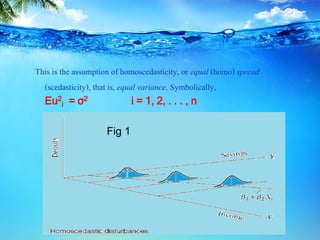
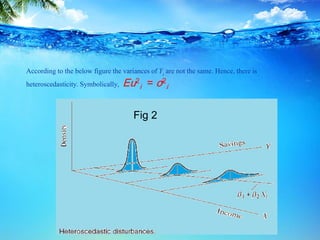
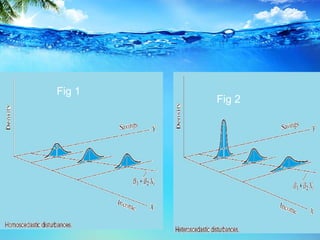
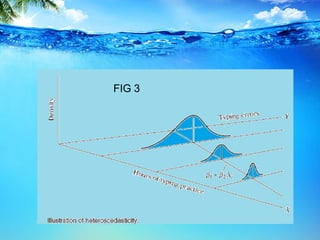
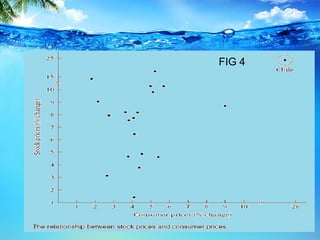
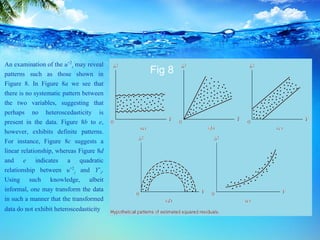
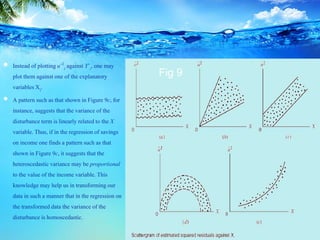
This document discusses heteroscedasticity, which occurs when the error variance is not constant. It provides examples of when the variance of errors may change, such as with income level or outliers. Graphical methods are presented for detecting heteroscedasticity by examining patterns in residual plots. Formal tests are also described, including the Park test which regresses the log of the squared residuals on explanatory variables, and the Glejser test which regresses the absolute value of residuals on variables related to the error variance. Detection of heteroscedasticity is important as it violates assumptions of the classical linear regression model.