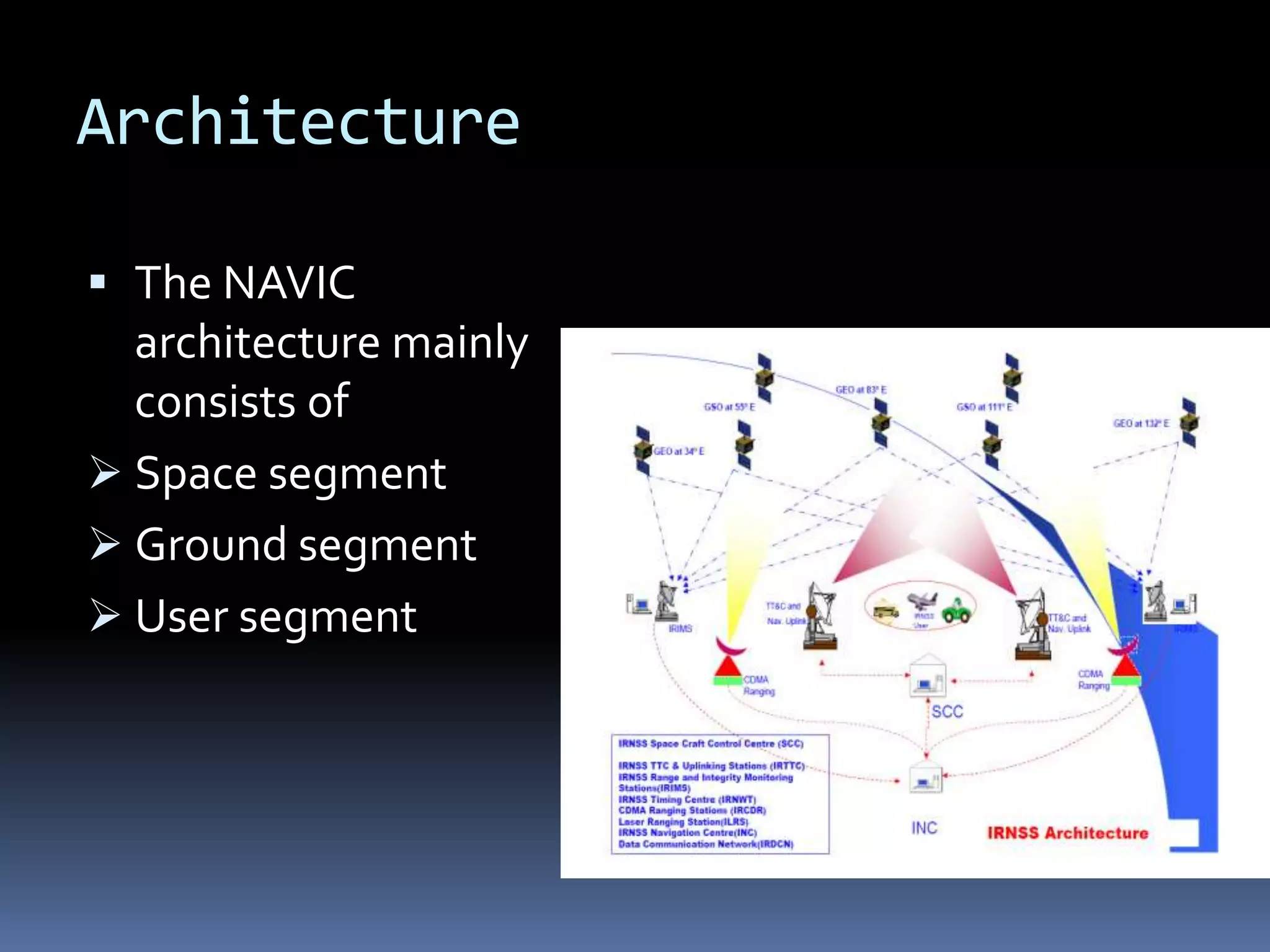
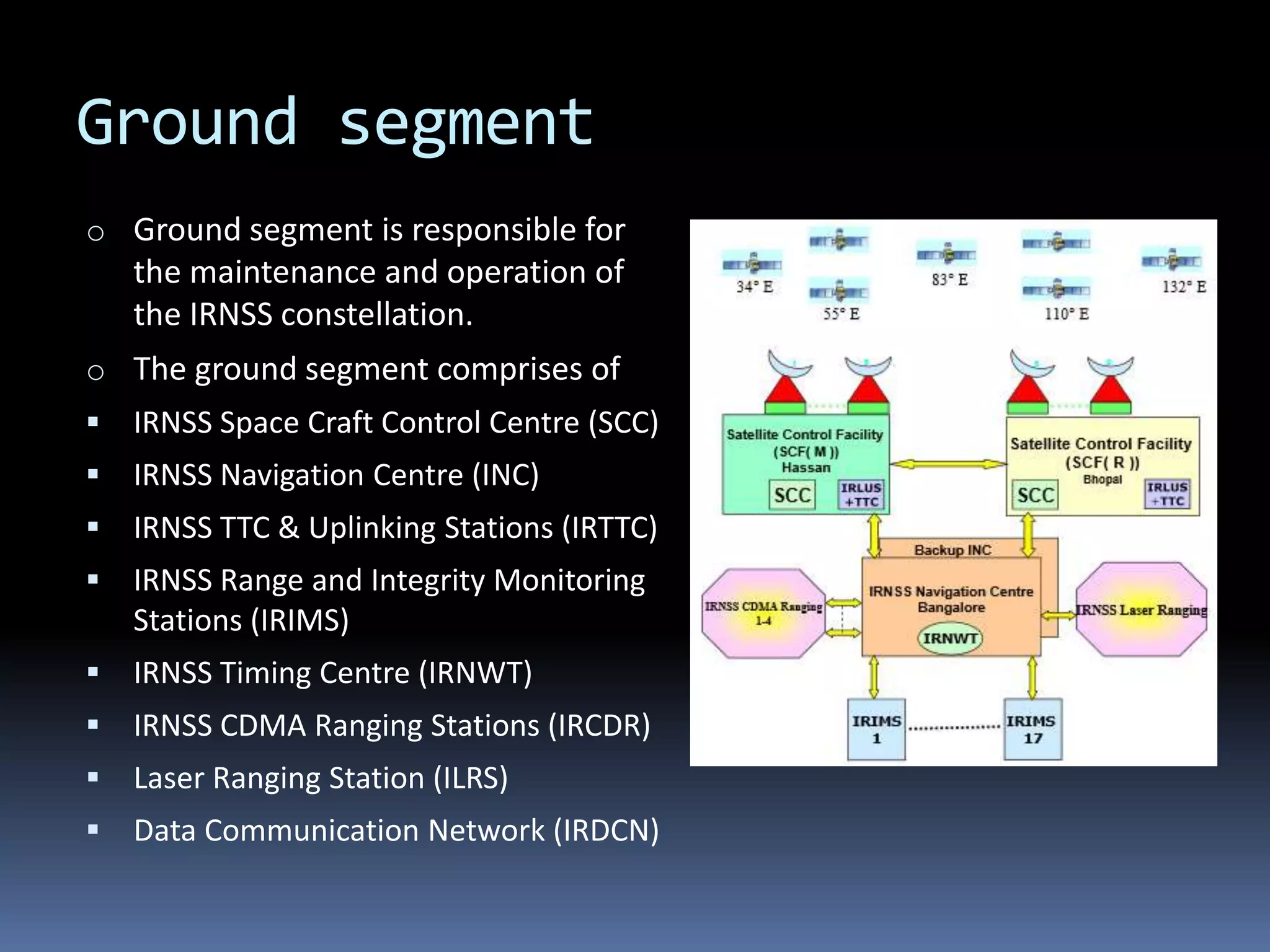
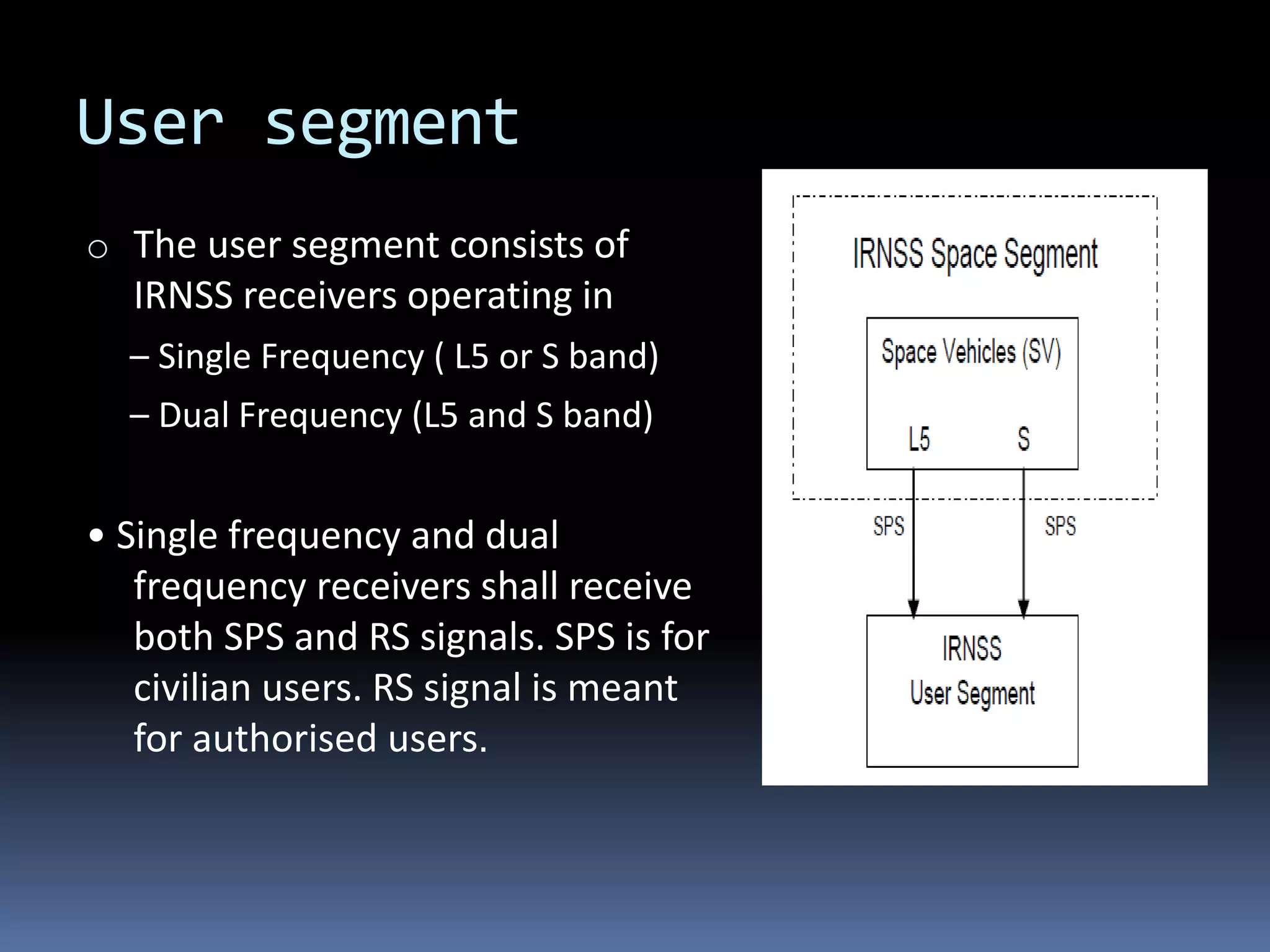
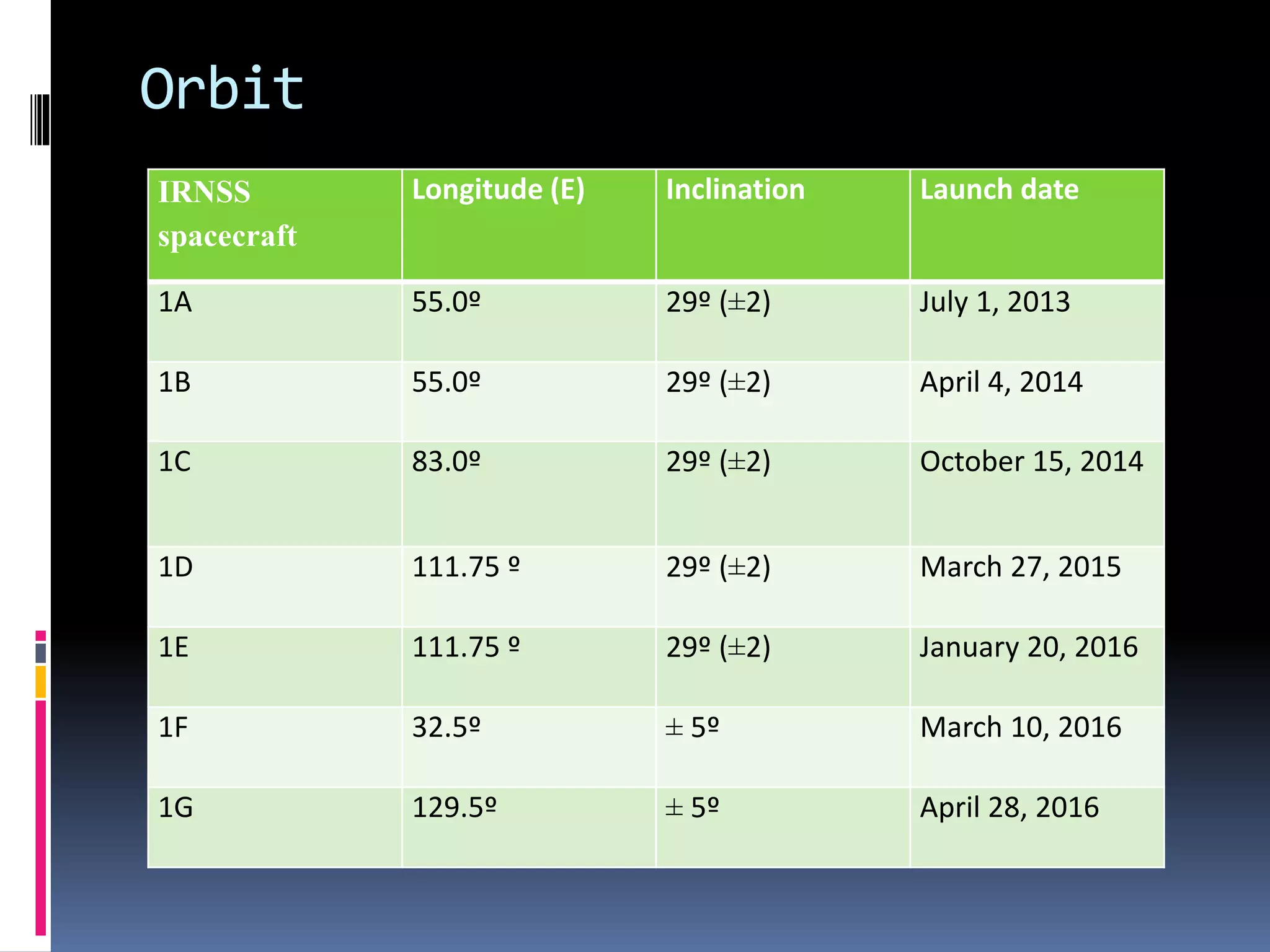
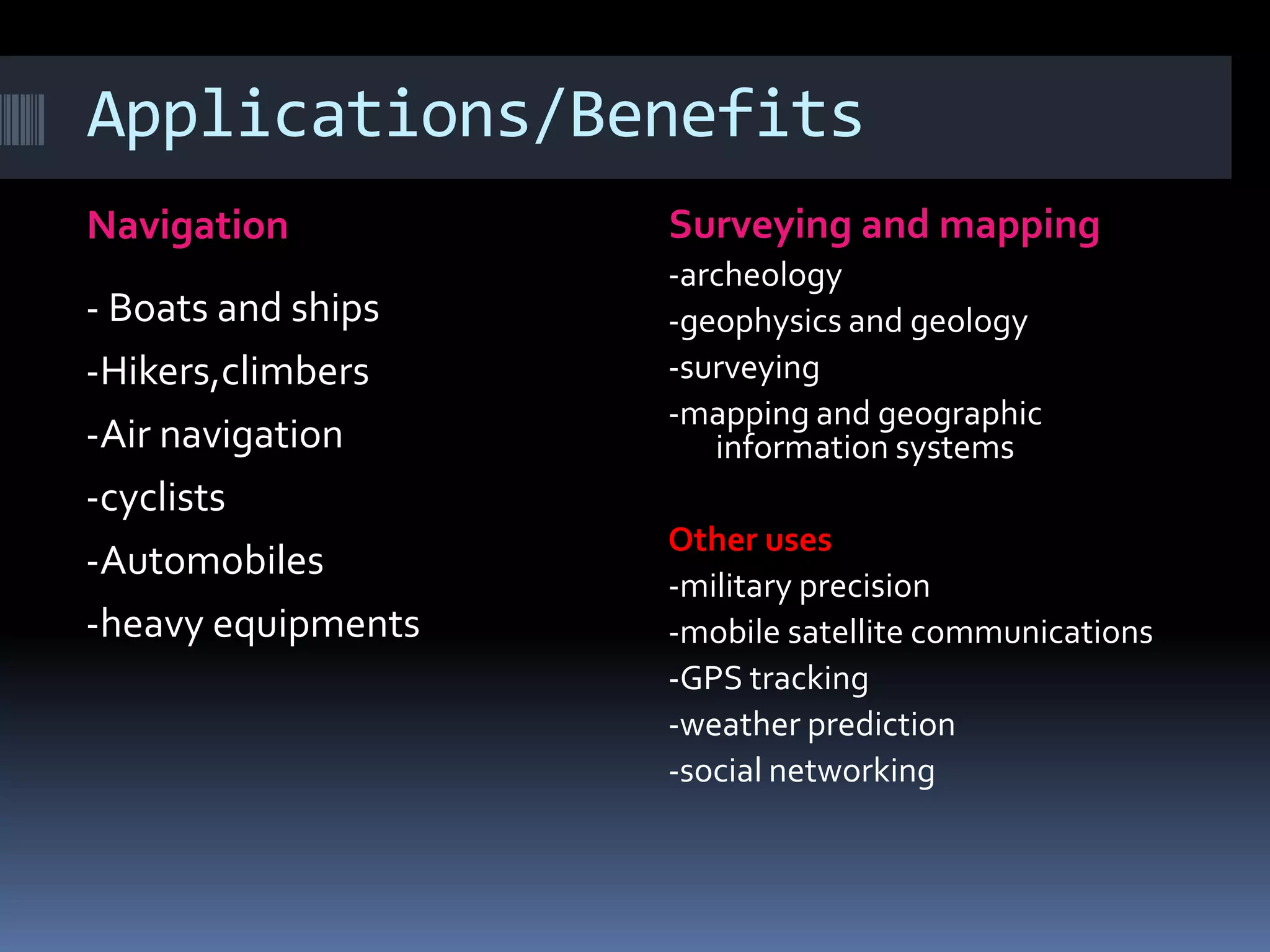
NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation, is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system launched by India in 2016, providing accurate real-time positioning and timing services over India and its surrounding region. The system comprises seven satellites, including three in geostationary and four in geosynchronous orbit, with applications in navigation, surveying, military, and more. Unlike foreign systems, NavIC offers a higher accuracy and is designed to function independently in hostile situations.