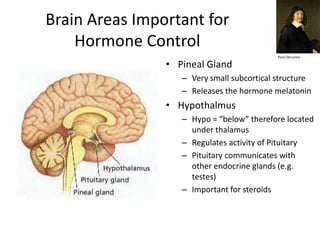
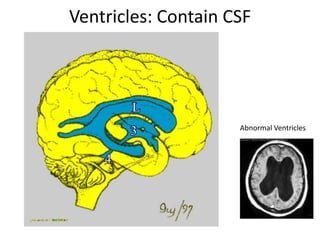
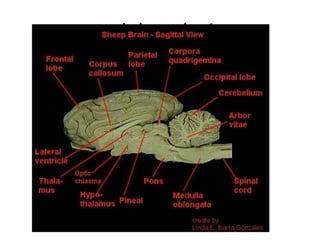
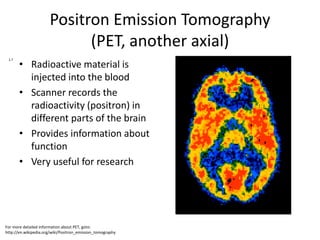
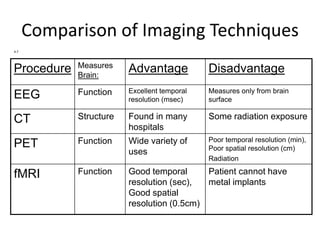
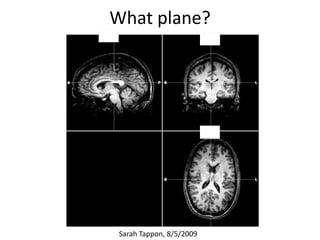
The document covers basic neuroanatomy, including major brain areas such as the cerebellum, thalamus, and hippocampus, along with their functions and associations with emotions and memory. It also discusses imaging techniques like CT, PET, and fMRI used to study brain structure and function, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it touches on some historical aspects and research implications in neuroanatomy.

![Brainstem
The Medulla [muh-
DUL-uh] is the base of
the brainstem that
controls heartbeat and
breathing.
Example: SIDS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04neuroanatomyf111b-120703220125-phpapp02/85/Introductory-Psychology-Brain-4-320.jpg)












![Amygdala
The Amygdala [ah-MIG-
dah-la] consists of two lima
bean-sized neural clusters
linked to the emotions of
fear and anger.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04neuroanatomyf111b-120703220125-phpapp02/85/Introductory-Psychology-Brain-20-320.jpg)