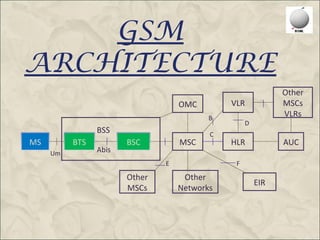
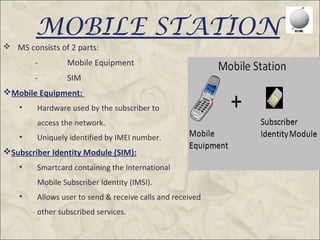
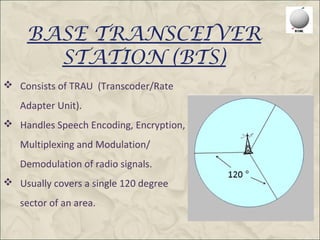
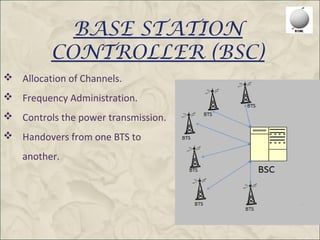
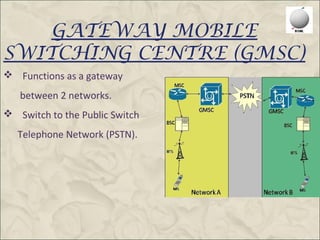
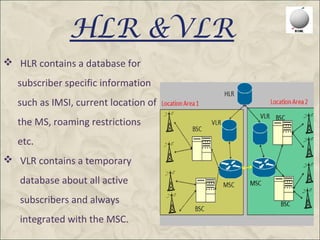
This document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). It discusses that GSM was created in 1982 to set a standard for mobile communications and the first system was deployed in 1991. The GSM architecture includes the mobile station, base station subsystem consisting of base transceiver stations and base station controllers, and the network and switching subsystem including mobile switching centers, home location register, and authentication center. GSM operates in the 900MHz and 1800MHz bands in India and uses frequency division duplex to provide communications between mobile devices and the network.