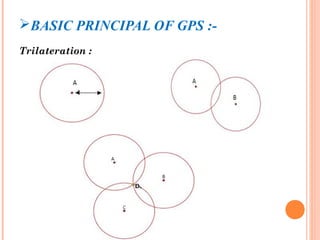
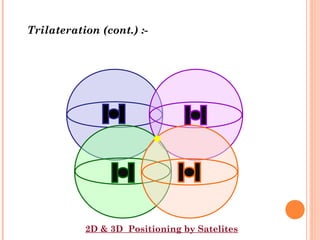
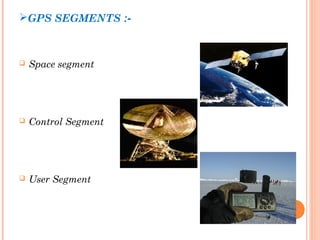
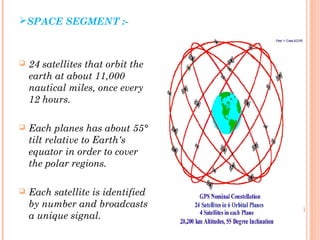
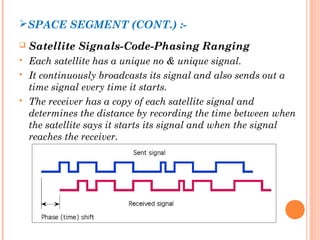
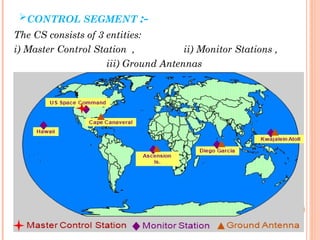
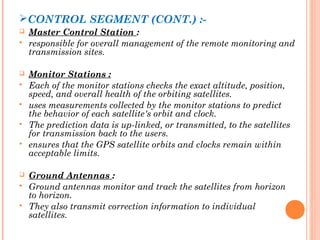
The document discusses the Global Positioning System (GPS). GPS is a satellite-based navigation system consisting of three segments - space, control, and user. The space segment includes 24 satellites that transmit radio signals used by GPS receivers to determine location, velocity, and time. The control segment monitors the satellites and updates their clocks. The user segment includes GPS receivers that calculate position by precisely timing signals from at least three satellites. Common sources of error and differential GPS for improving accuracy are also covered, as well as many applications of GPS technology.