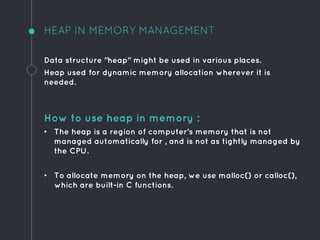
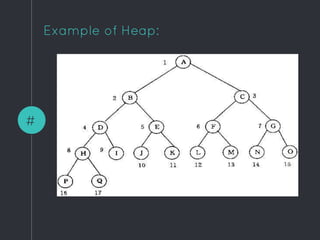
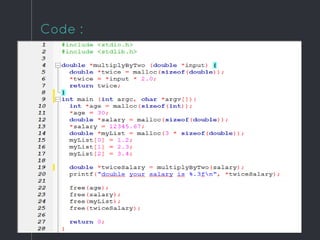
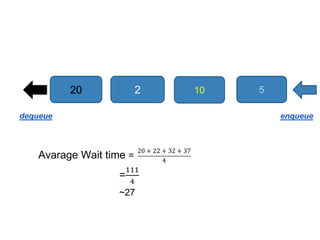
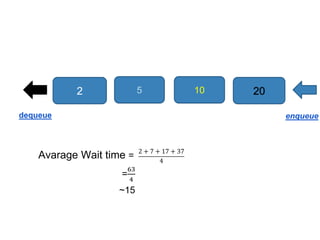
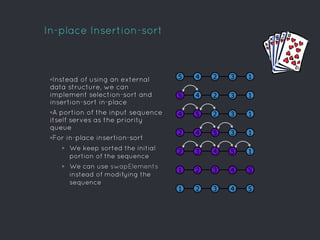
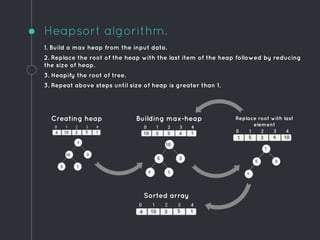
Heap data structures can be used for sorting and memory management. Heapsort uses a max heap to sort an array by repeatedly replacing the root with the last element and heapifying the reduced heap. Heaps are also used to manage memory dynamically by allocating and resizing memory blocks on the heap using functions like malloc() and realloc(). Priority queues, which can be implemented efficiently using binary heaps, are used for applications that require fast retrieval of the highest or lowest priority element, such as scheduling tasks.


![void heapSort(int arr[], int n)
{
for(int i = n/2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
}
}
#
Heapsort Code:
Creating max- heap
heapify(arr, n, i);
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
heapify(arr,i,0);
Creates max heap on
reduced array
Swaps the first and last
node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heap-tel-170804052124/85/Presentation-on-Heap-Sort-5-320.jpg)