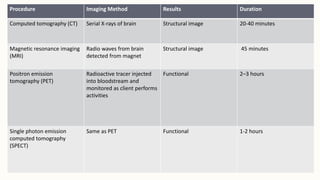
The document discusses various brain imaging techniques including Computed Tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), detailing their procedures, duration, and diagnostic capabilities. Each method varies in terms of image detail, function examined, and patient requirements, such as lying still and potential for claustrophobia or allergic reactions. Limitations include the risk of allergic reactions, cost of equipment, and availability constraints.