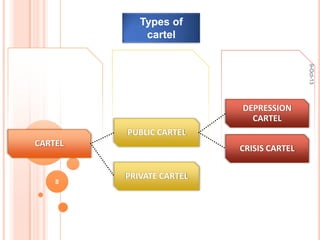
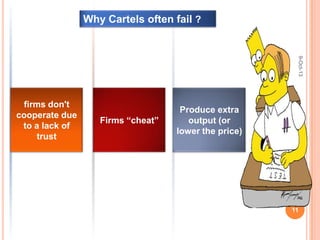
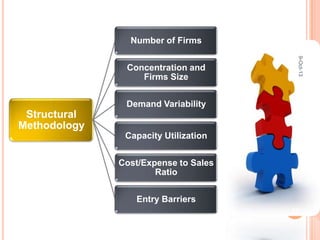
This document discusses cartels, which are formal agreements among competing firms or countries to fix prices, marketing, and production to raise profits. It defines cartels and describes different types. Conditions for cartel success include the ability to detect and prevent cheating between members. However, cartels often fail due to a lack of trust between firms and cheating by overproducing or lowering prices. Examples of cartels discussed include OPEC and historical oil companies. American antitrust law prohibits cartel practices that reduce competition or create monopolies. The document concludes that cartel agreements are unstable and incentives remain to re-form broken cartels.