This document discusses the IS-LM model of macroeconomic equilibrium. It provides the following key points:
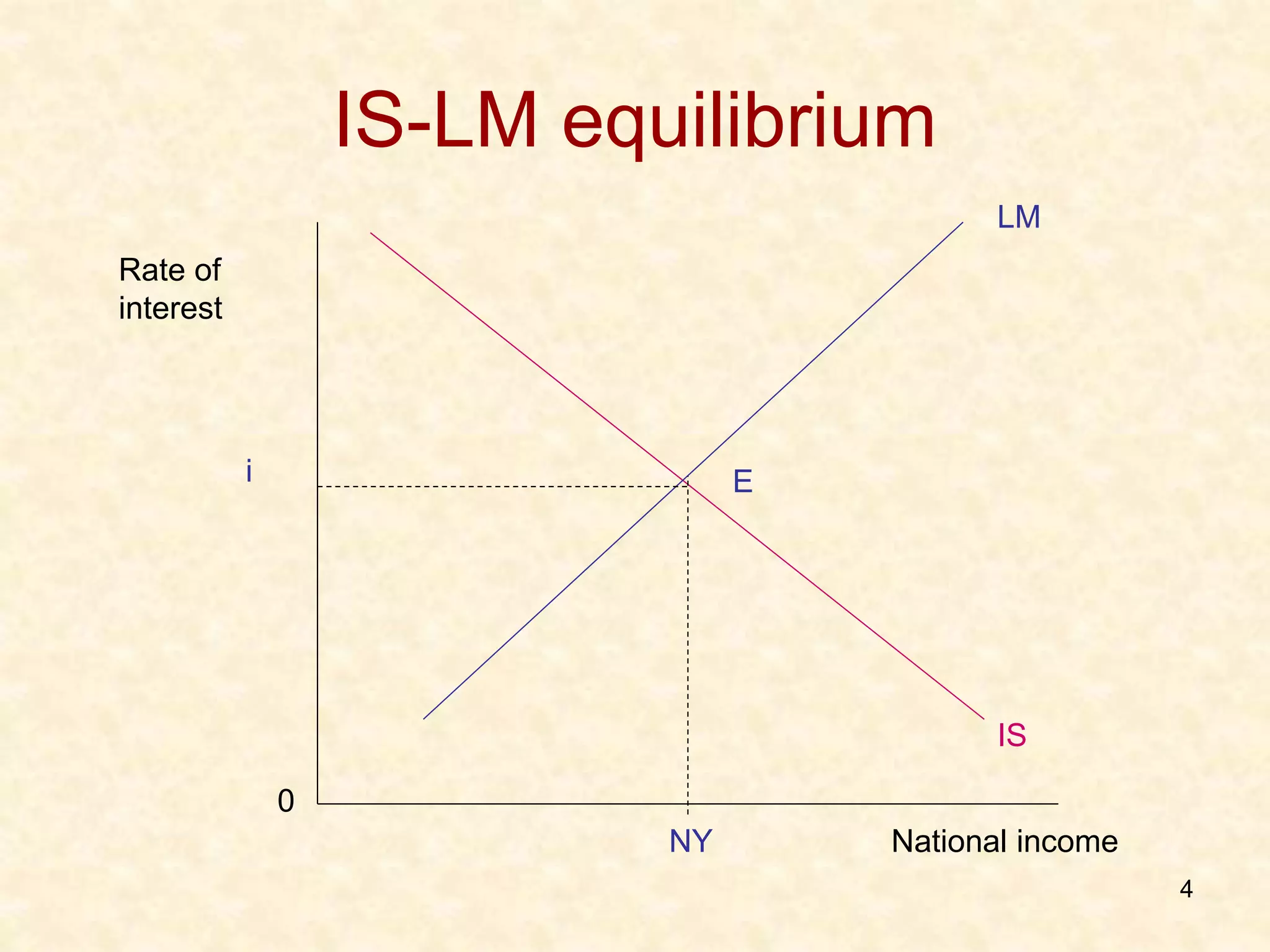
1. The IS curve and LM curve represent equilibrium in the goods/commodity market and money market respectively, with their intersection representing overall macroeconomic equilibrium.
2. At the equilibrium point, aggregate demand equals aggregate supply in the goods market, and money demand equals money supply.
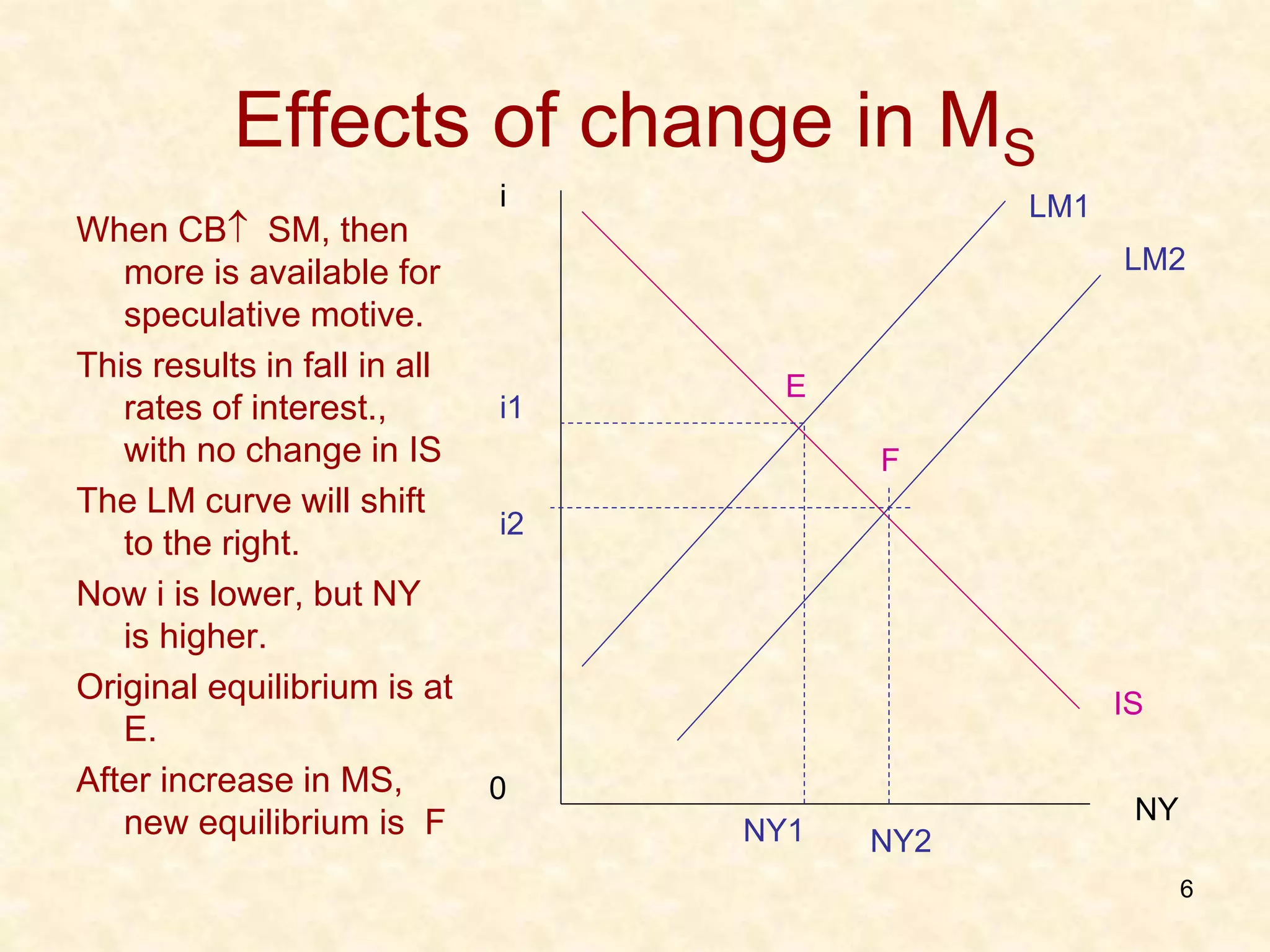
3. The IS-LM model integrates monetary and fiscal policy and is based on factors like investment demand, consumption, and money demand/supply. Changes to these factors shift the curves and alter the equilibrium level of income.
4. The model is criticized for assuming interest rates are flexible and markets are independent,