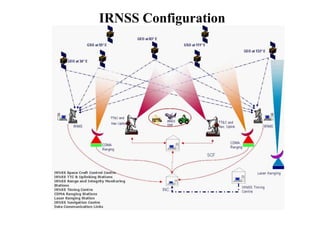
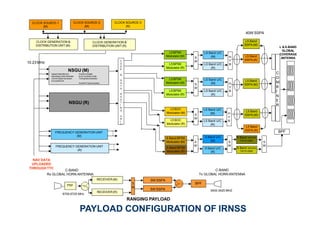
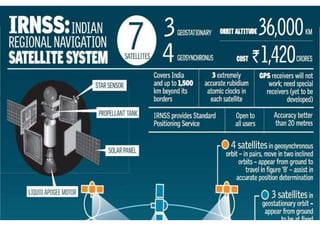
IRNSS is India's independent regional navigation satellite system consisting of seven satellites providing accurate positioning to users in India and within 1500 km of its borders. The system includes space, ground, and user segments. The space segment uses three geostationary and four geosynchronous orbiting satellites. The ground segment controls and maintains the satellites. The user segment utilizes dual-frequency receivers. IRNSS aims to provide positioning accuracy under 20 meters within its coverage area for various navigation and timing applications.