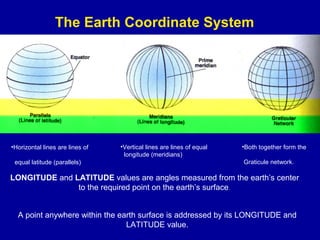
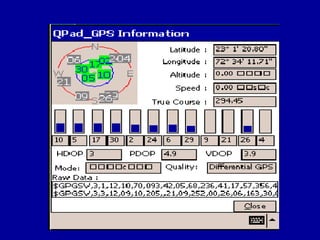
The document provides information about the Global Positioning System (GPS). It discusses how GPS uses a constellation of 24 satellites with atomic clocks to accurately determine the location of a GPS receiver anywhere on Earth. It explains how GPS measures the distance to multiple satellites to triangulate a user's 2D or 3D position via calculations based on the speed of light and signal travel times. Sources of error and techniques to improve accuracy like differential GPS are also summarized. The document outlines applications of GPS technology and its importance for navigation and other location-based services.