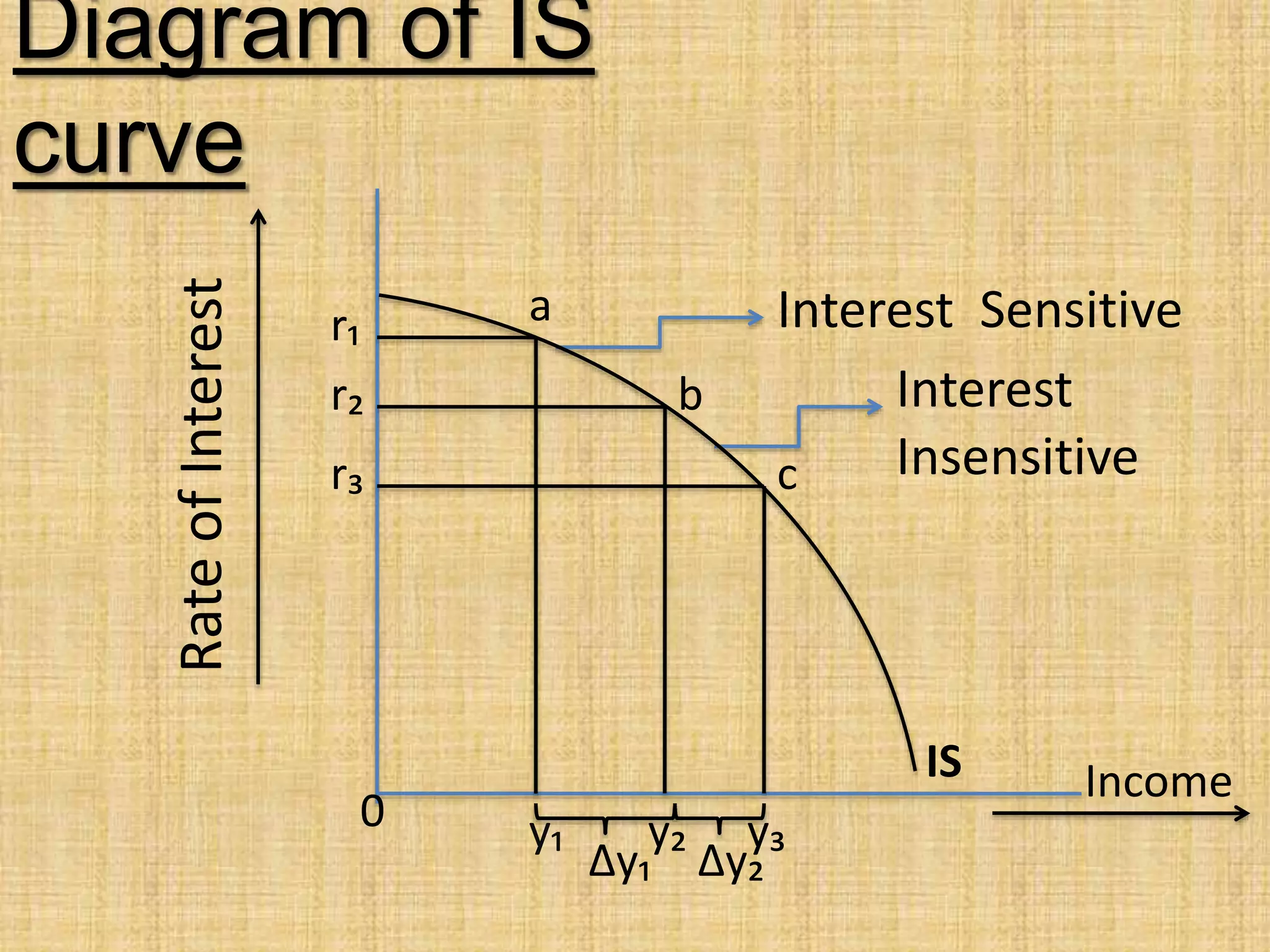
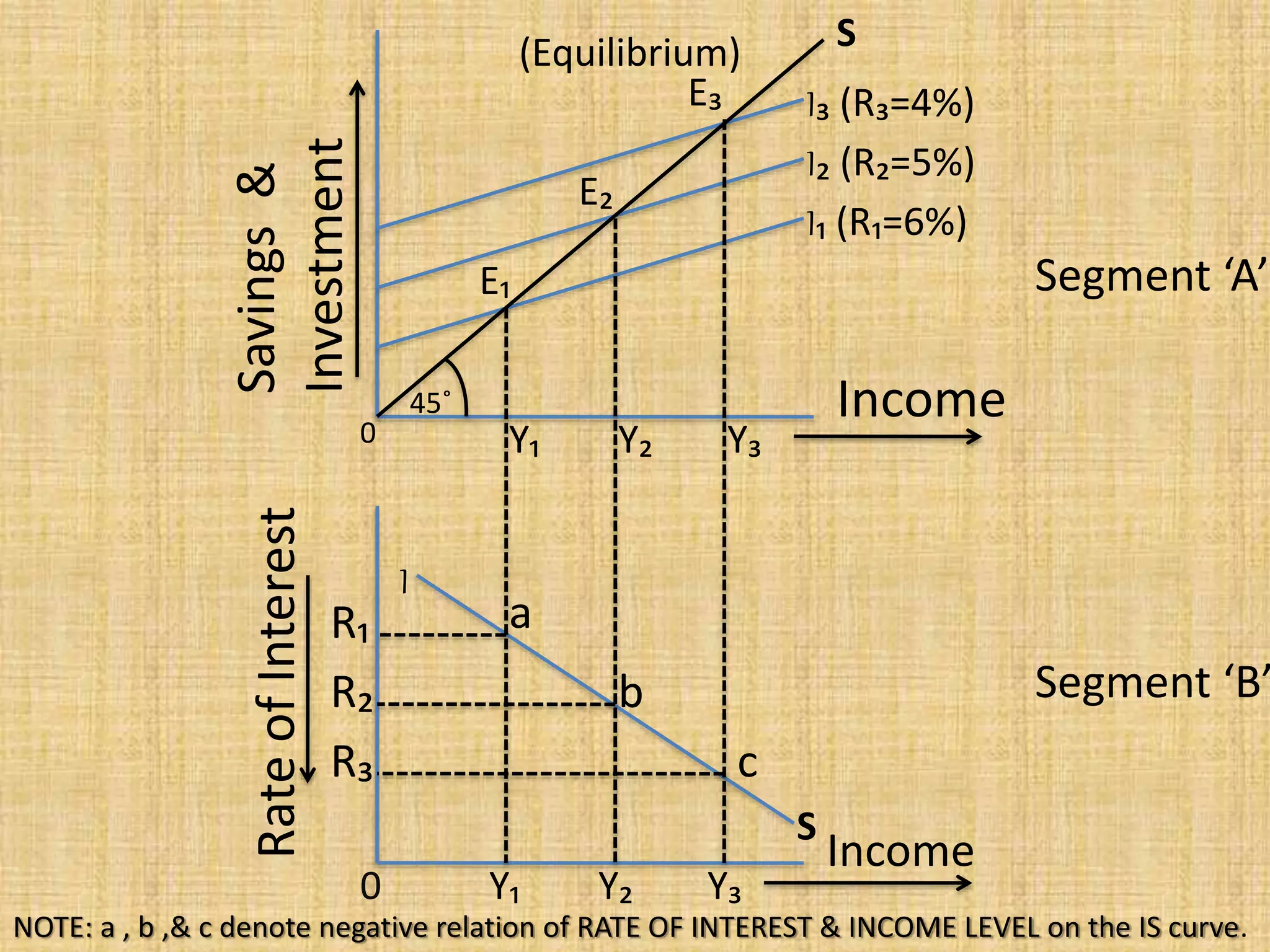
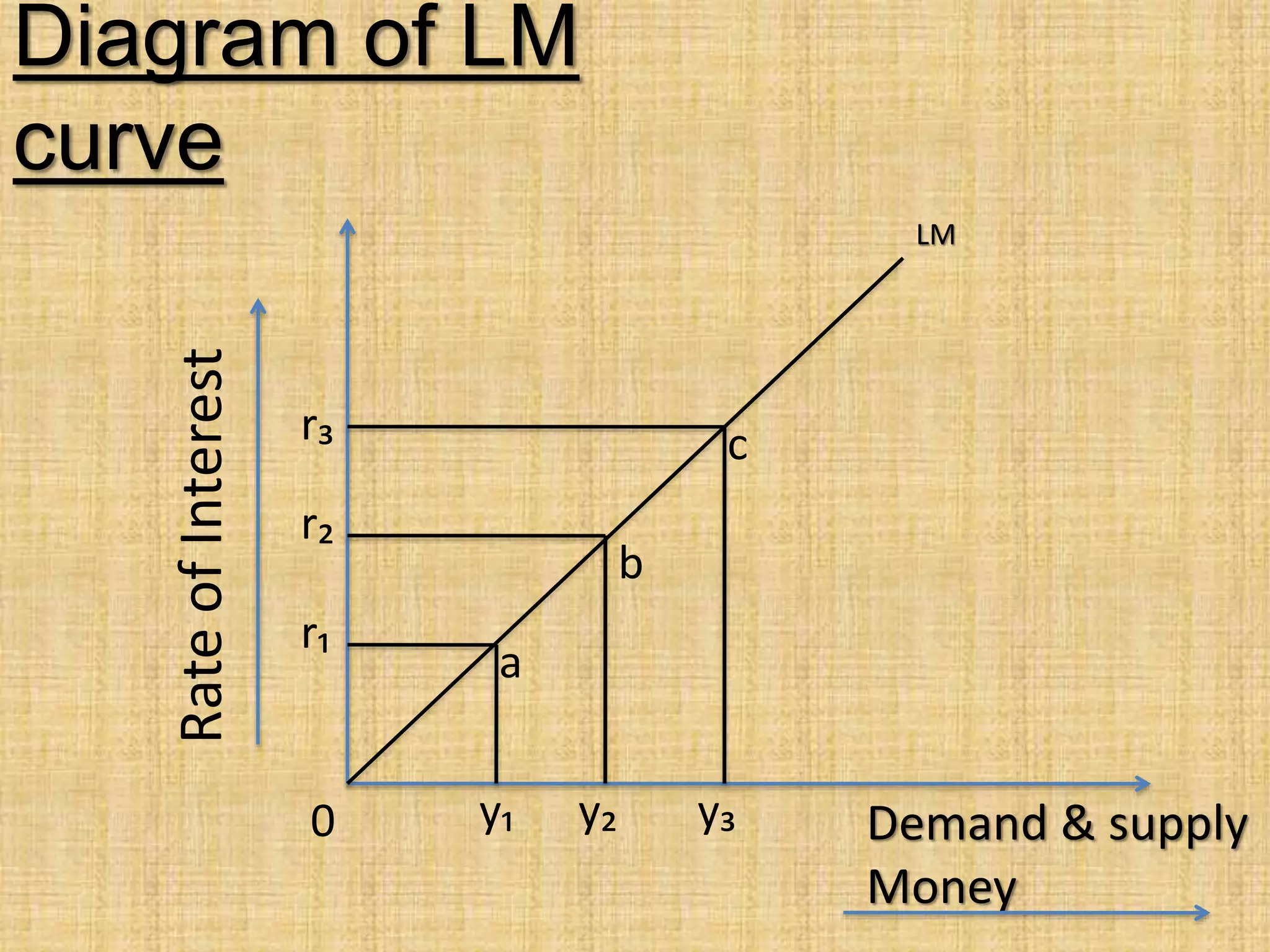
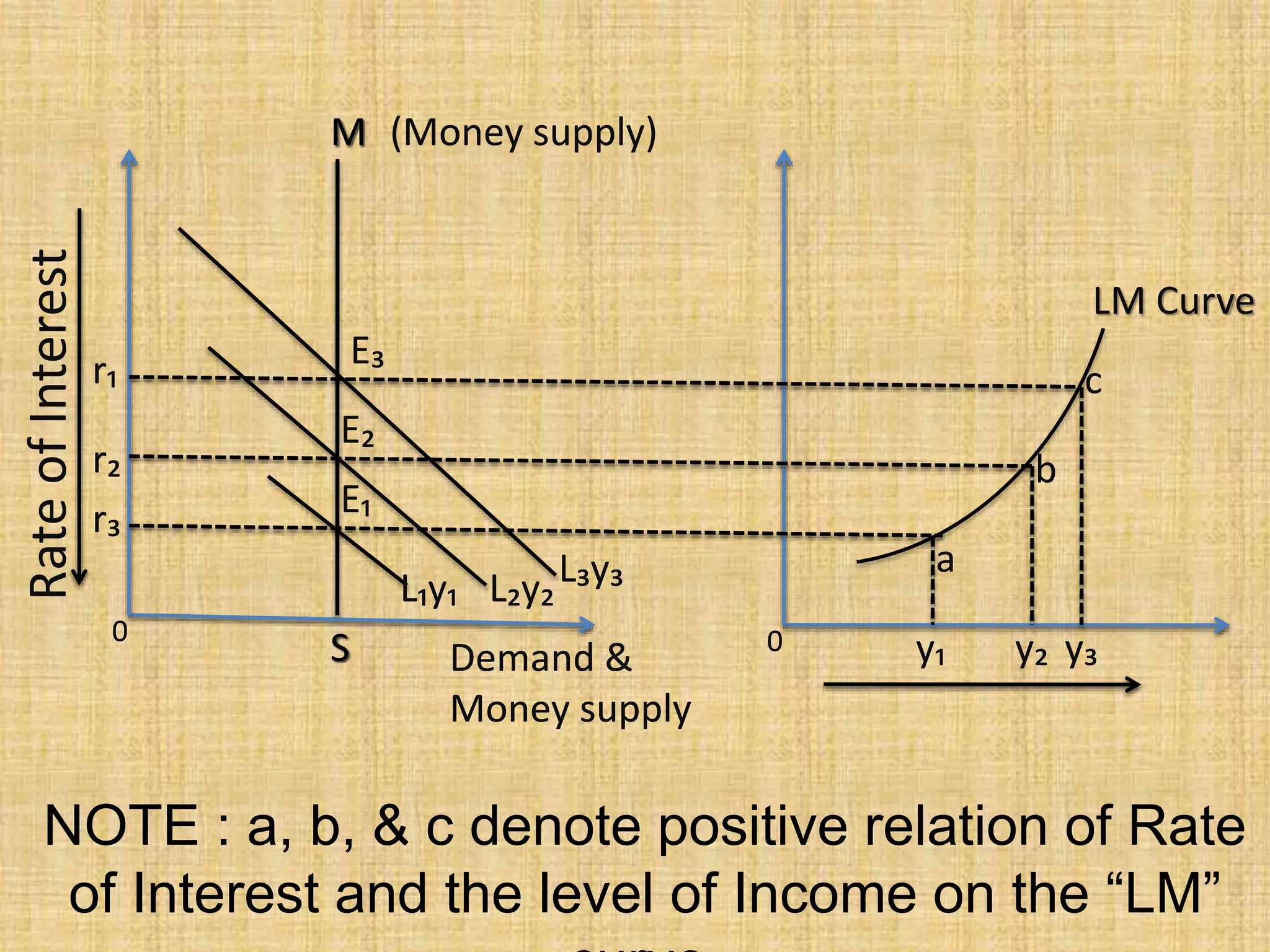
The document presents an overview of the IS-LM model, formulated by John Hicks in 1937, which combines Keynesian and neoclassical economic theories to analyze equilibrium in goods and money markets. It emphasizes the negative relationship between the interest rate and income level on the IS curve, and the potential shifts of the LM curve due to changes in monetary policy. Overall, the model illustrates how the investment demand function and fixed prices influence output and employment levels in an economy.