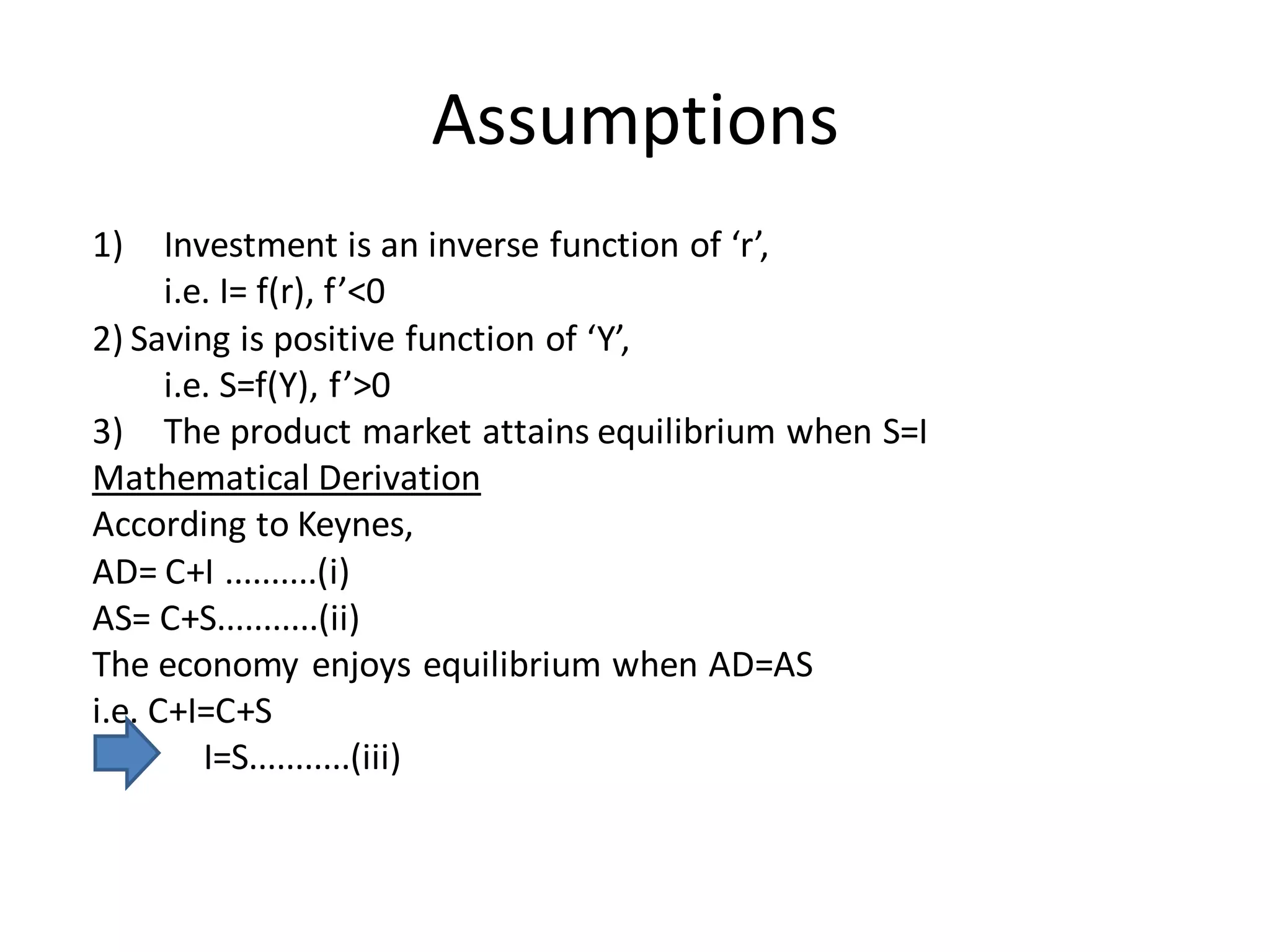
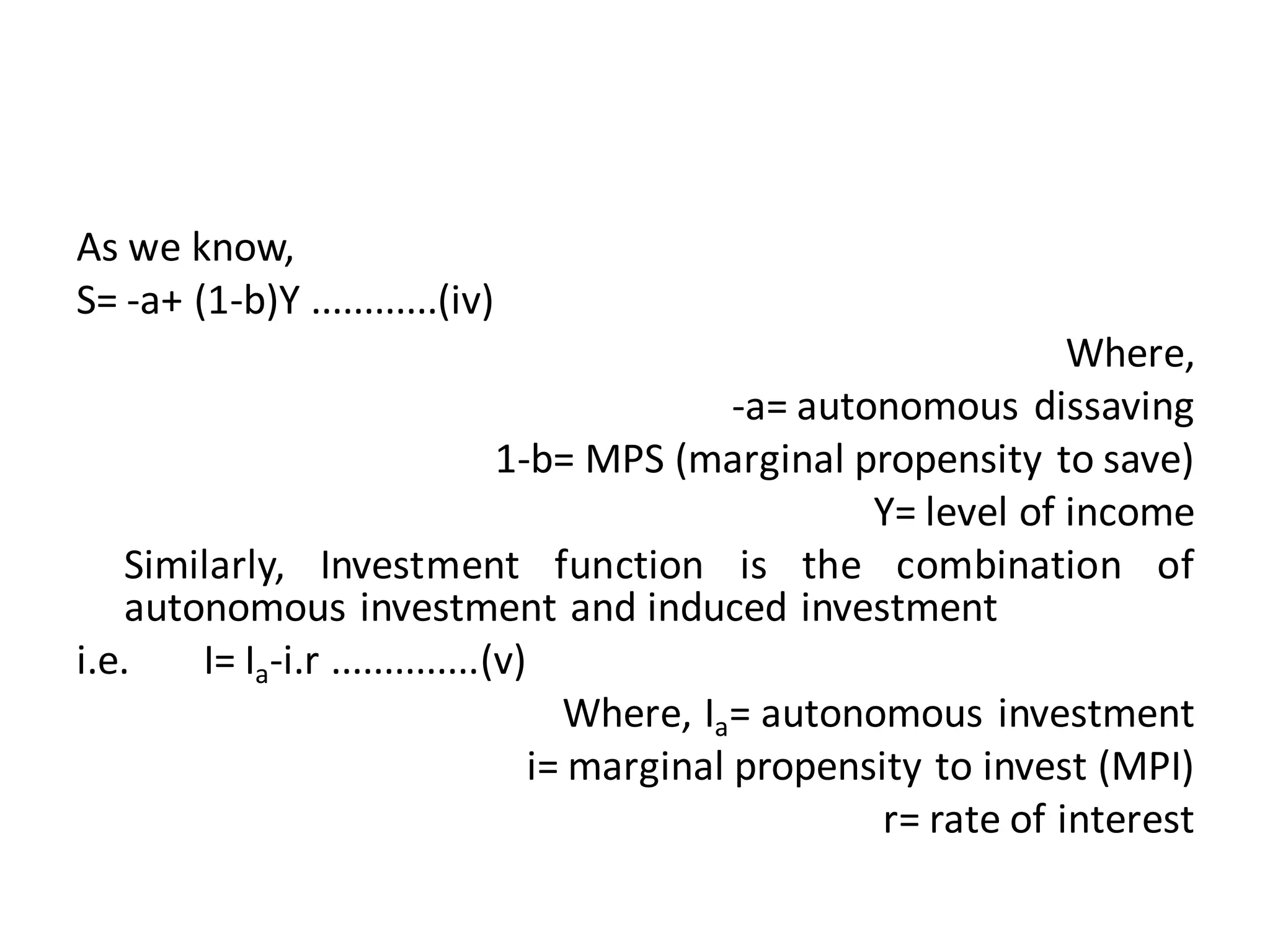
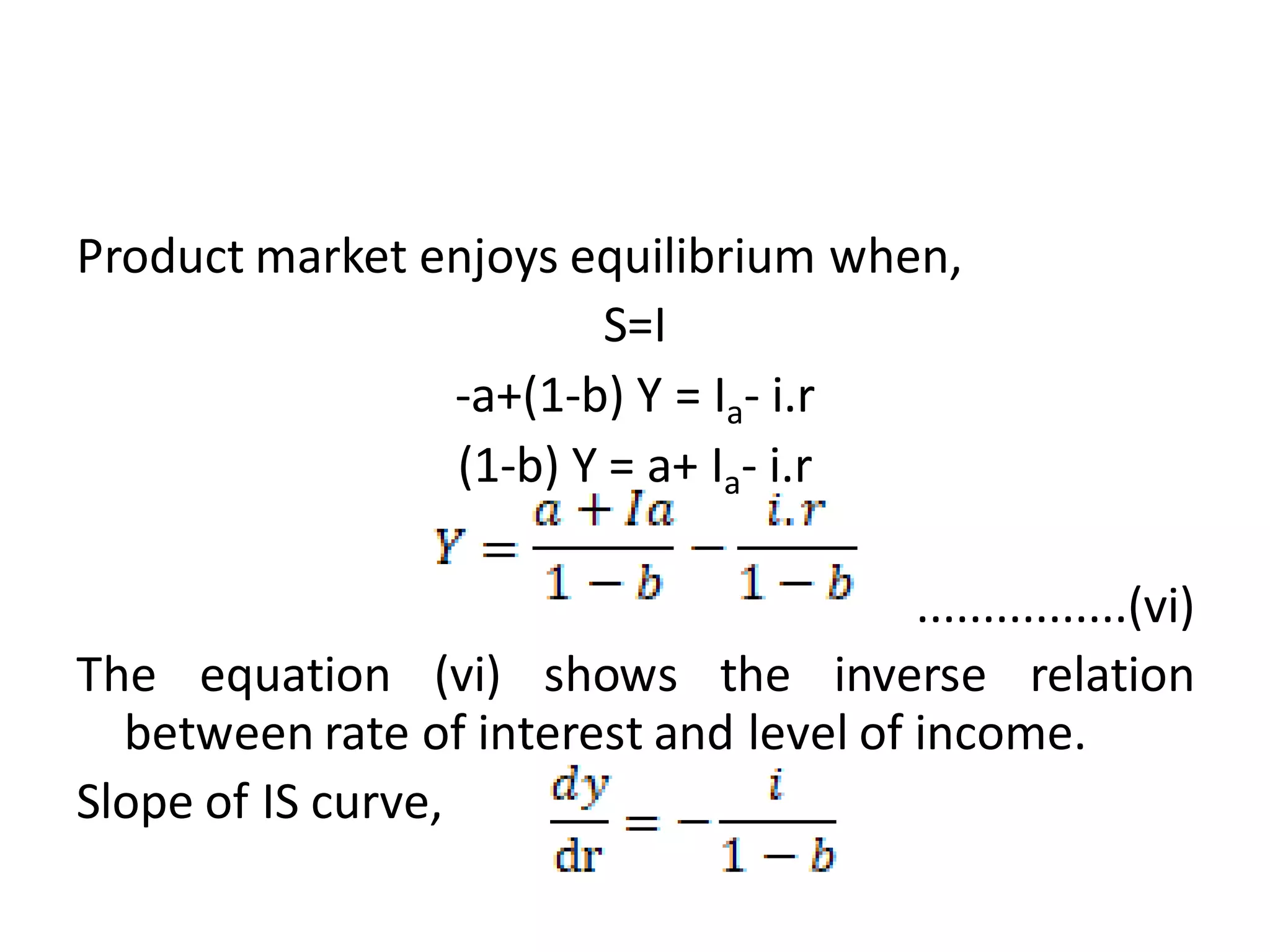
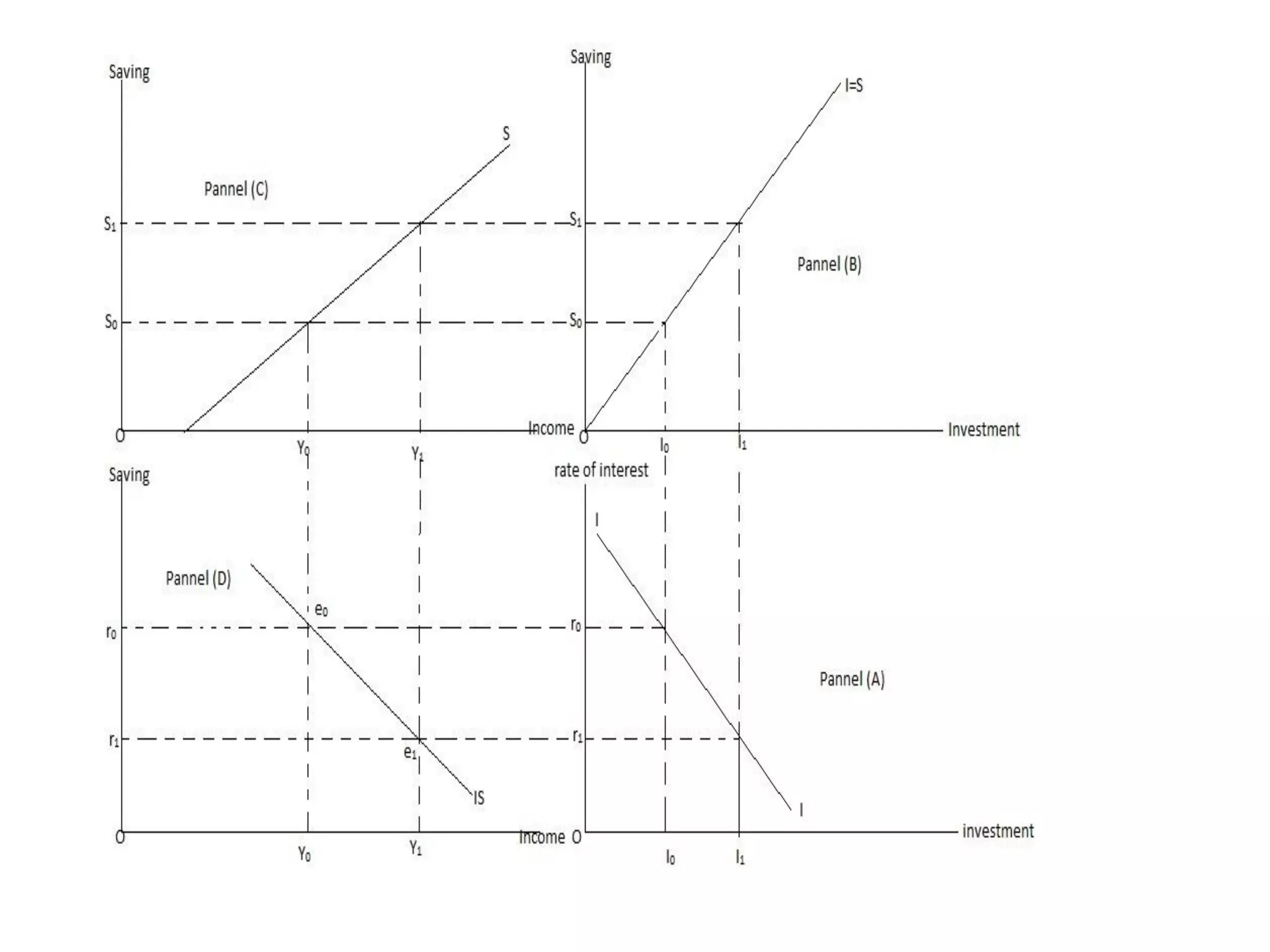
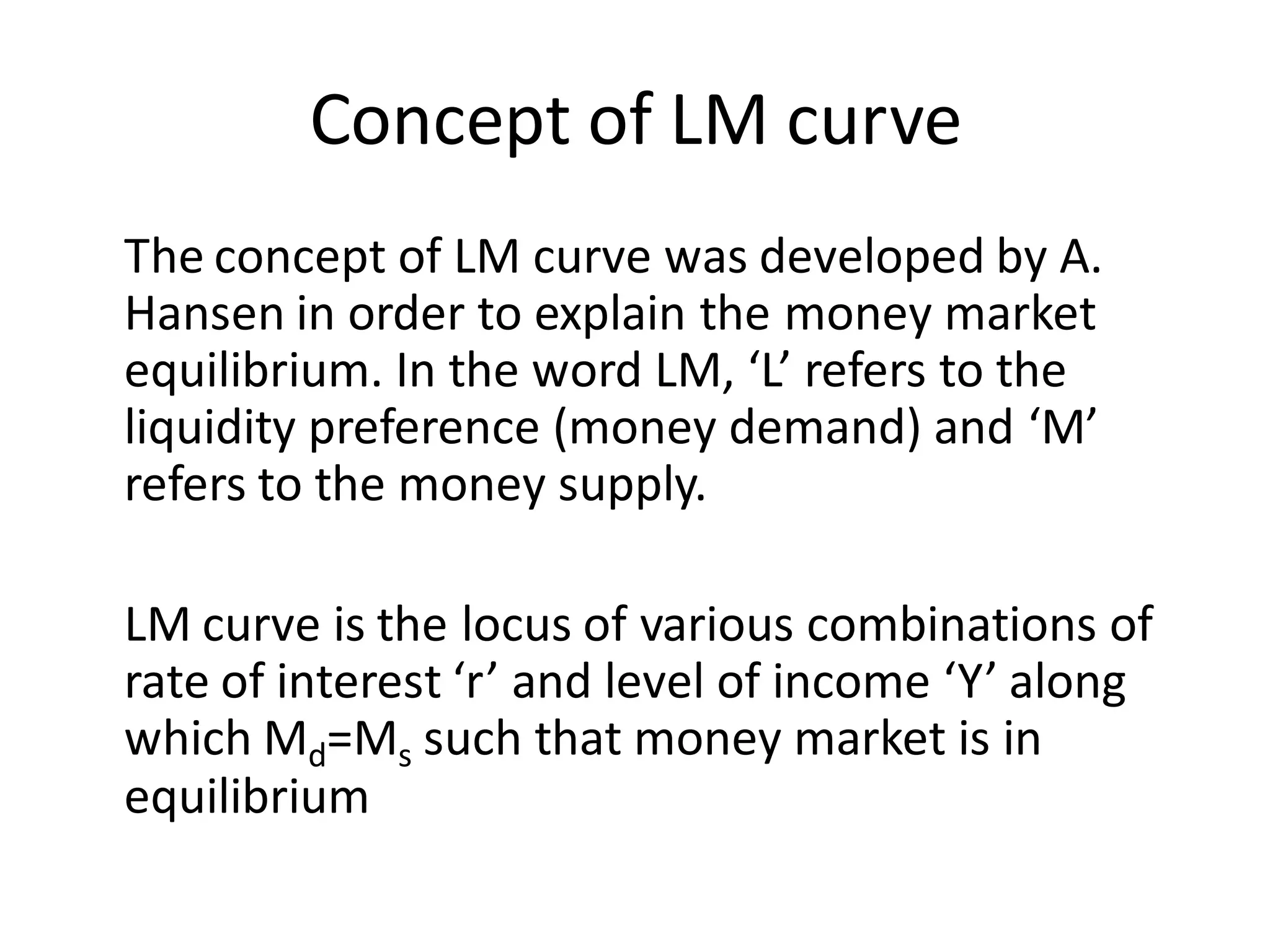
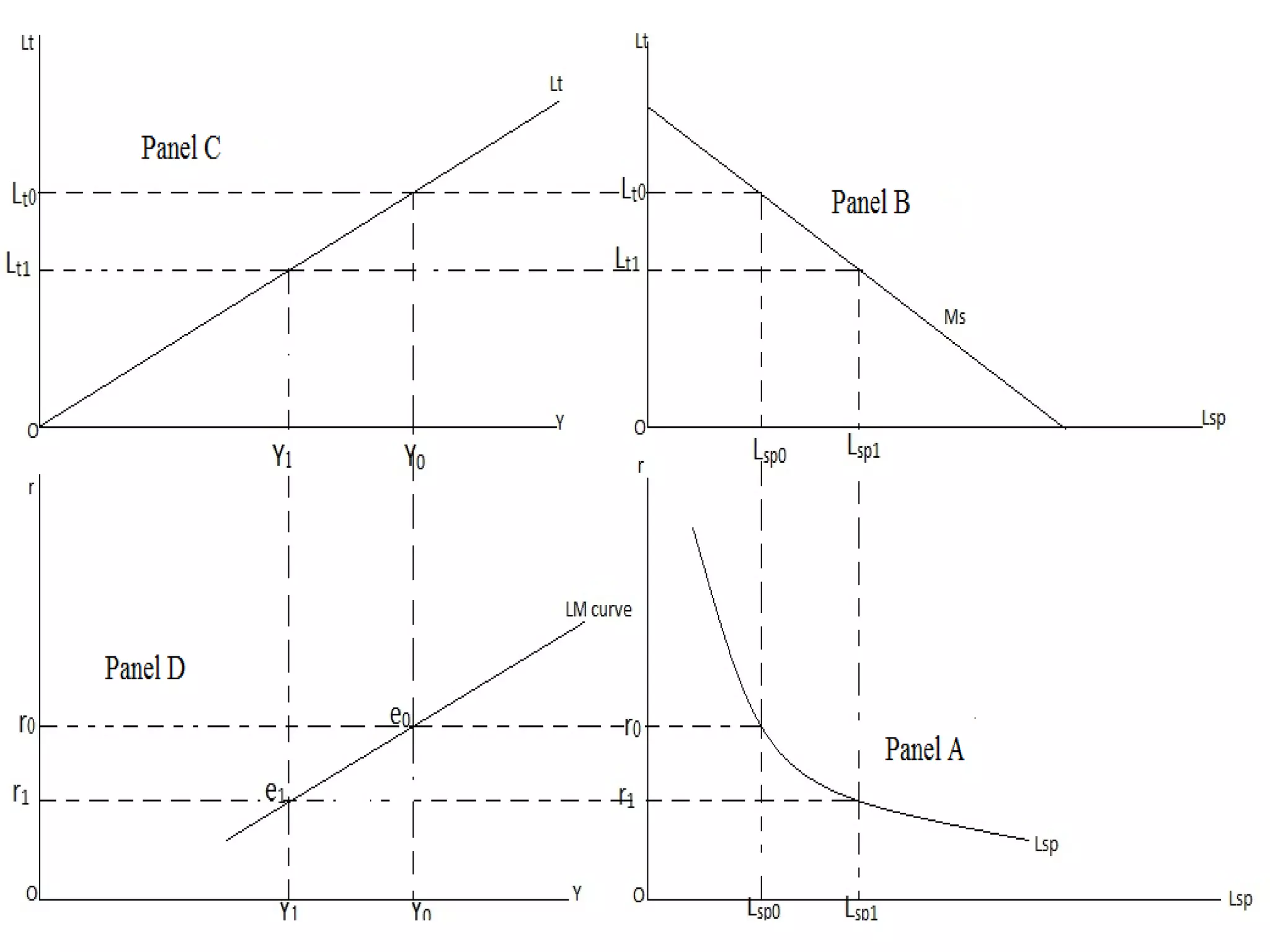
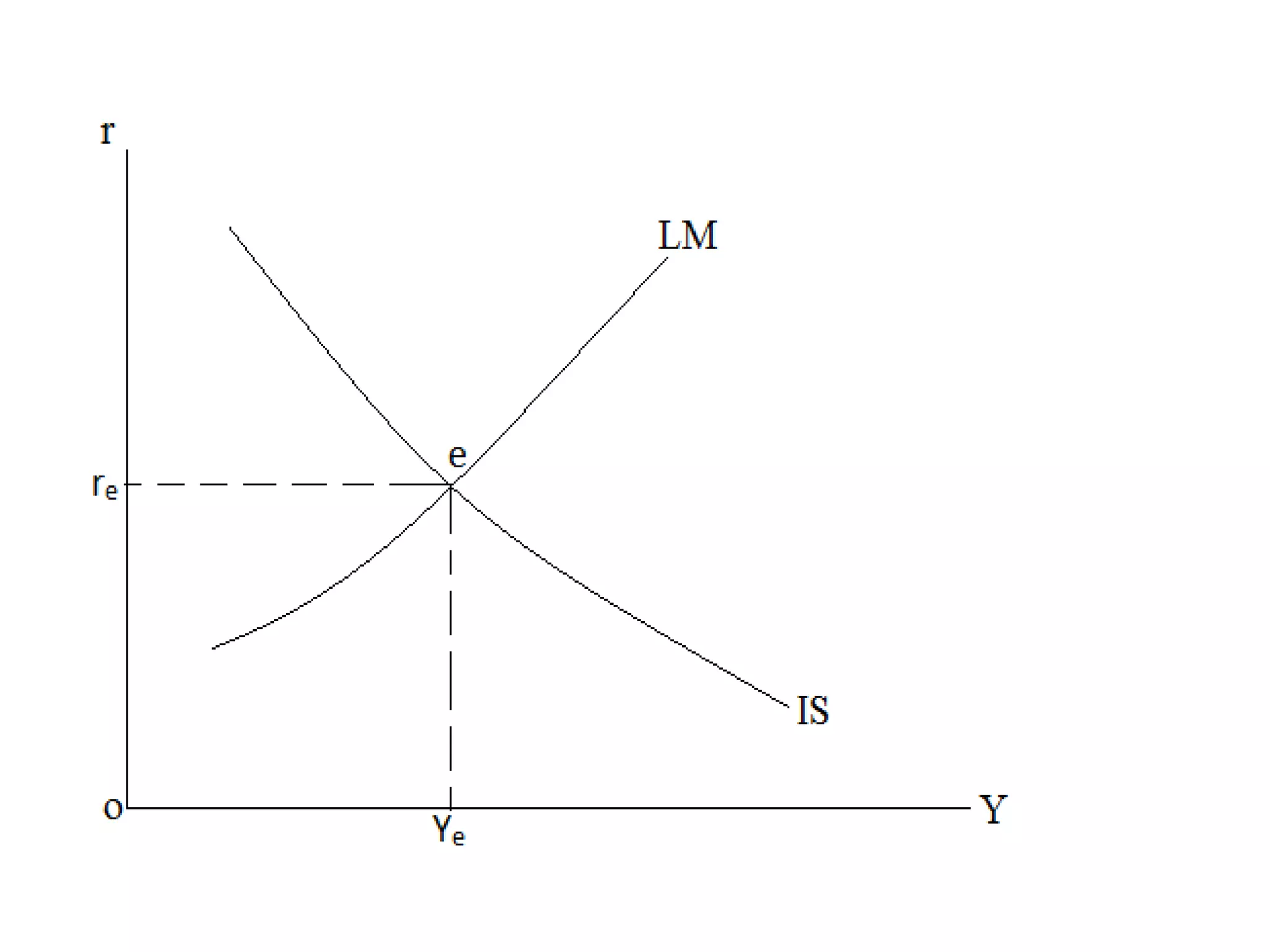
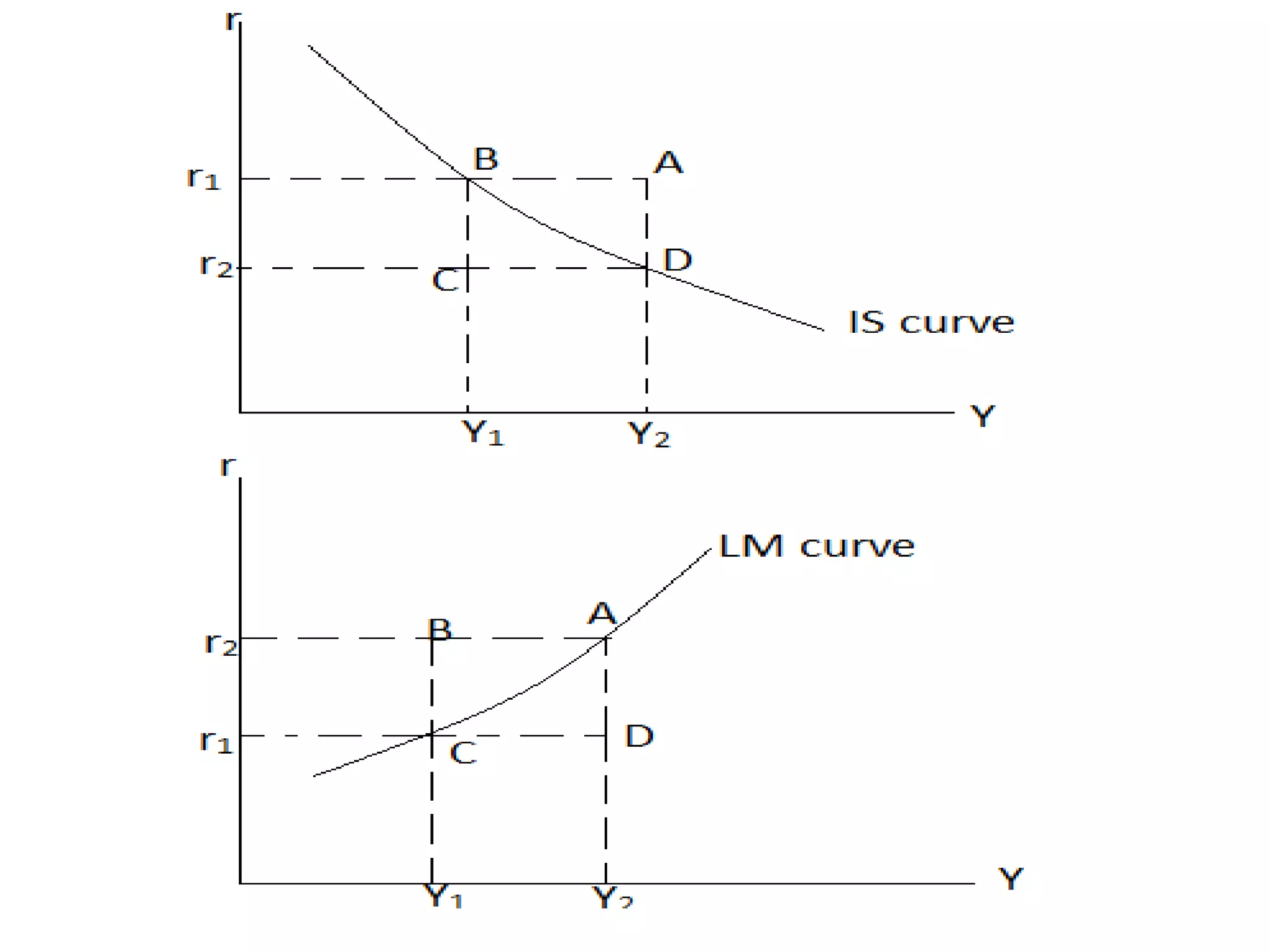
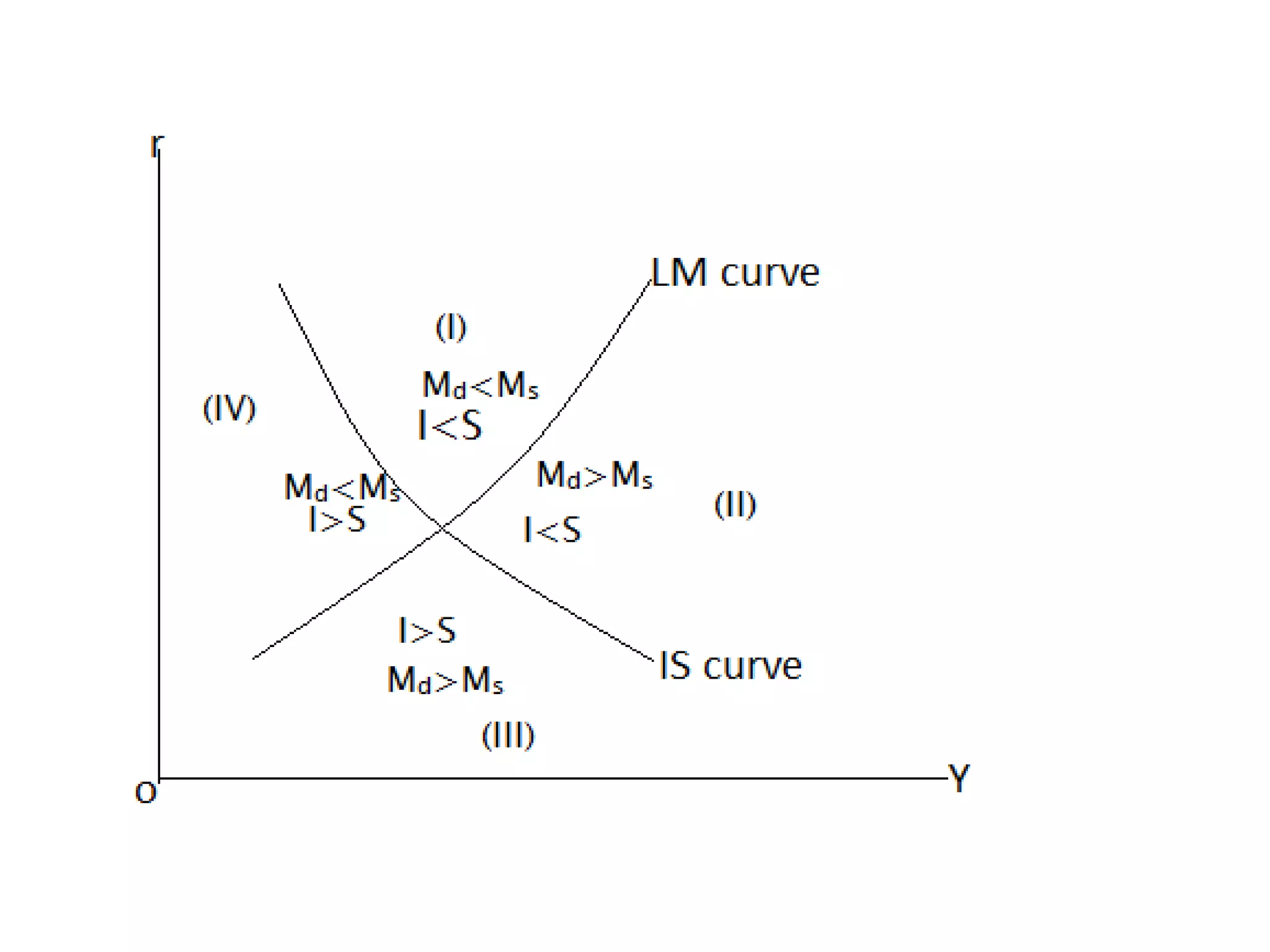
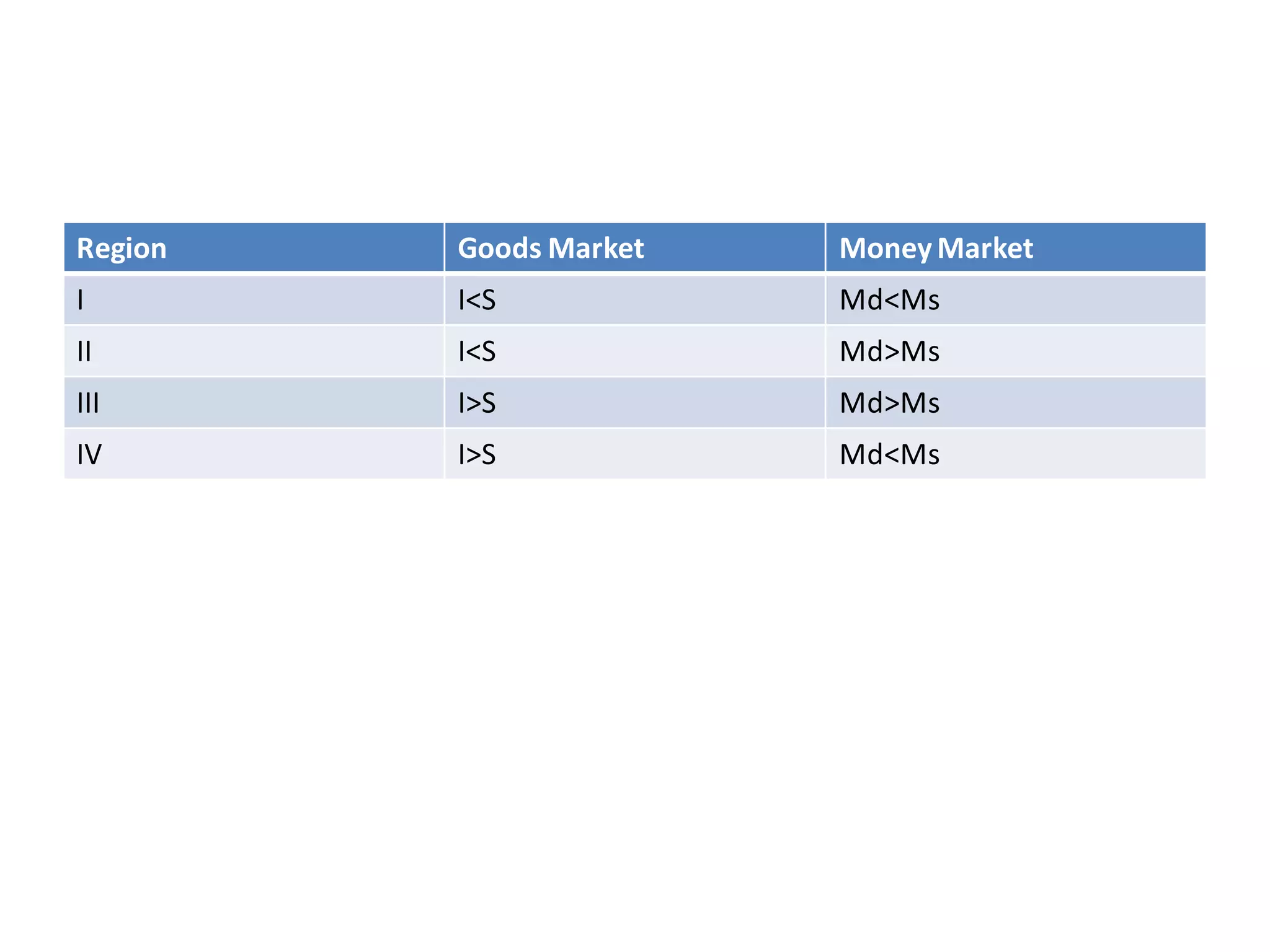
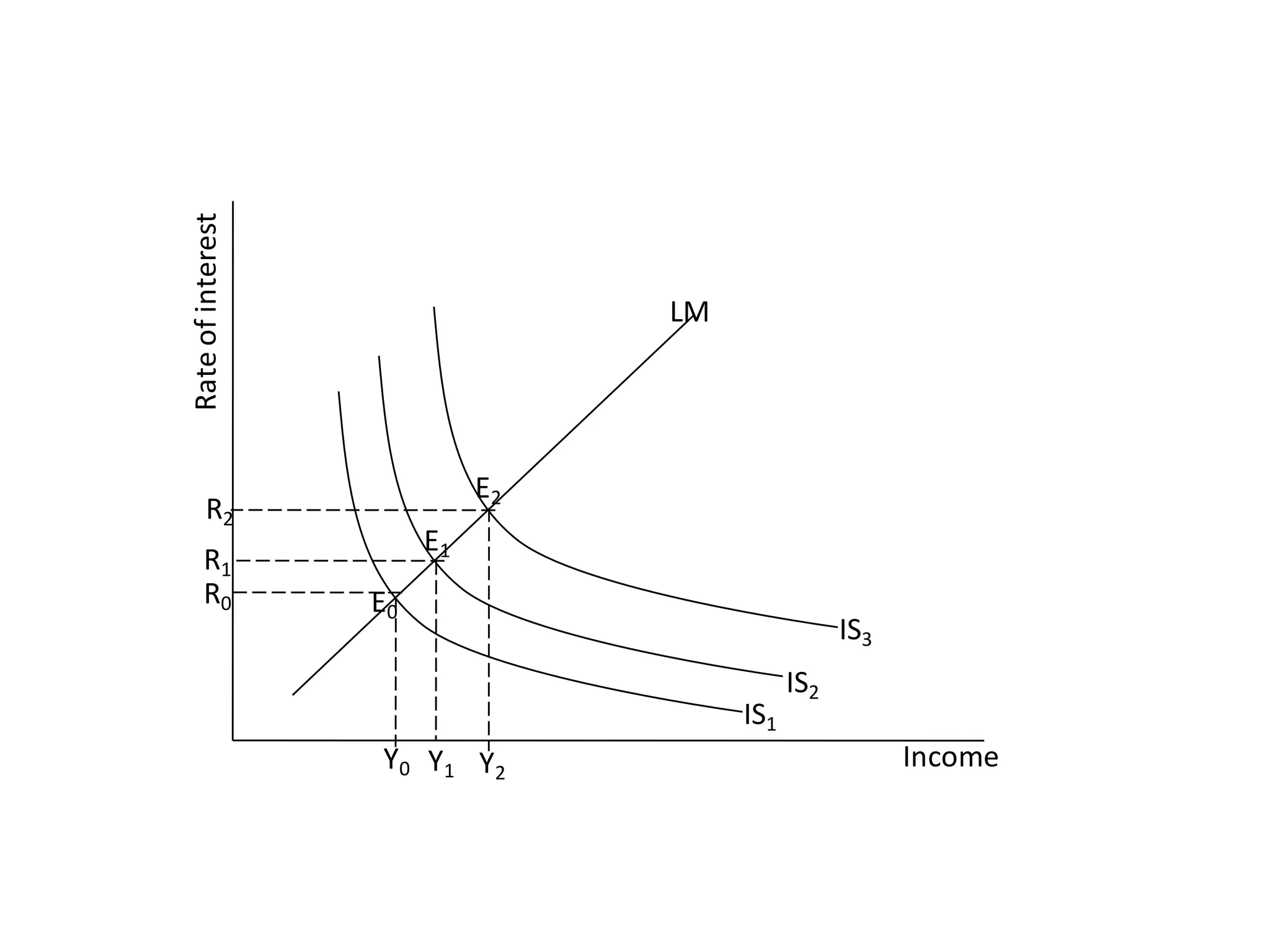
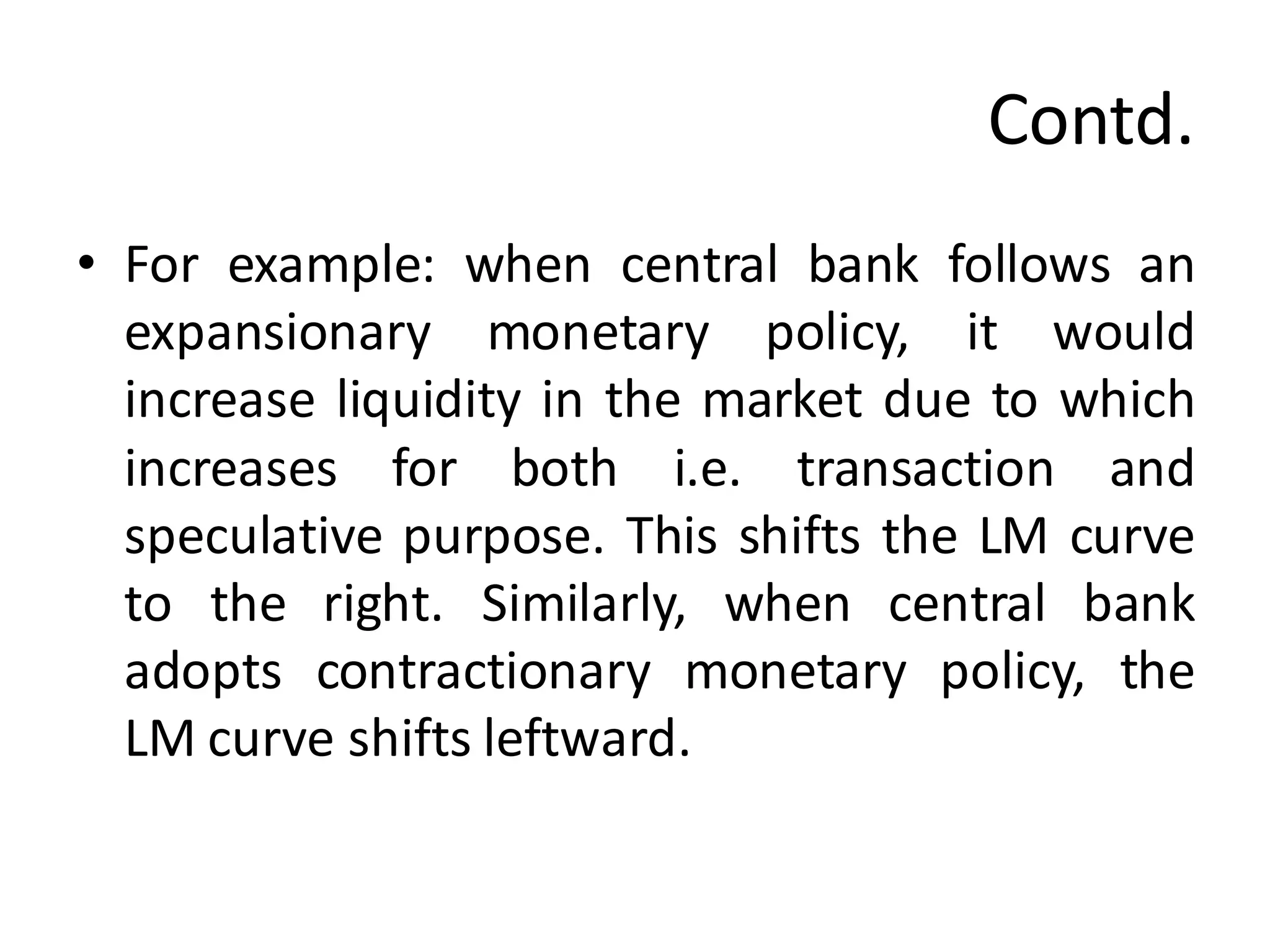
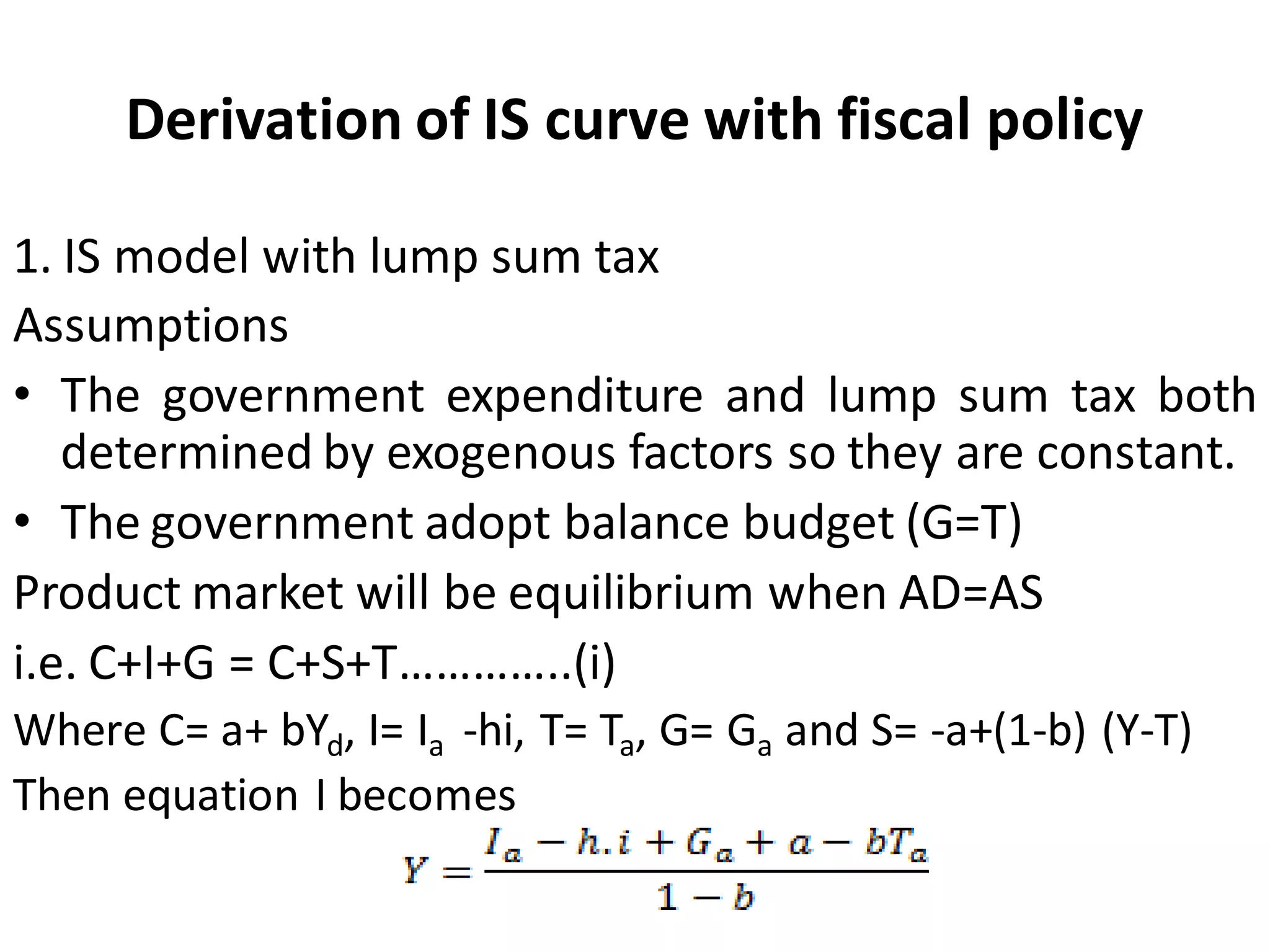
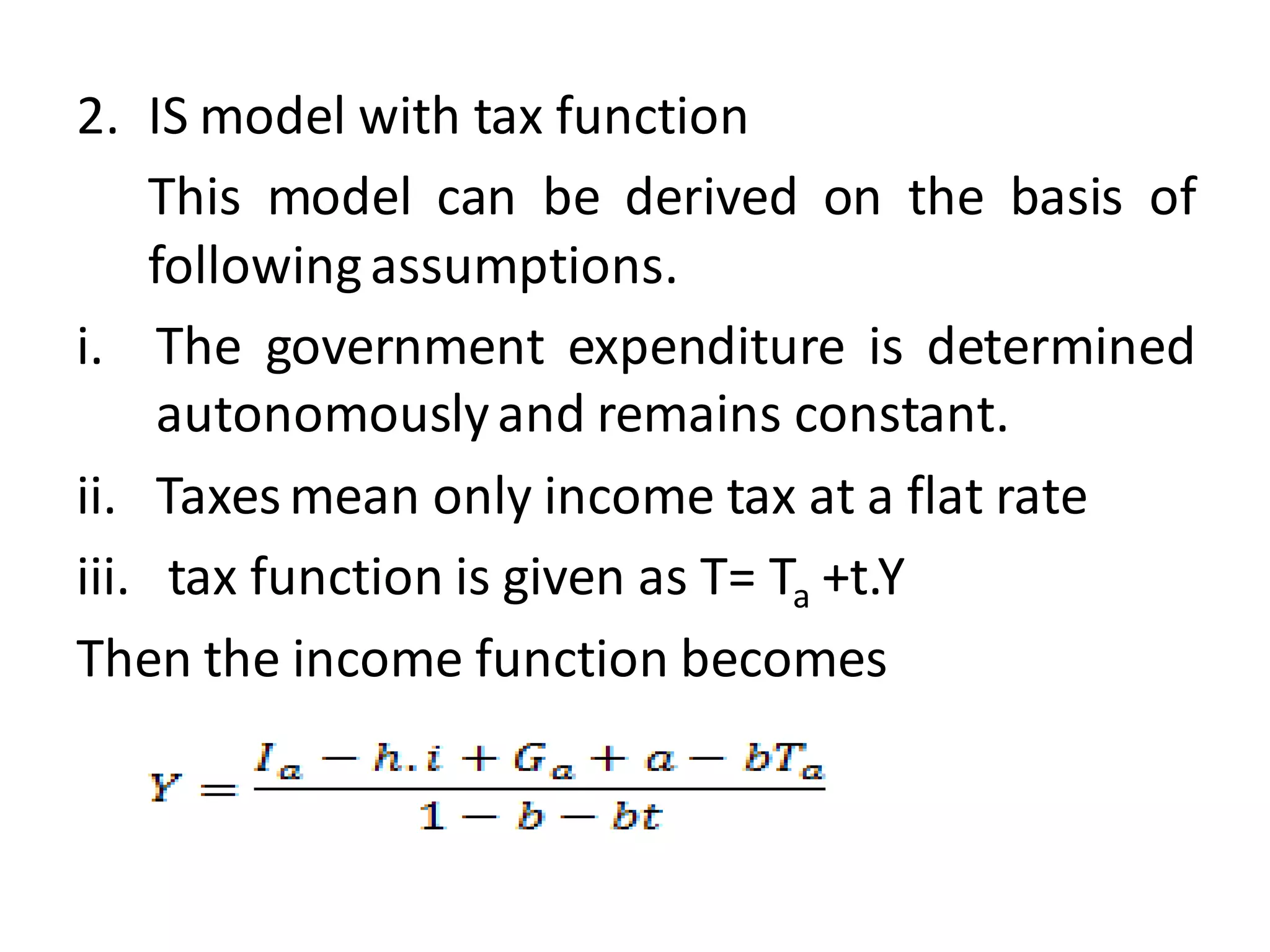
The document provides an overview of the IS-LM model, which explains how the goods market and money market reach equilibrium in an economy. It defines the IS curve as the locus of interest rate-income combinations where investment equals savings. The LM curve similarly shows combinations where money demand equals supply. The intersection of the IS and LM curves indicates the general equilibrium point where both markets clear simultaneously. The summary analyzes how shifts in fiscal or monetary policy can cause the IS and/or LM curves to shift, changing the equilibrium interest rate and level of income in the economy.