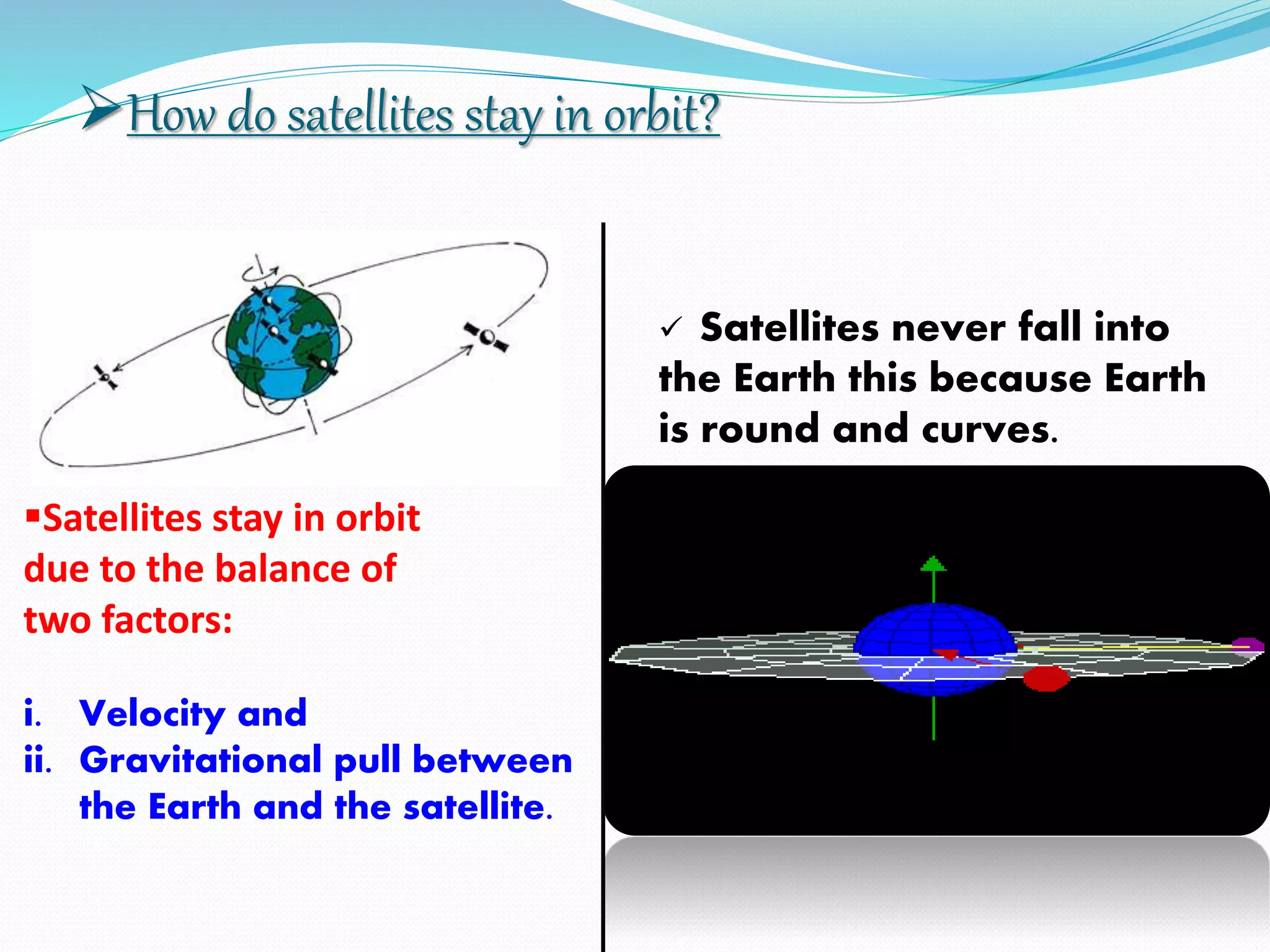
The document discusses India's regional satellite navigation system called IRNSS. It provides a brief history of satellites, including India's first communication satellite Aryabhatta launched in 1975. It describes the range coverage of IRNSS as 1500-2000 km from the border with an orbital height of 36,000 km. The document outlines the components and configuration of IRNSS and explains how satellites stay in orbit through balance of velocity and gravitational pull. It concludes that satellites remain the best utilization for communication and other sectors due to their speed and advantages.