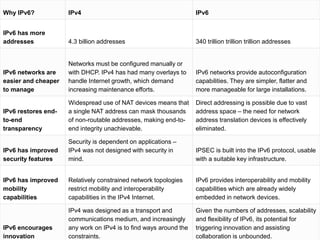
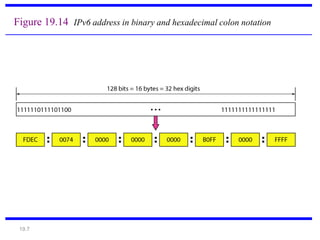
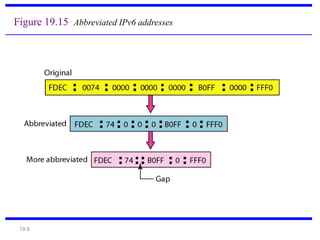
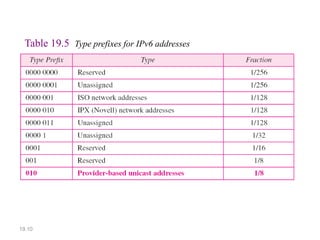
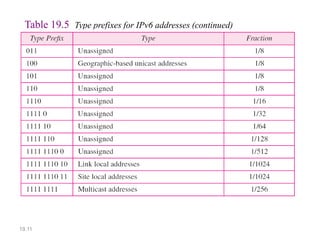
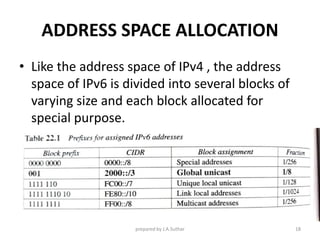
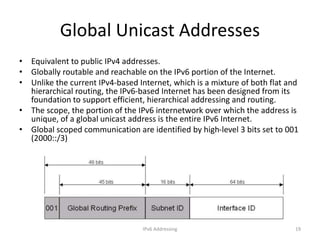
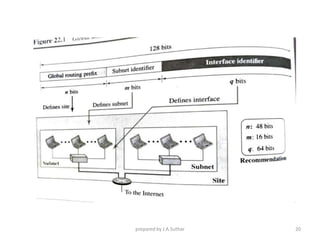
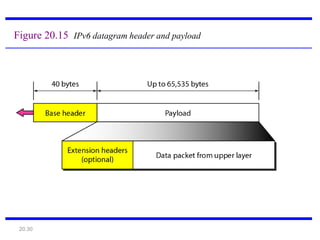
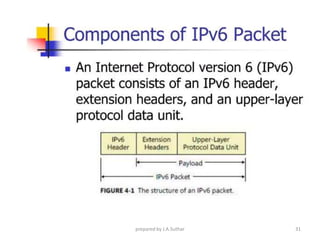
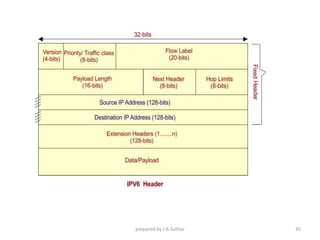
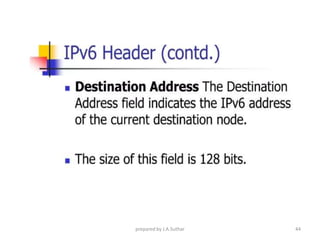
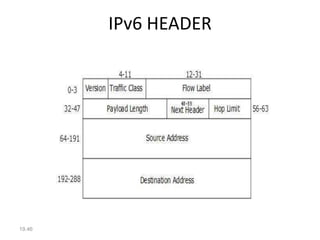
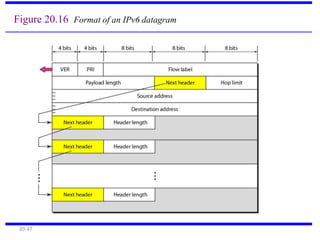
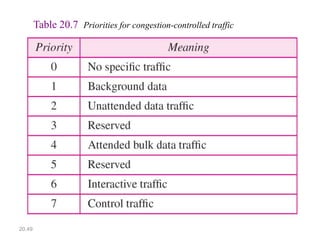
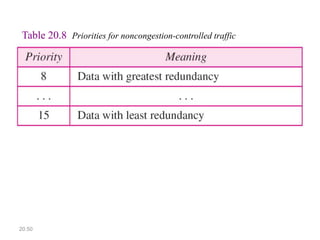
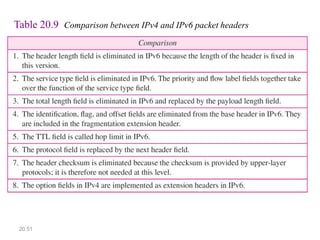
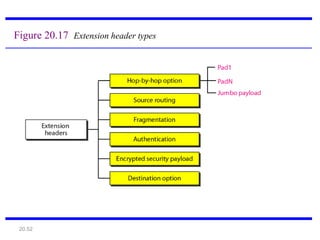
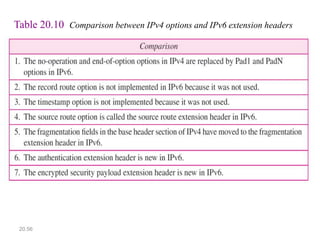
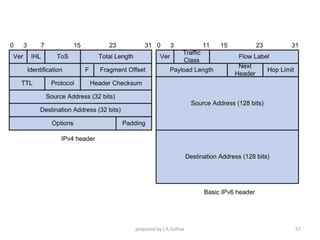
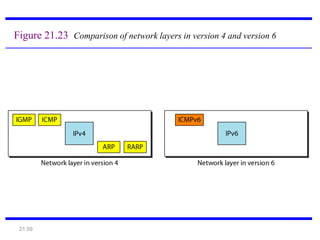
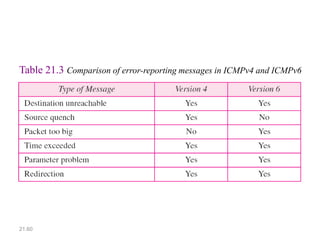
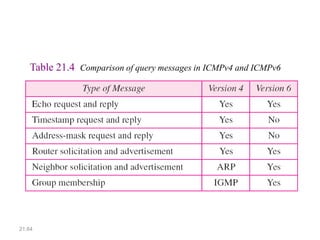
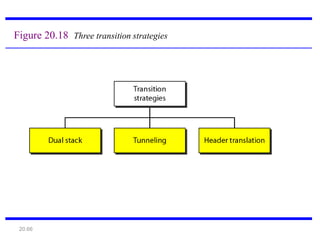
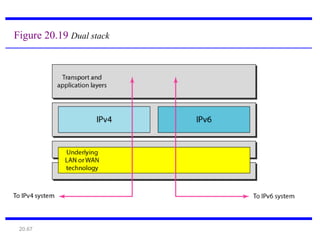
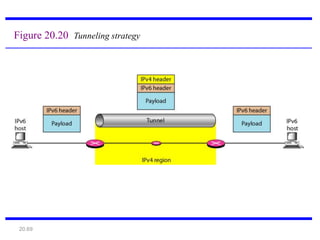
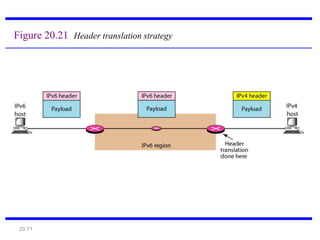
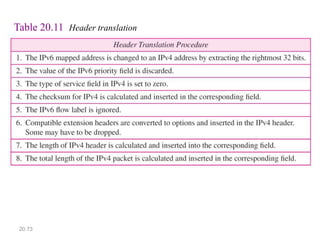
IPv6 was developed to address the limitations of IPv4, such as its limited 32-bit address space that is nearly exhausted. IPv6 features a 128-bit address space providing vastly more addresses. It allows for automatic configuration of addresses, simpler header format, and built-in security features. IPv6 addresses are represented through eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons. The address space is hierarchically allocated into global unicast, unique local, link-local, multicast, and unspecified addresses.