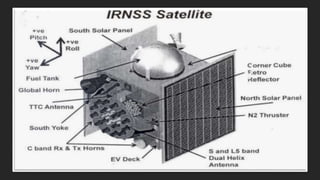
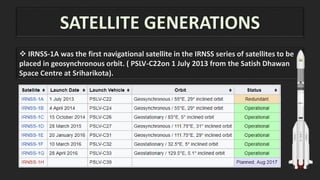
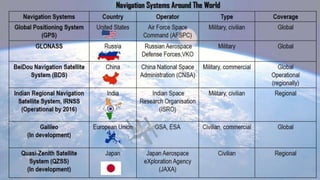
The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) is India's independent regional navigational satellite system. It consists of 7 satellites in geostationary orbit that provide navigation services to users in India and the surrounding 1500-2000 km region. IRNSS aims to provide accurate position information services to users in India as well as the surrounding region. It is intended to provide two types of services: special position service and precision service.