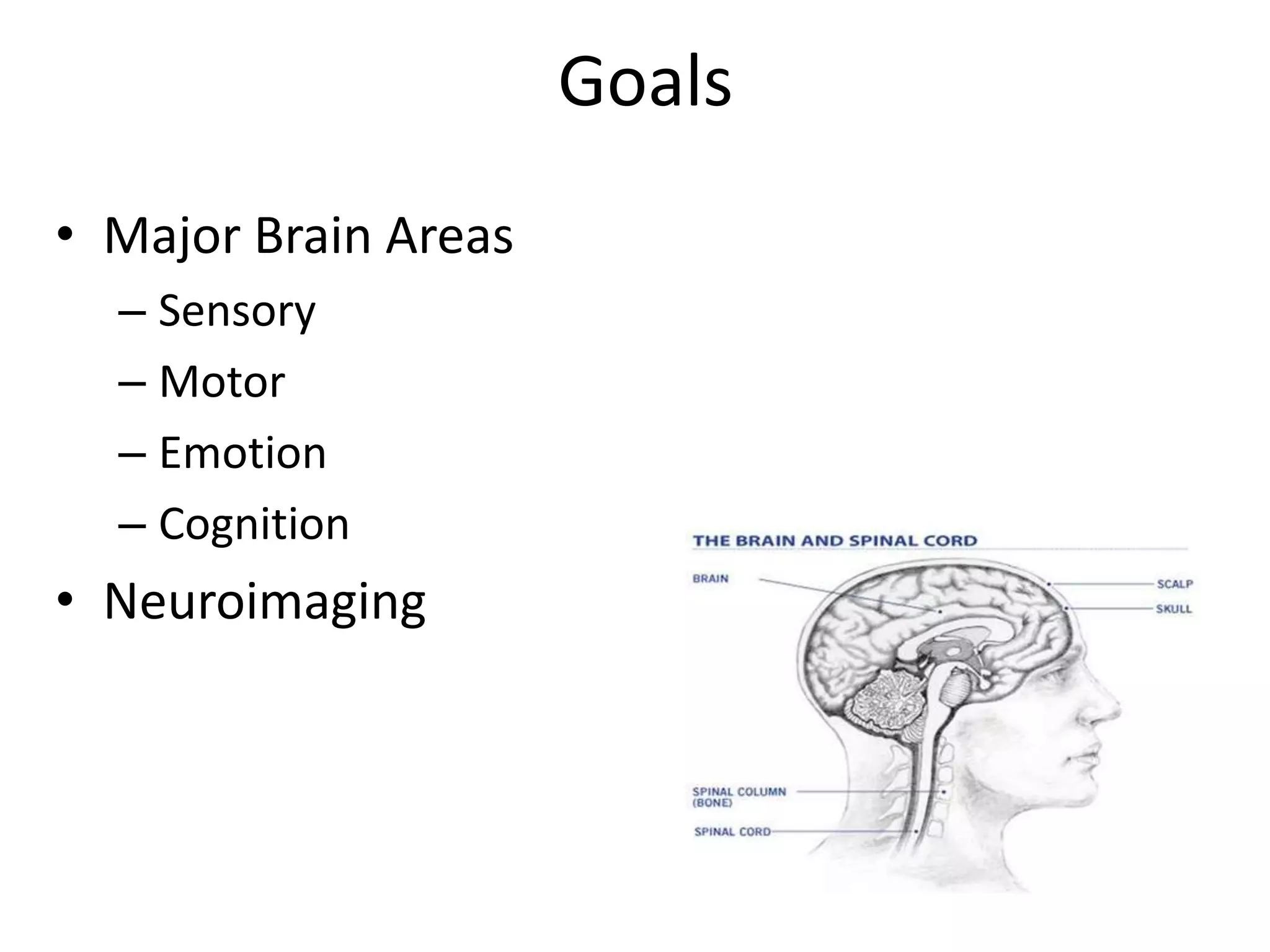
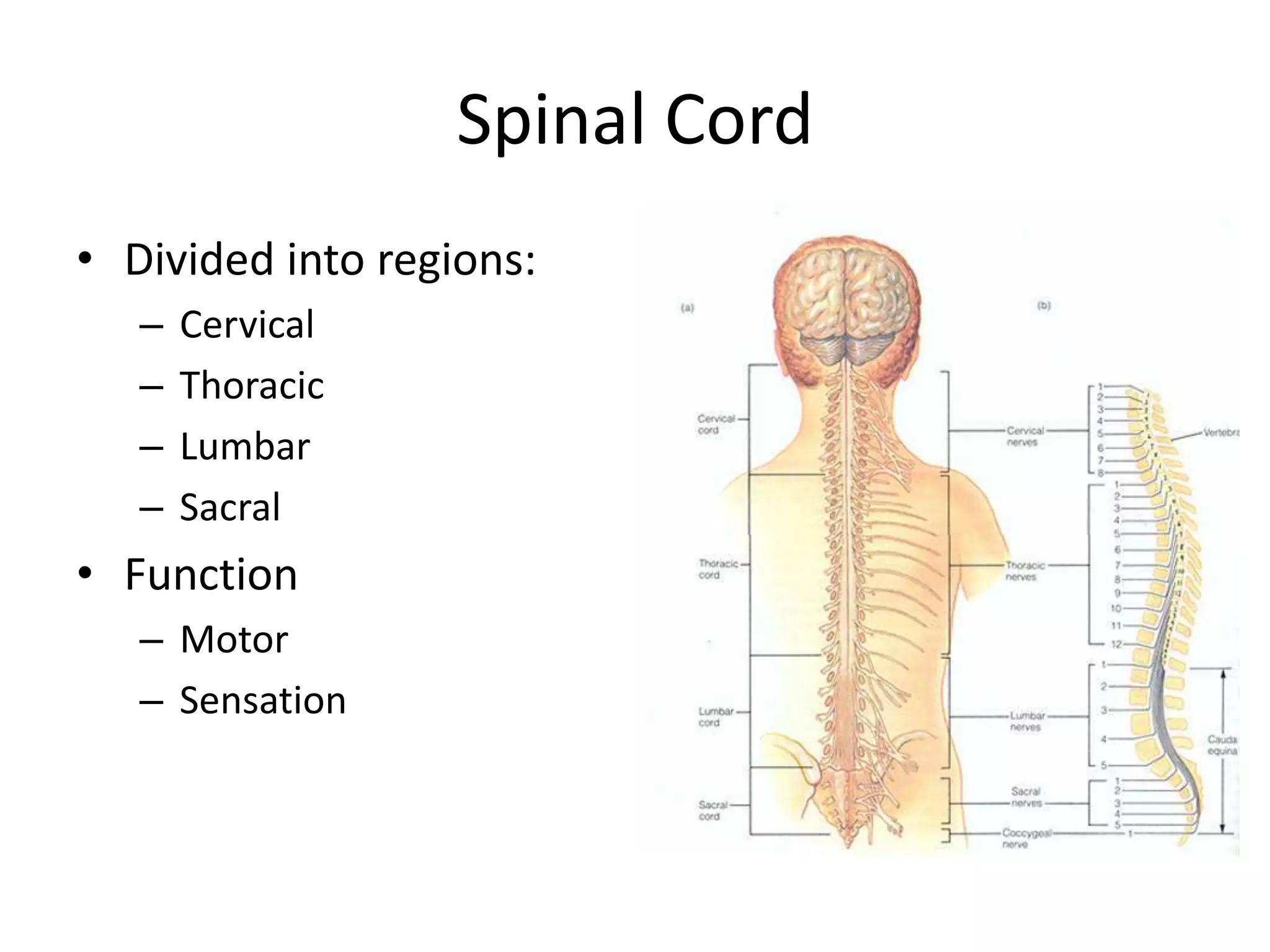
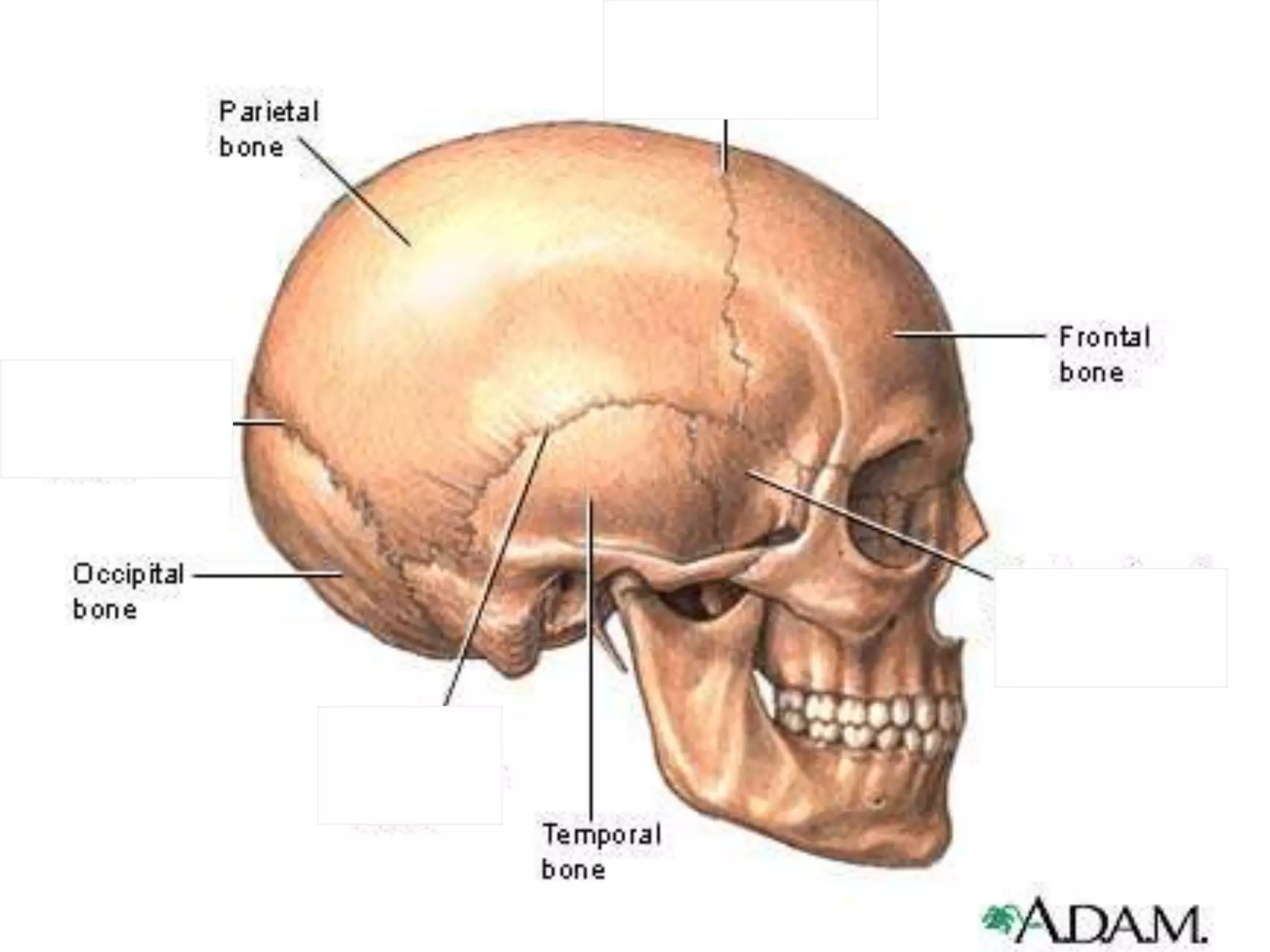
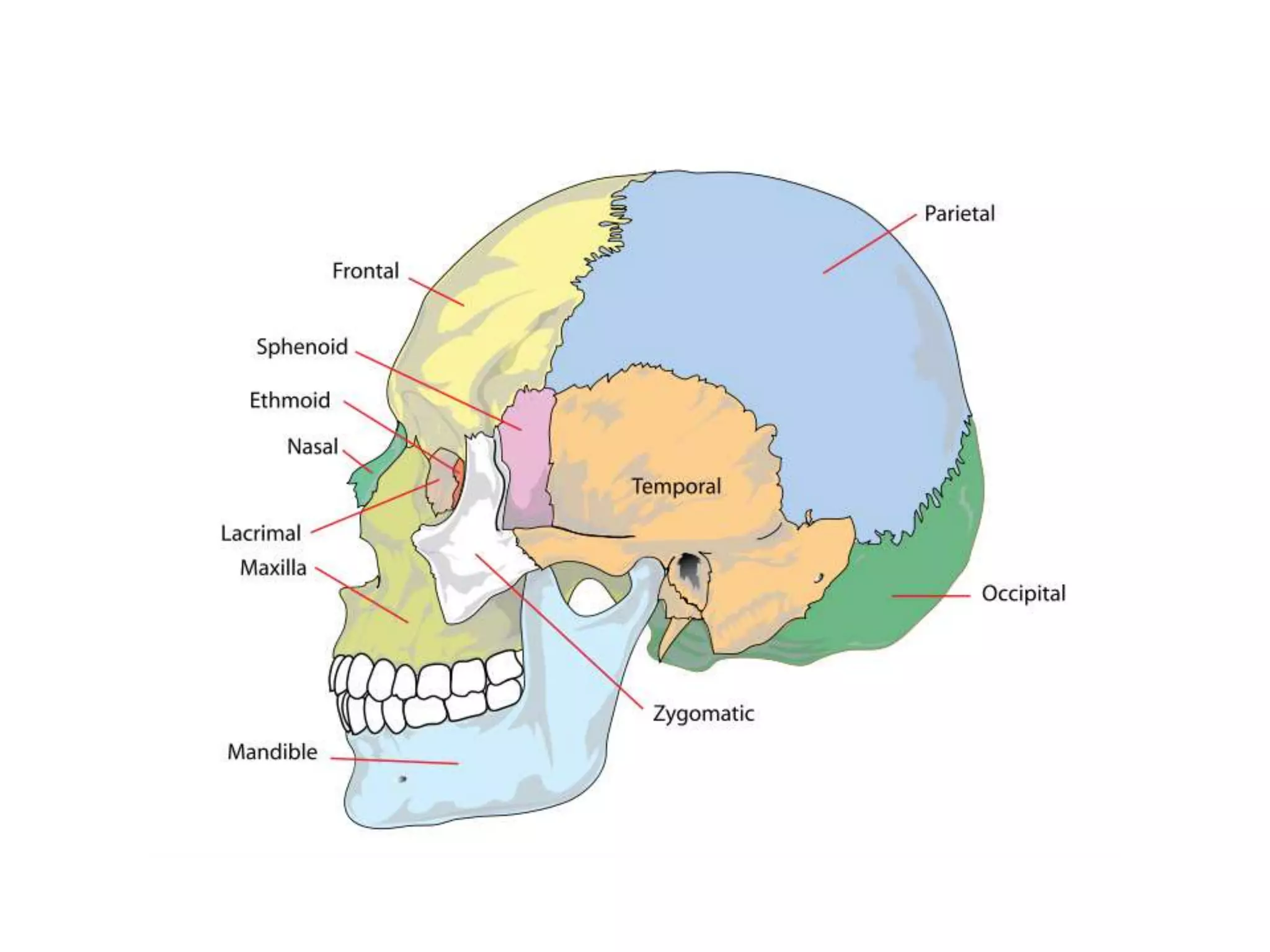
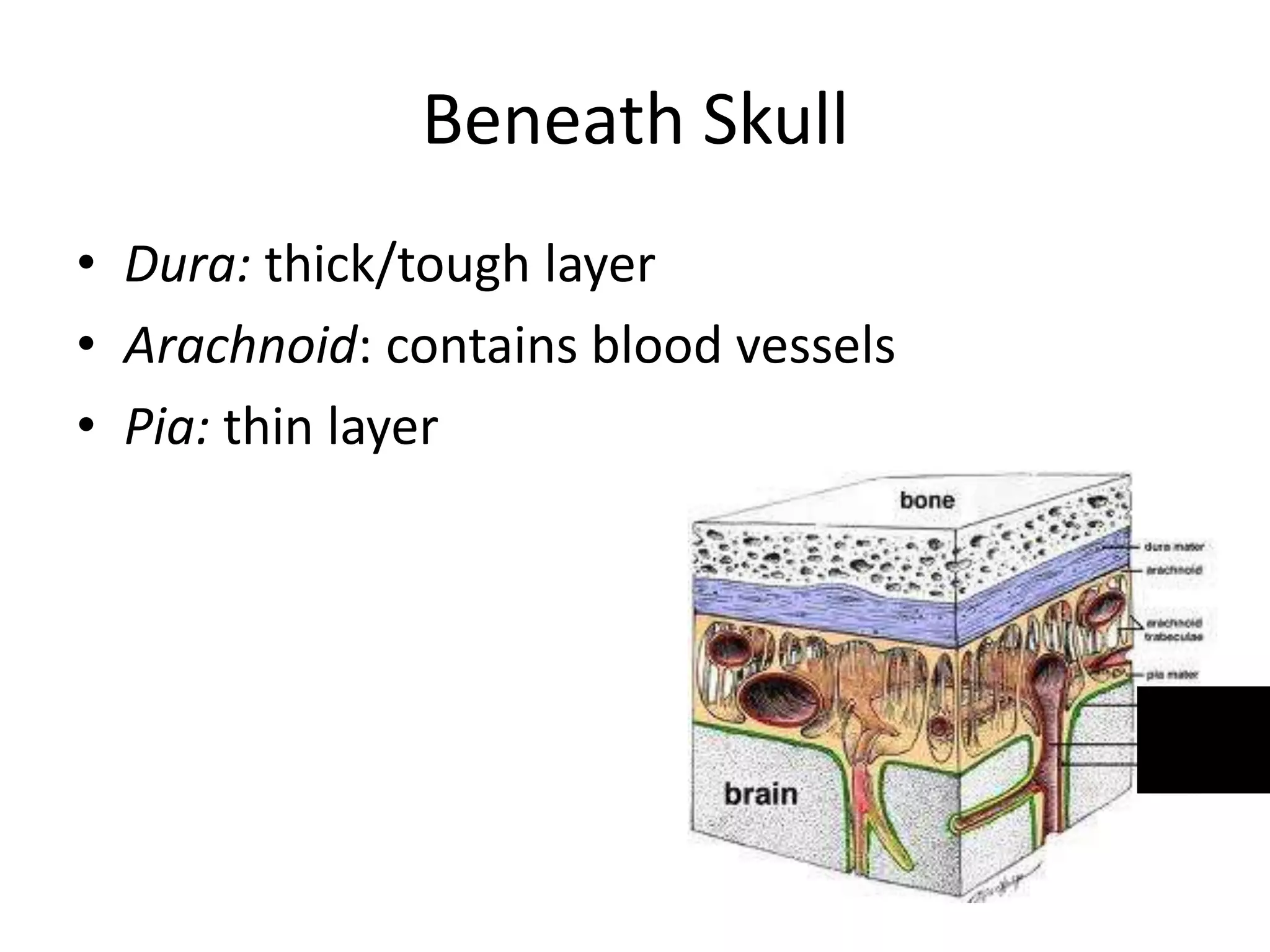
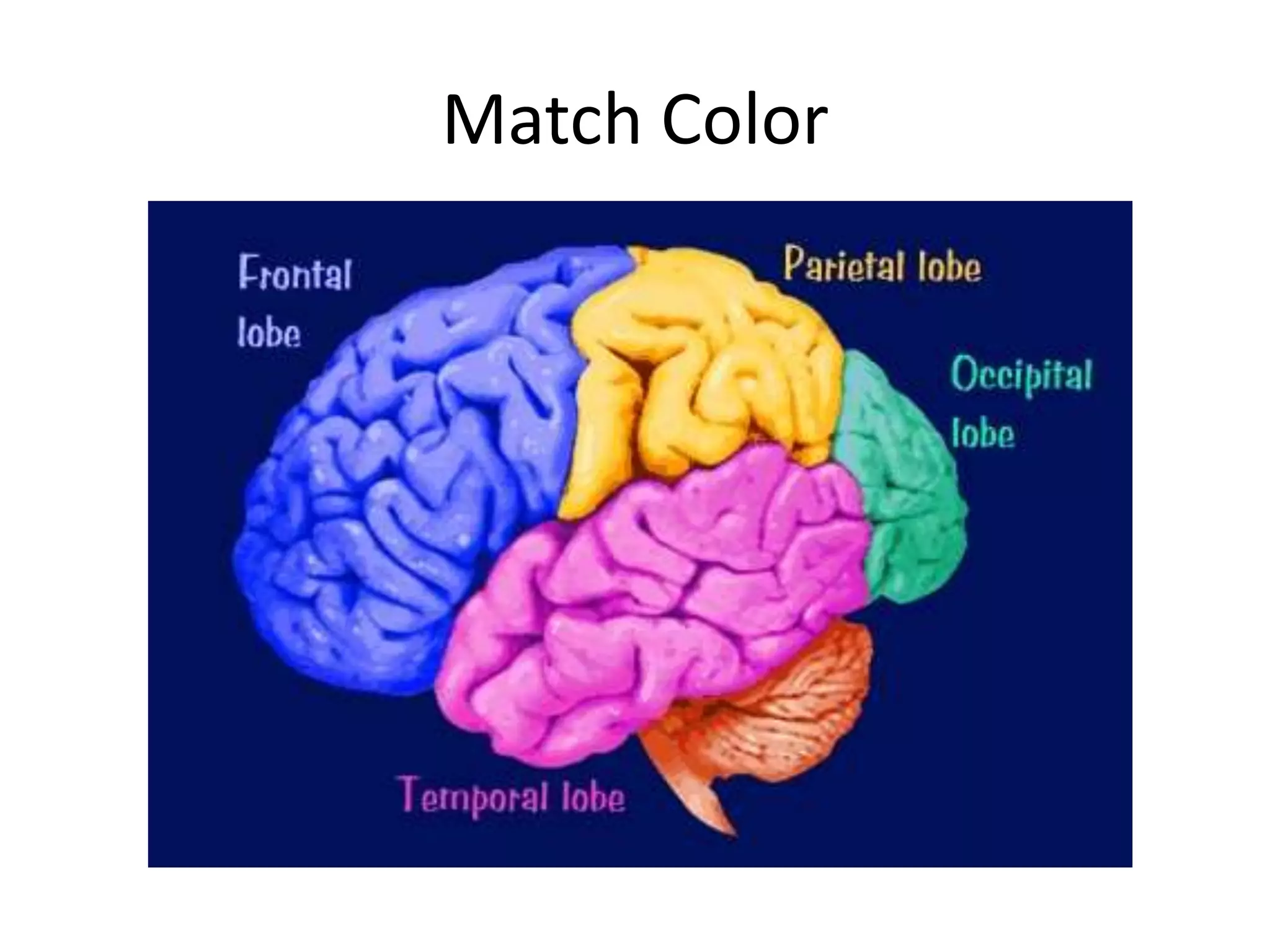
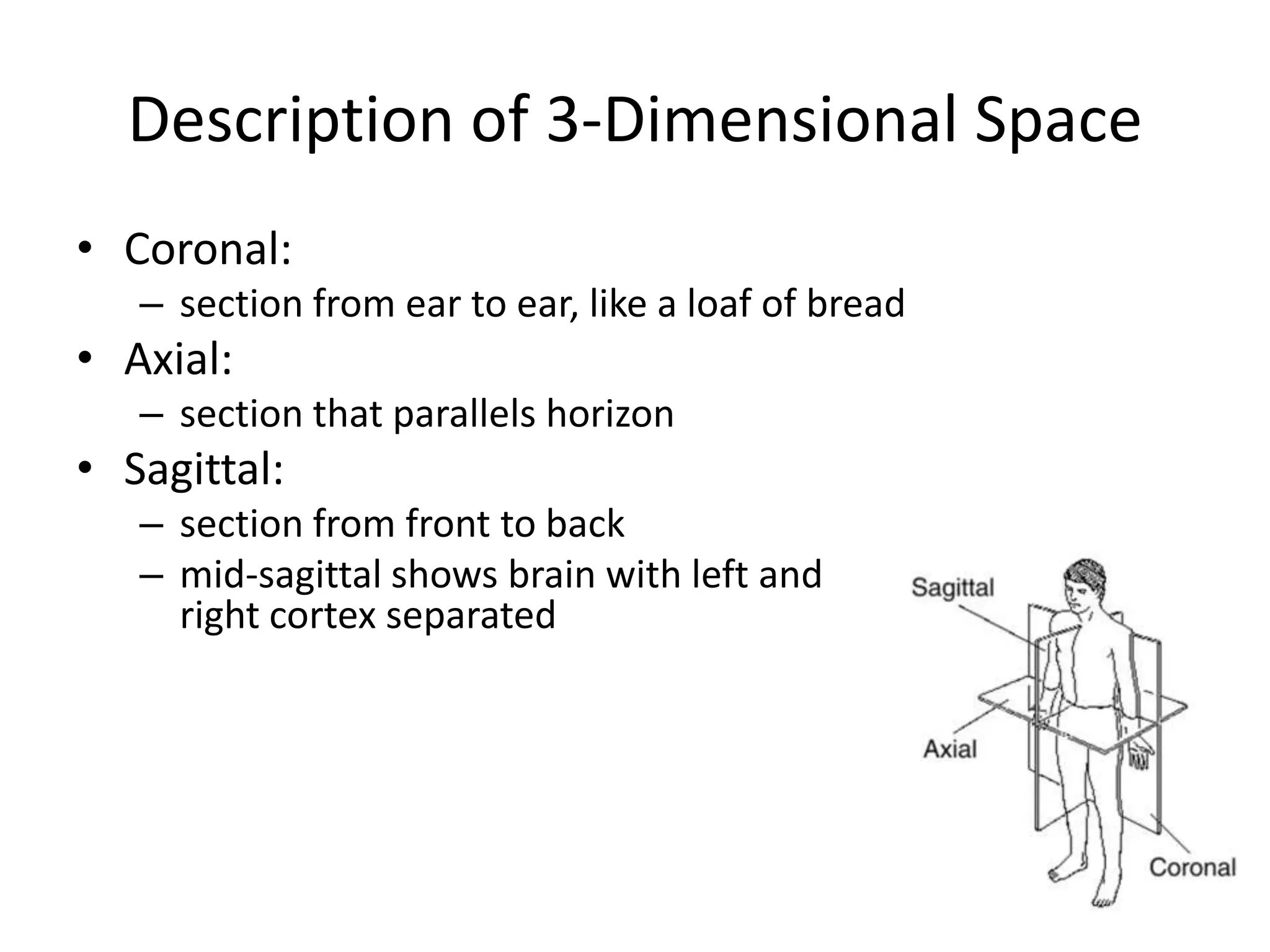
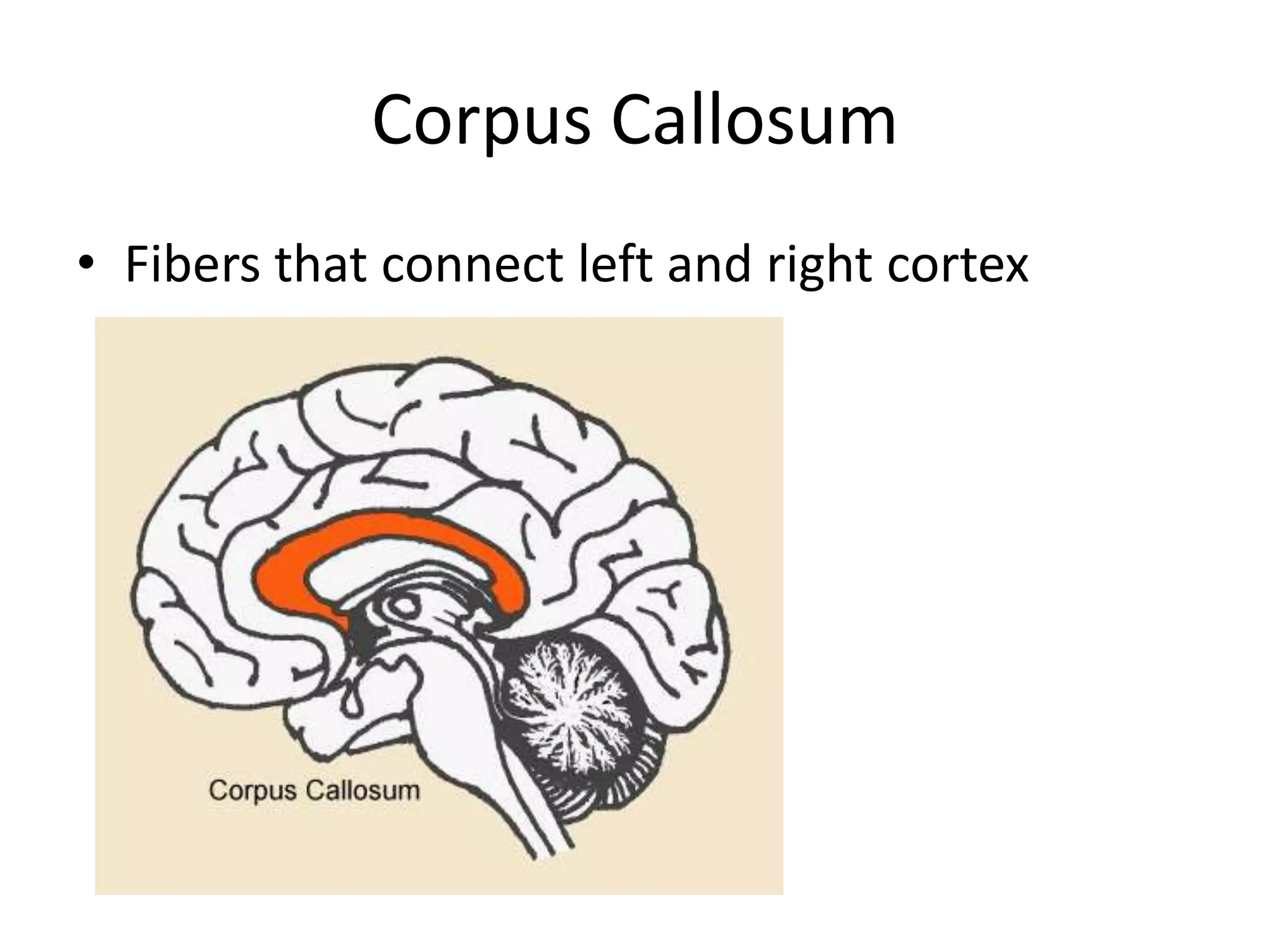
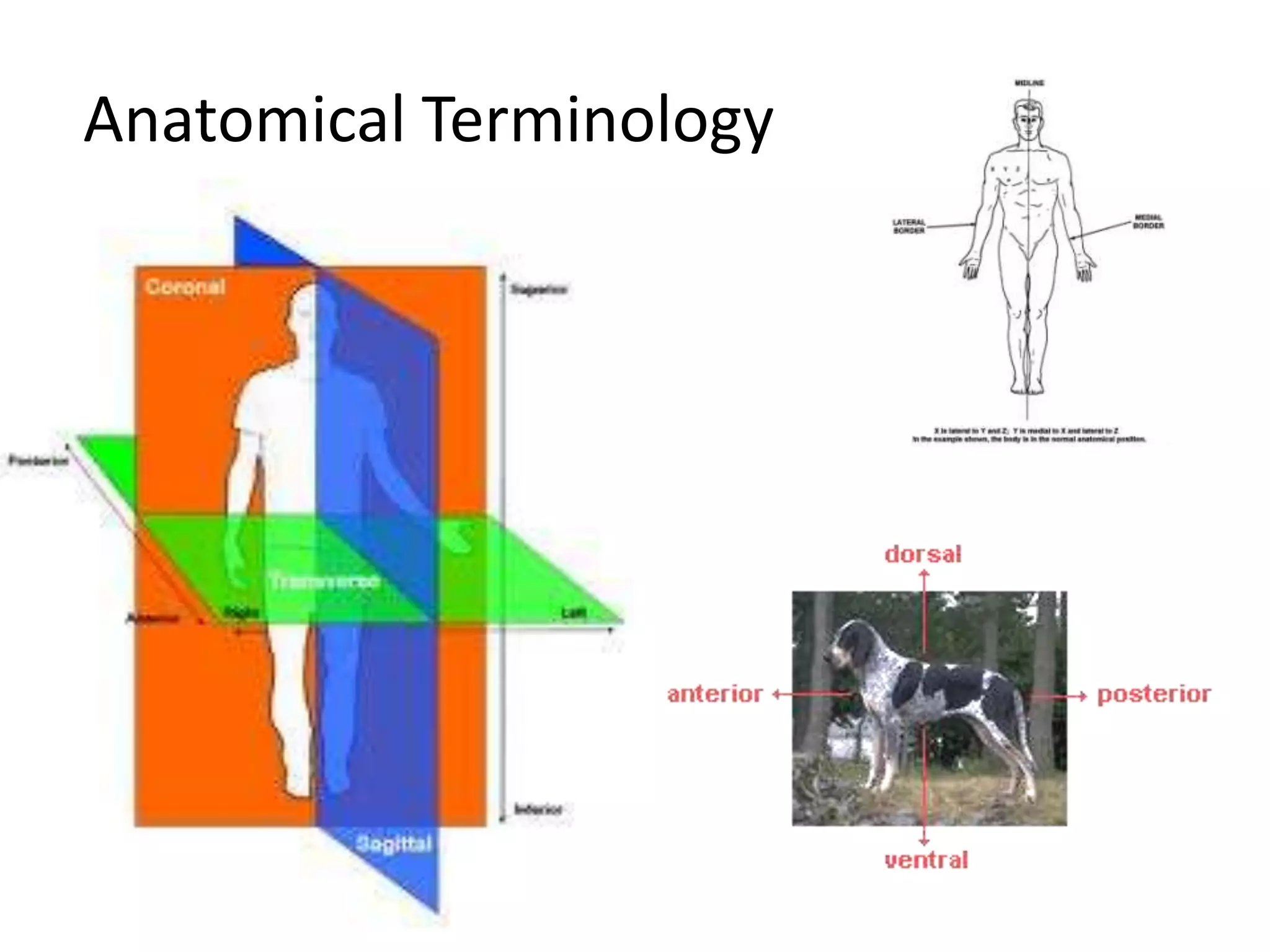
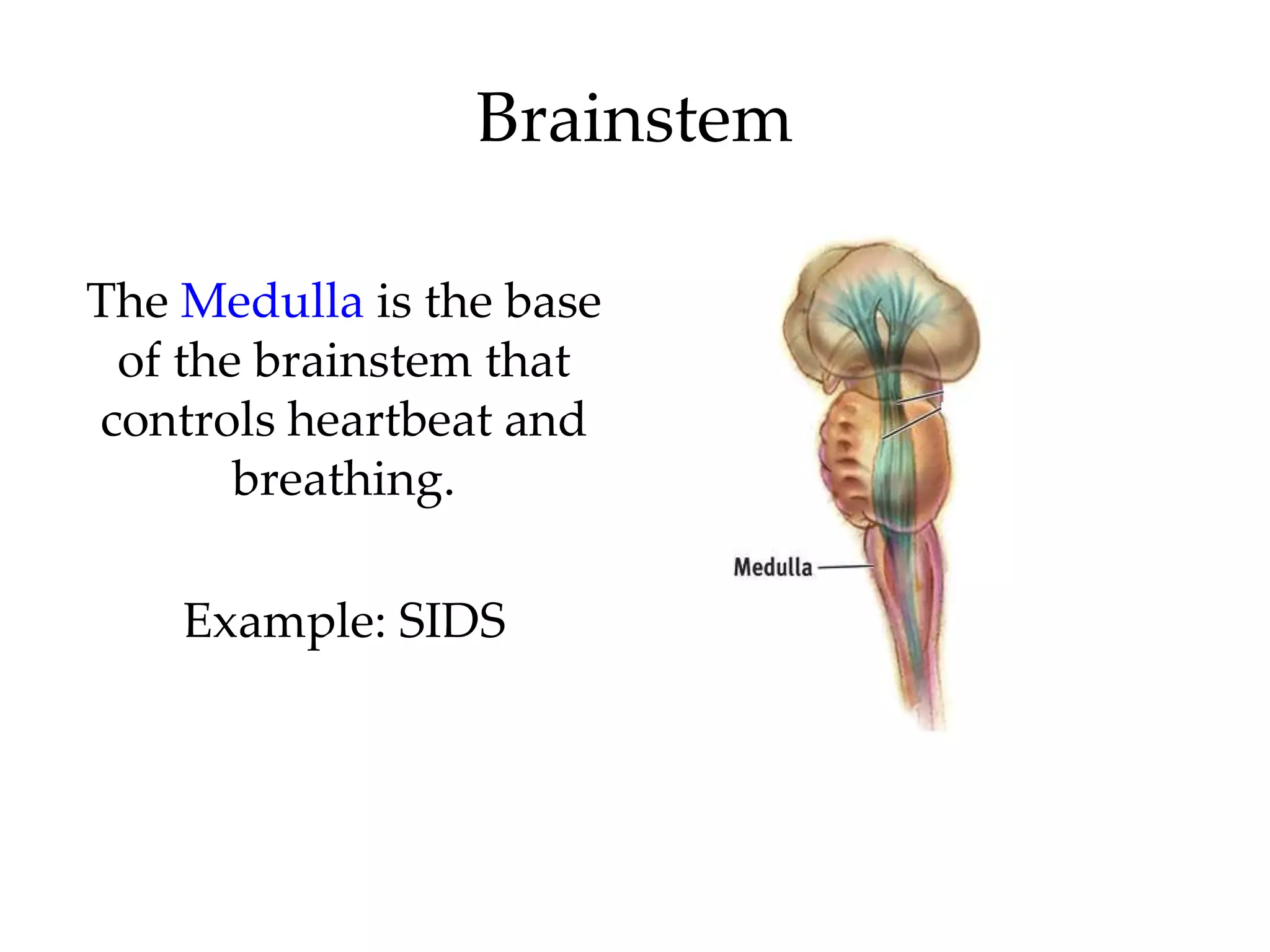
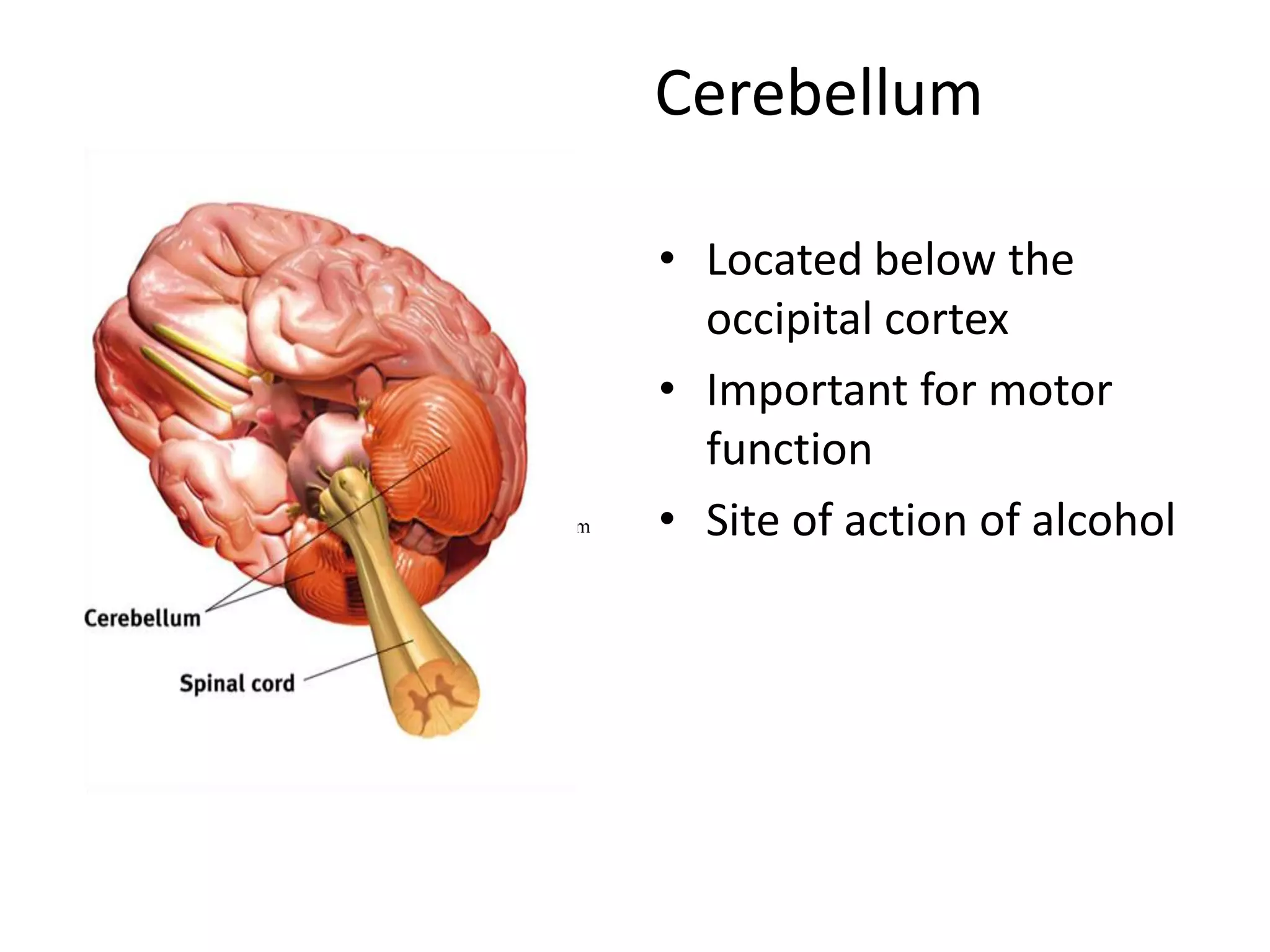
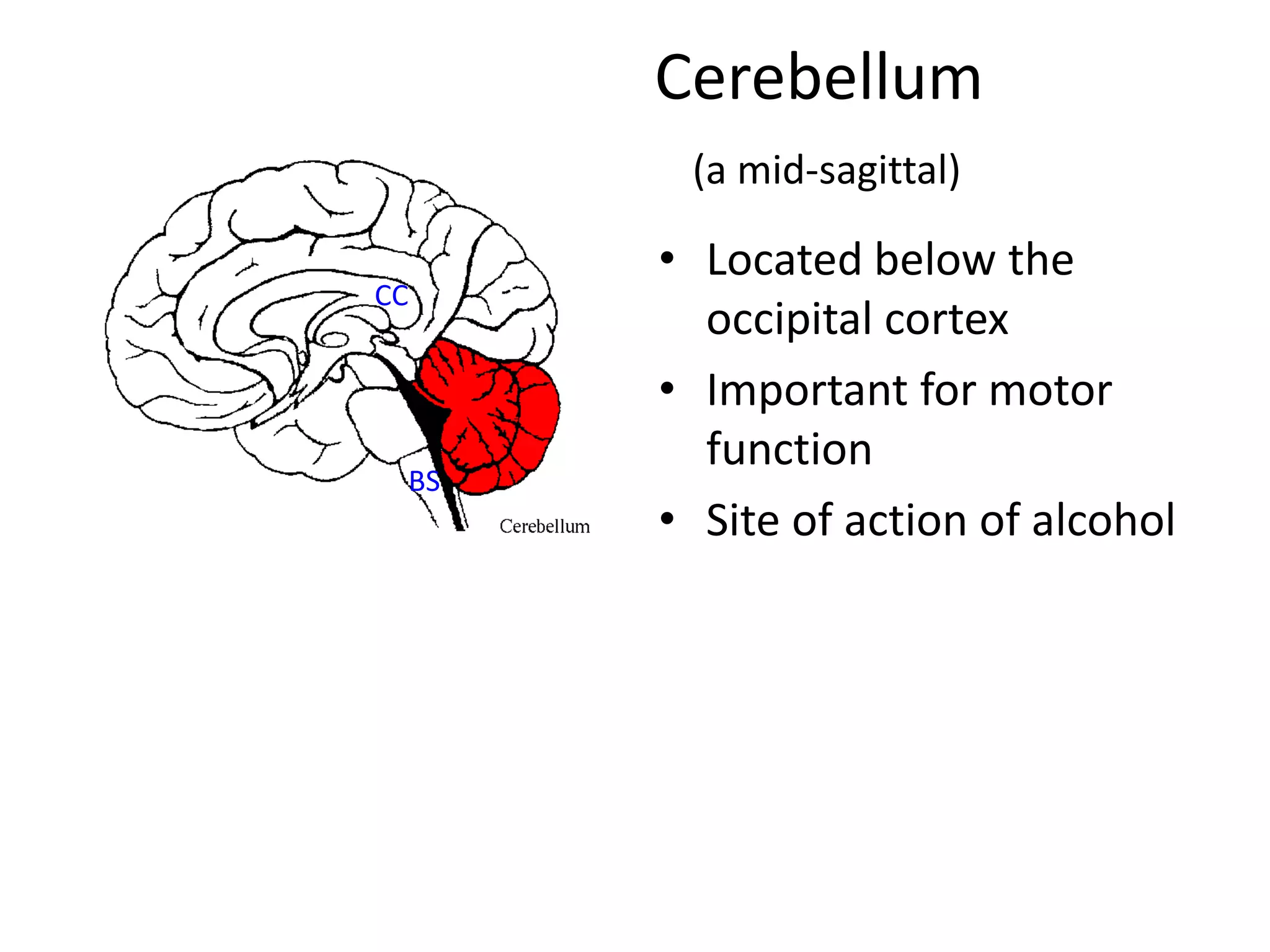
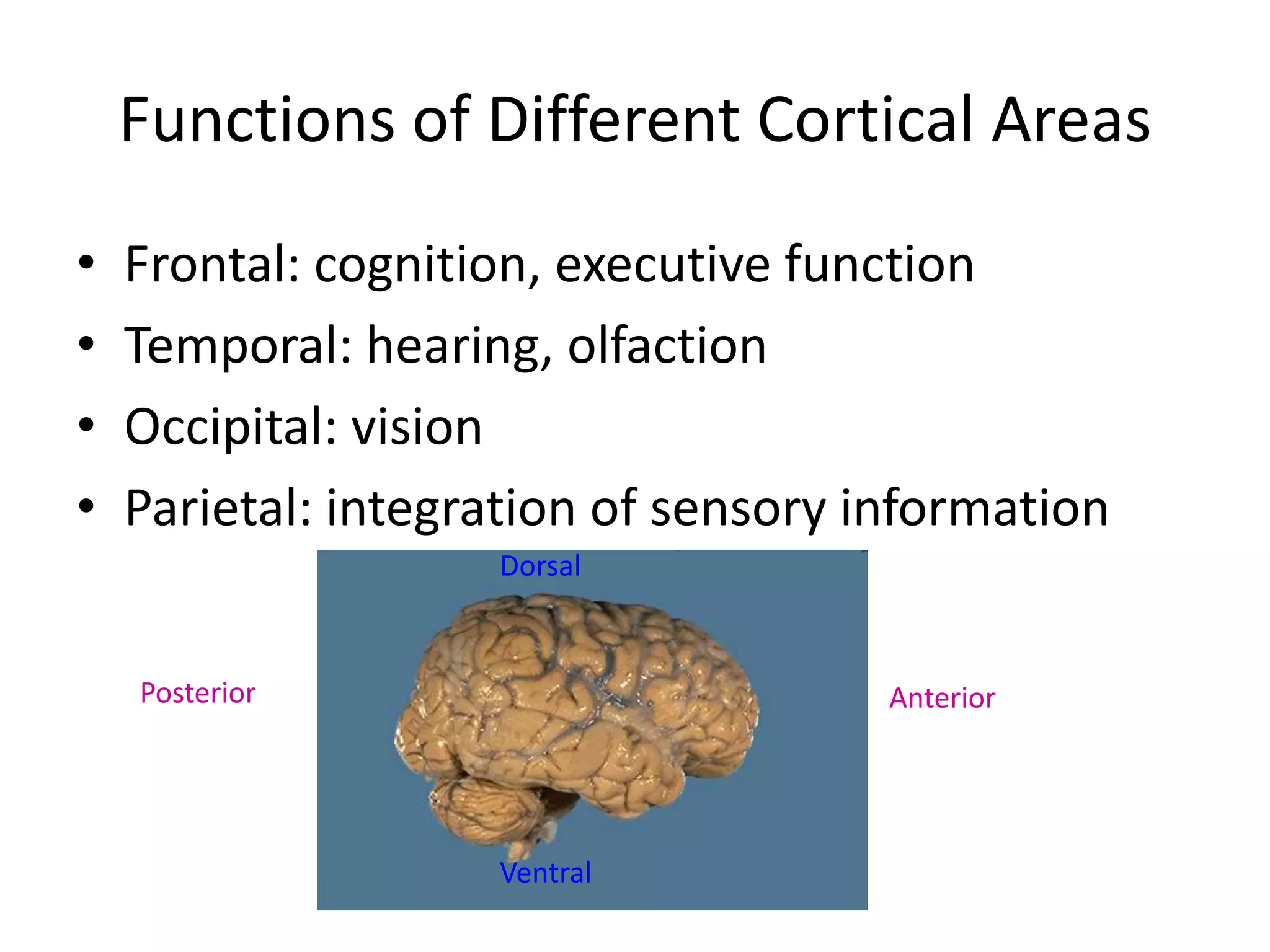
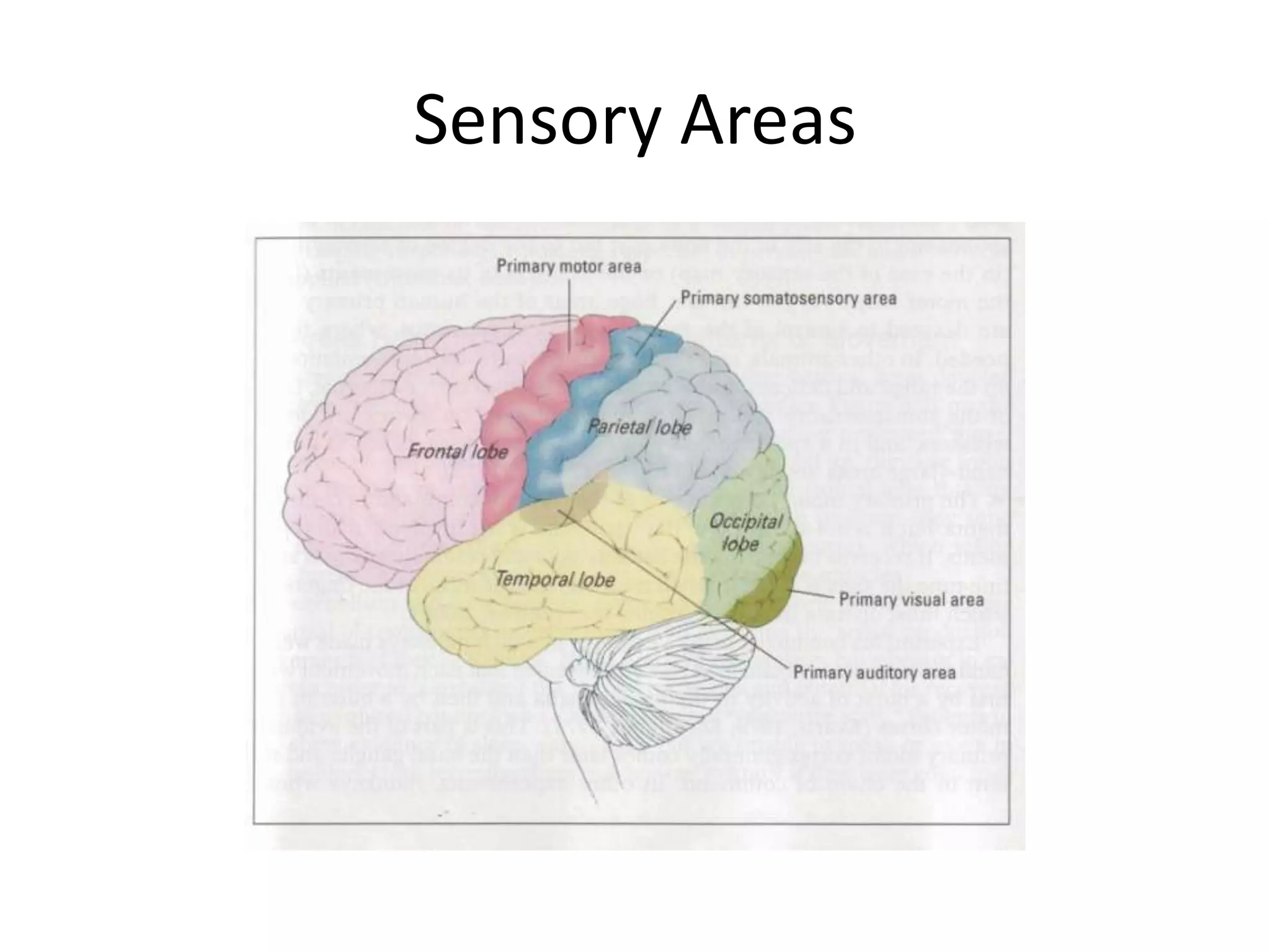
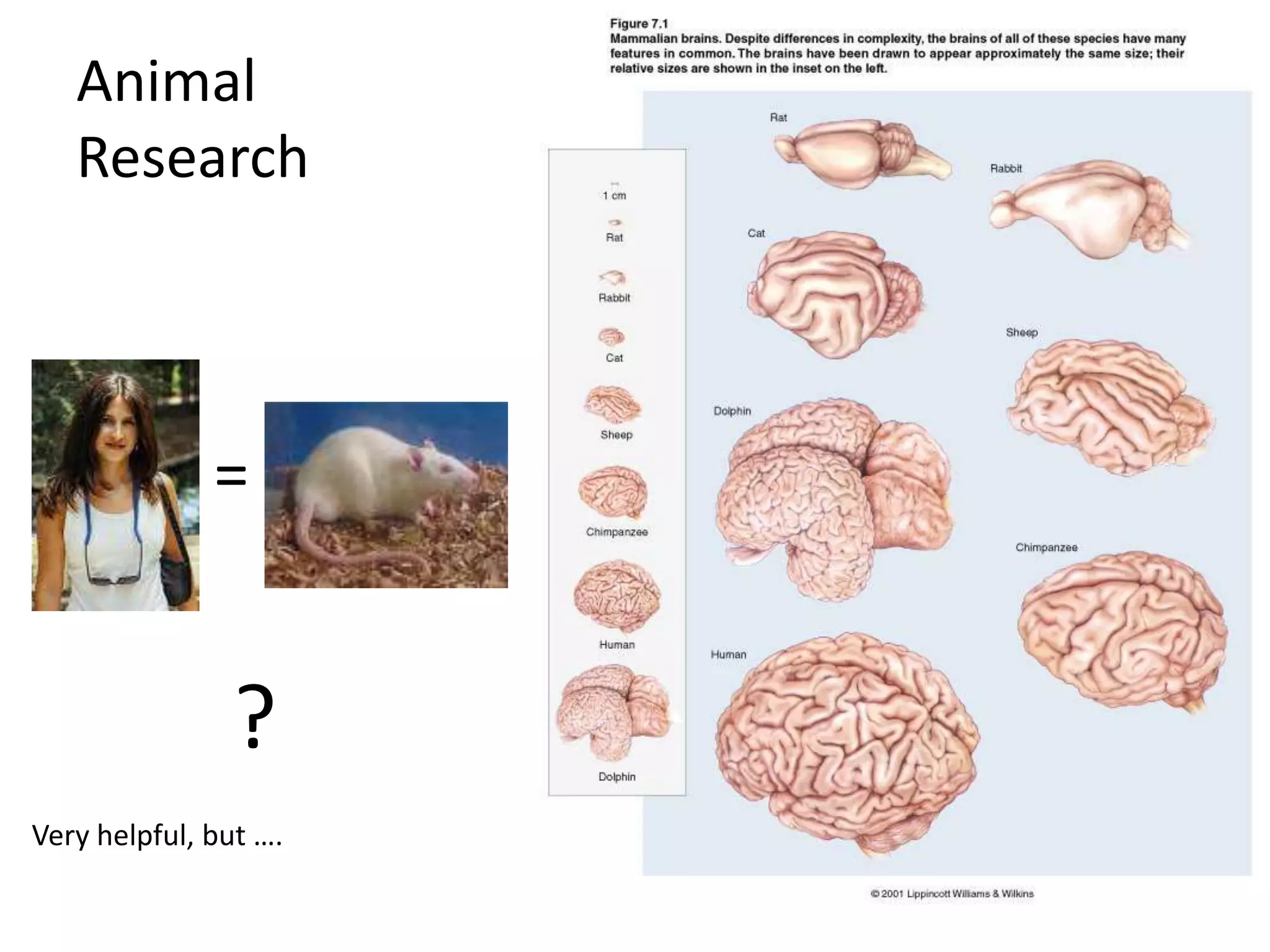
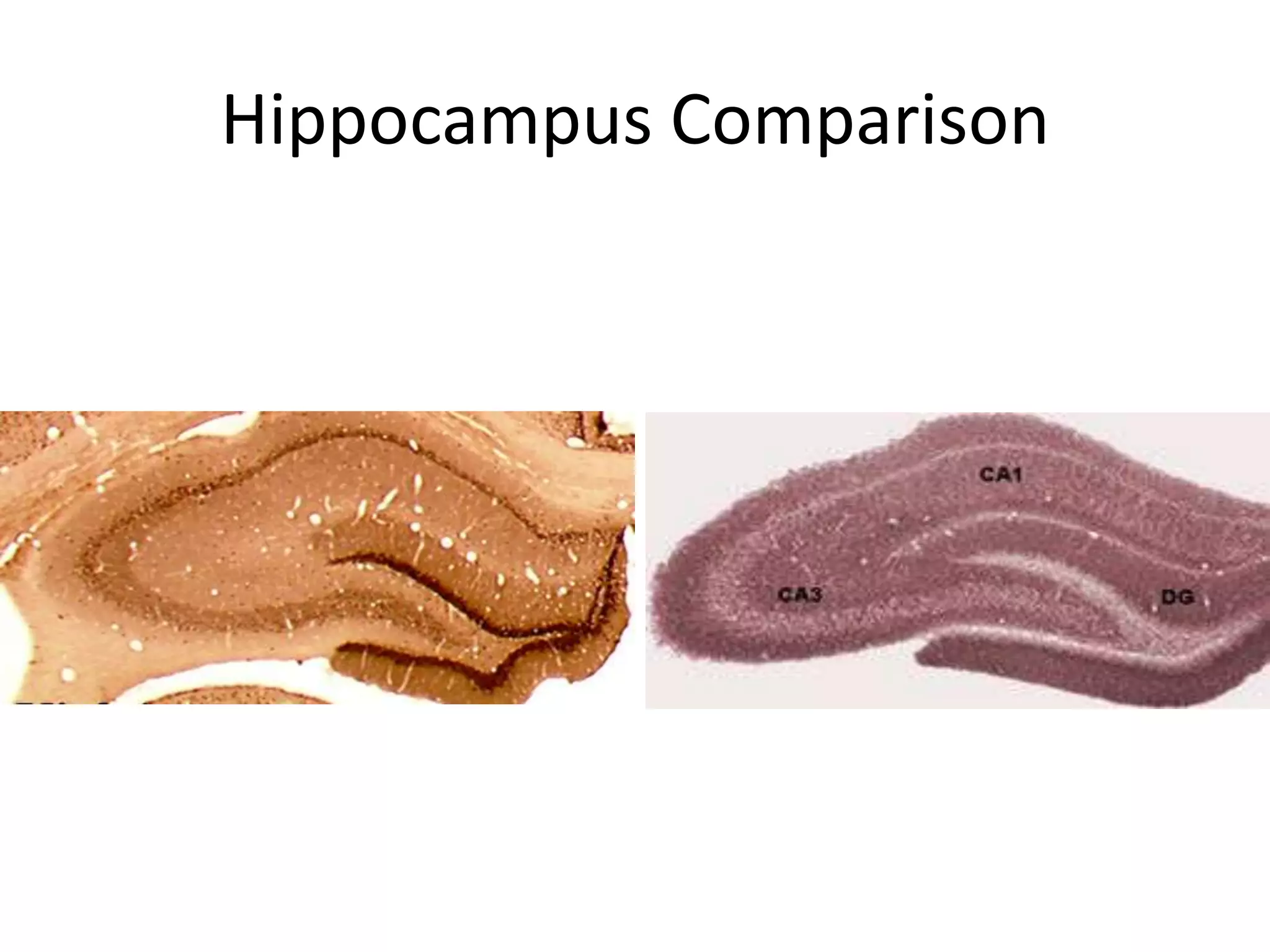
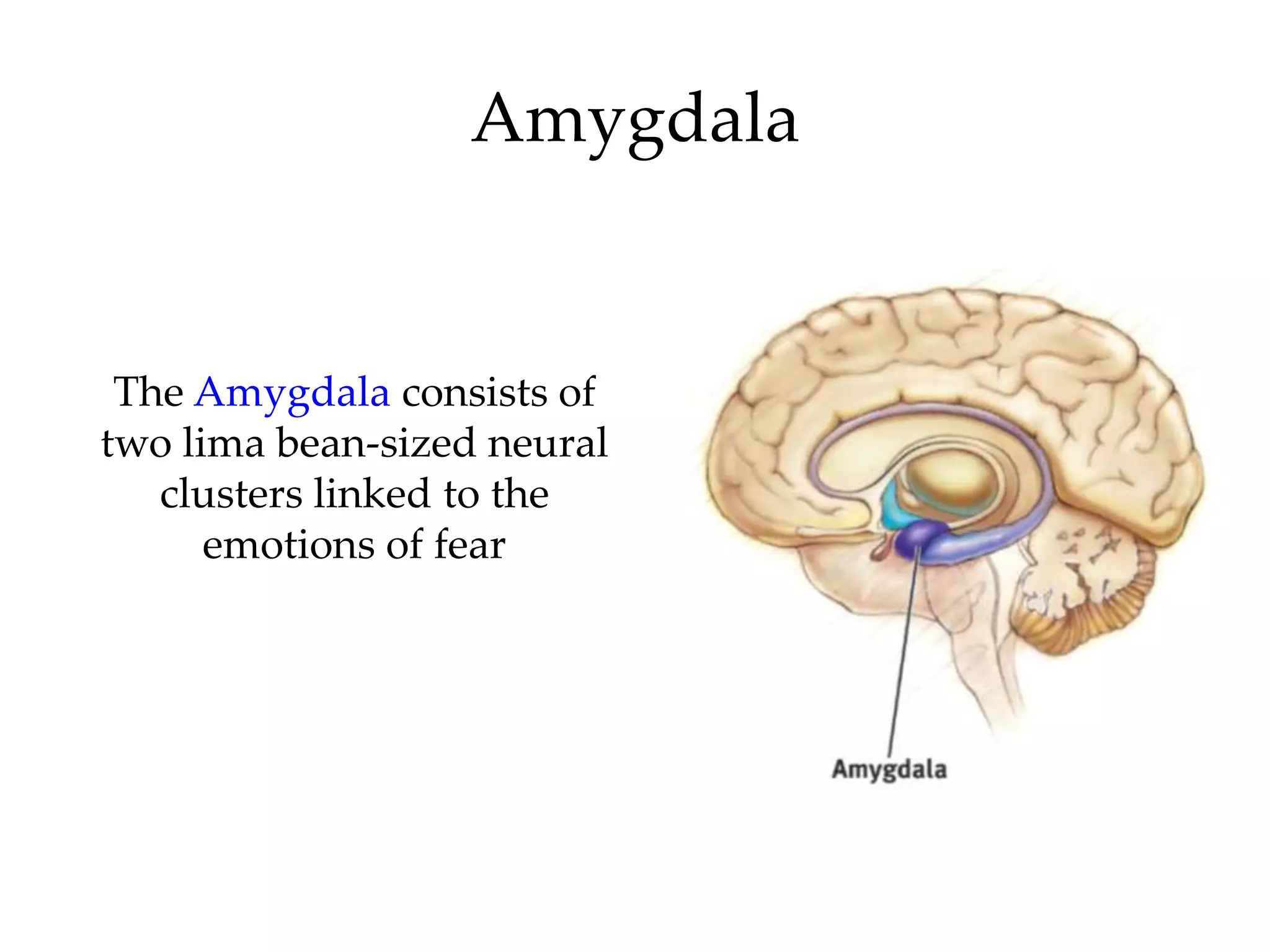
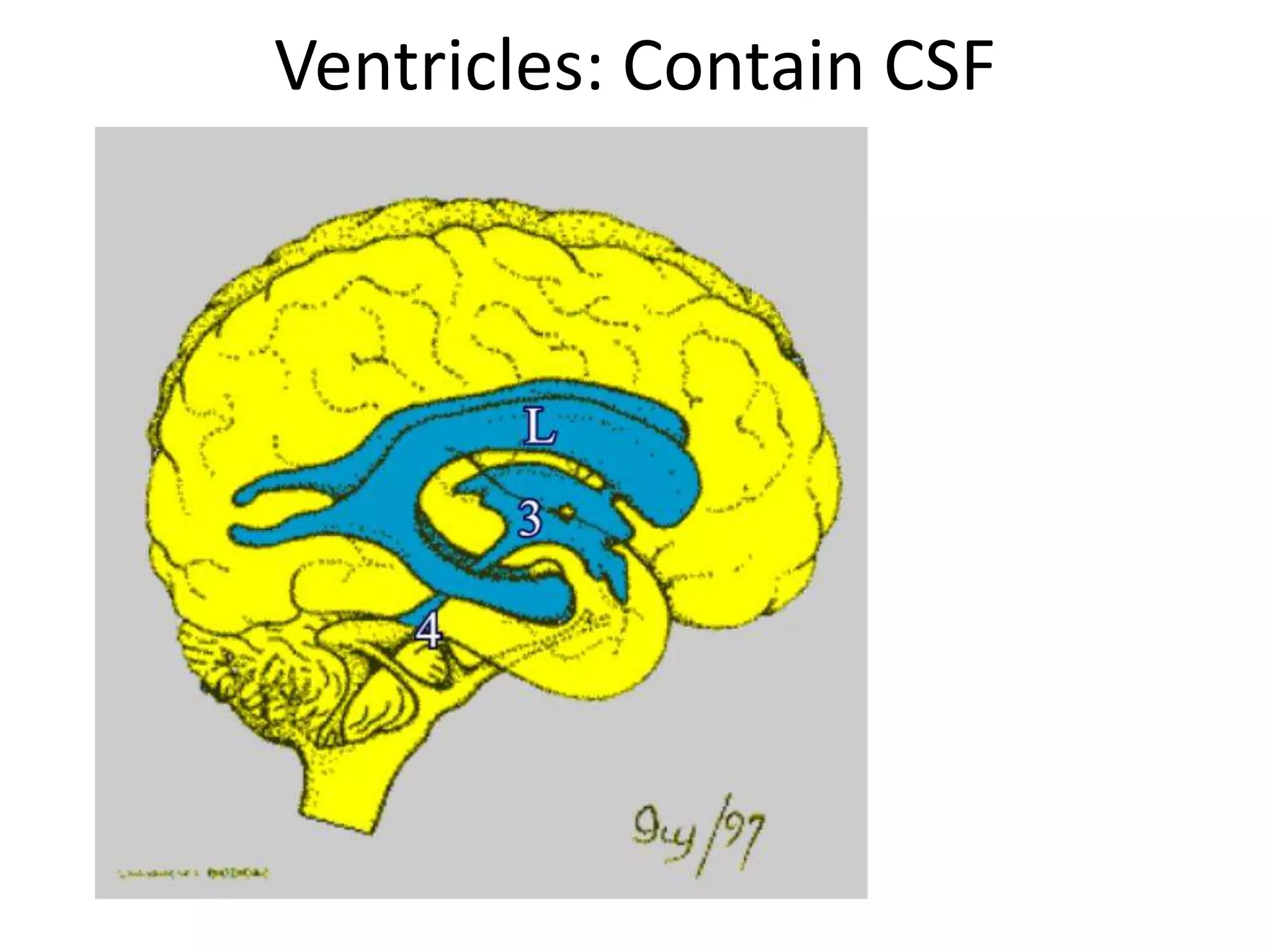
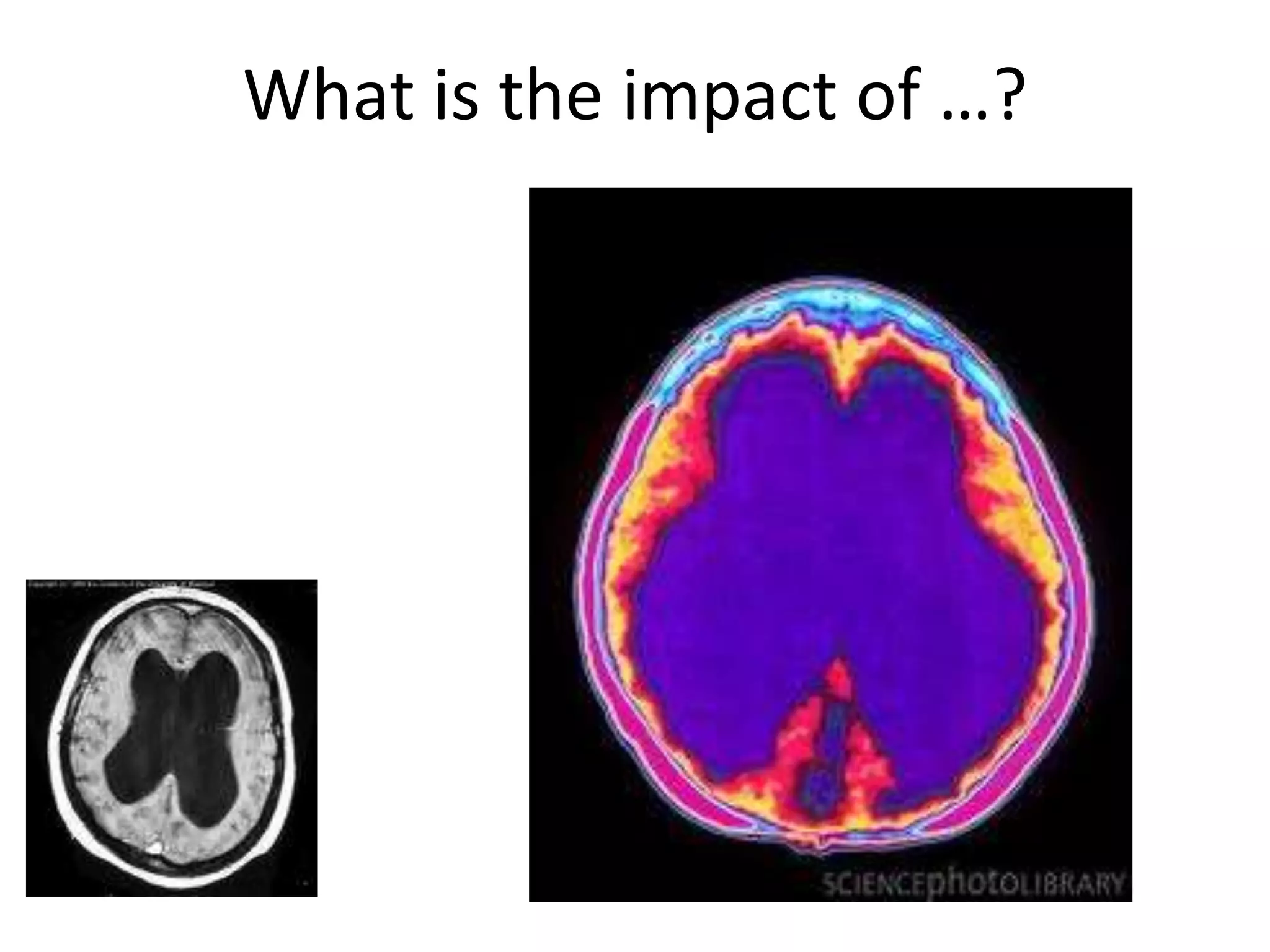
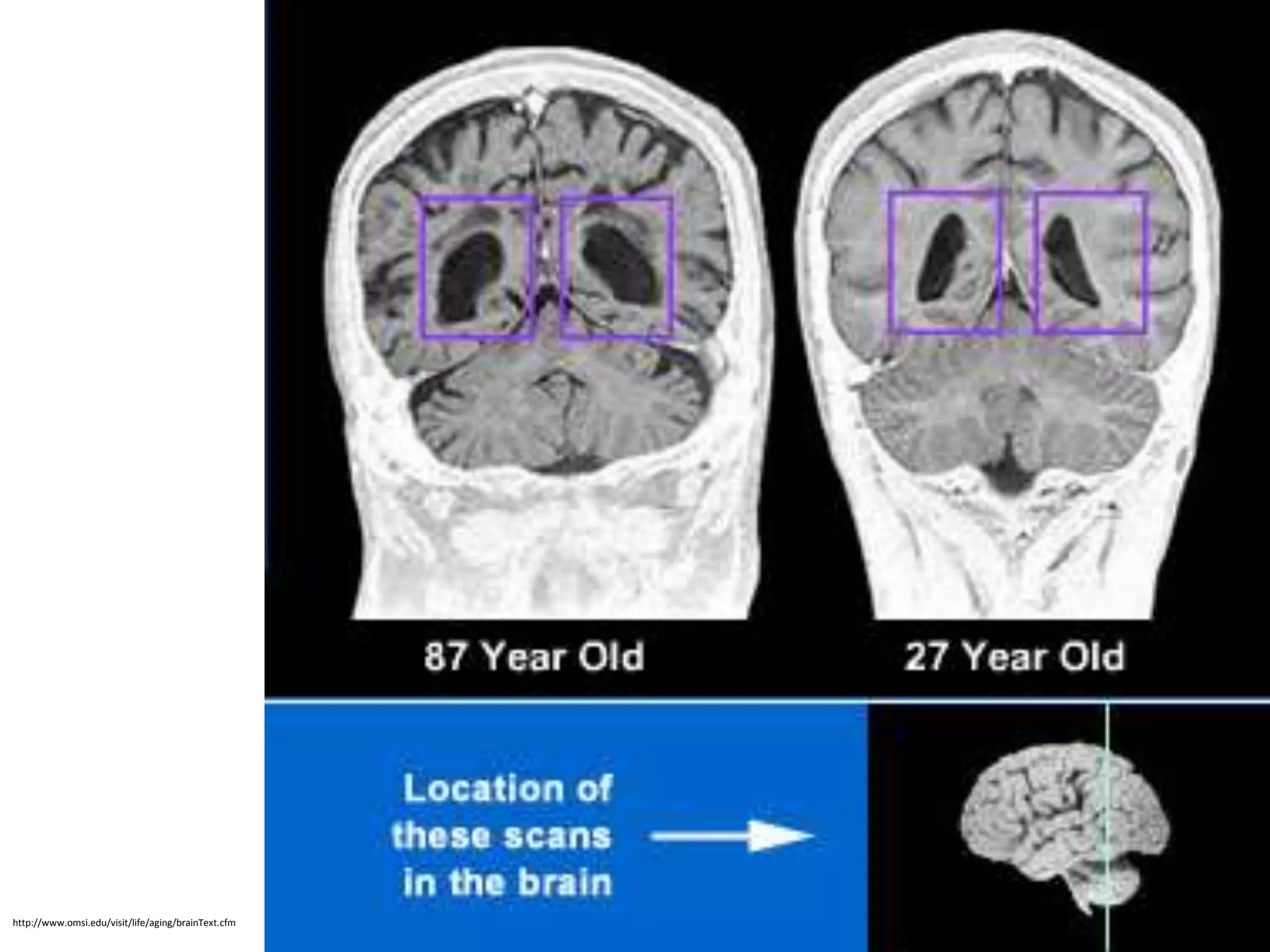
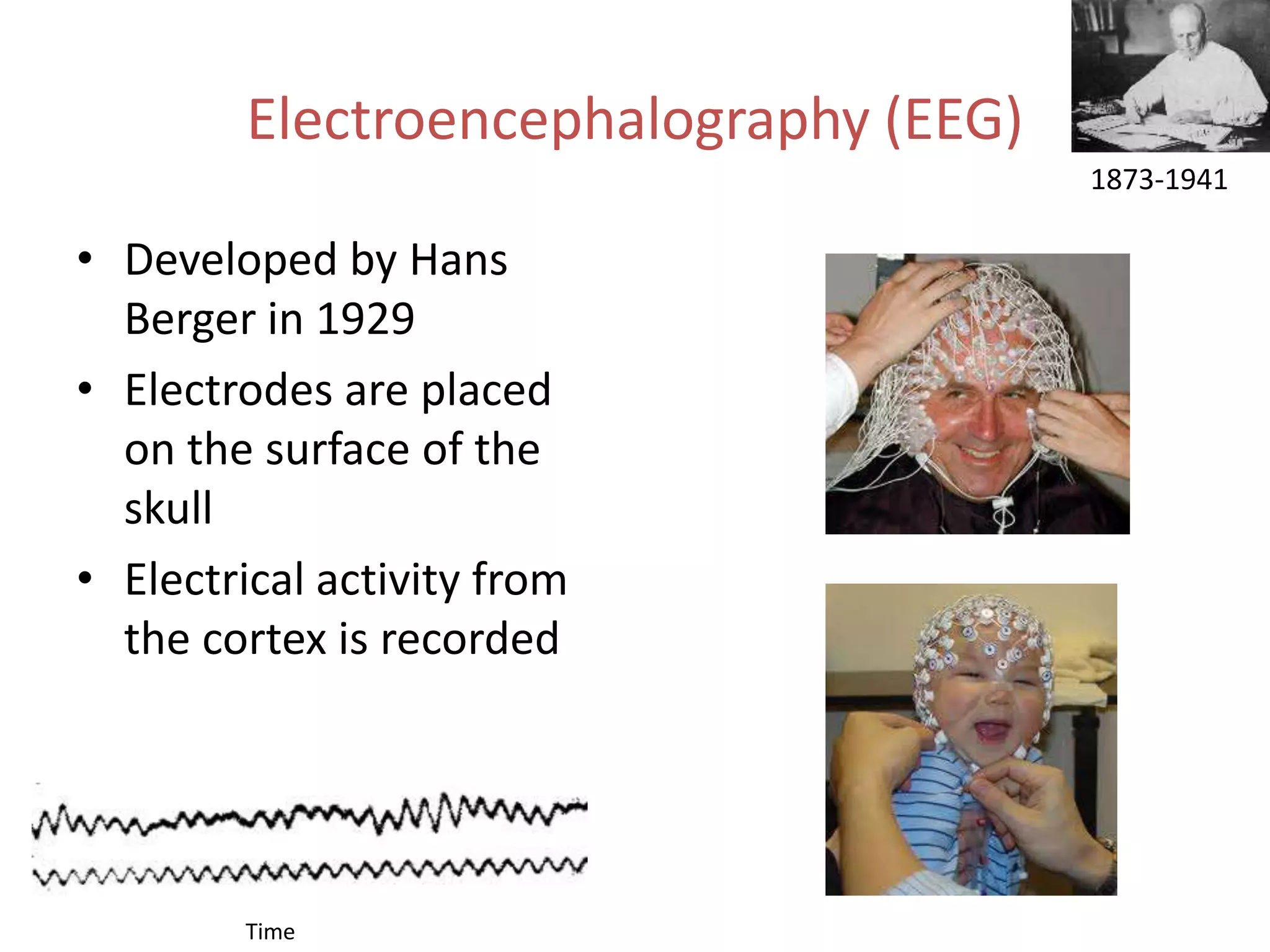
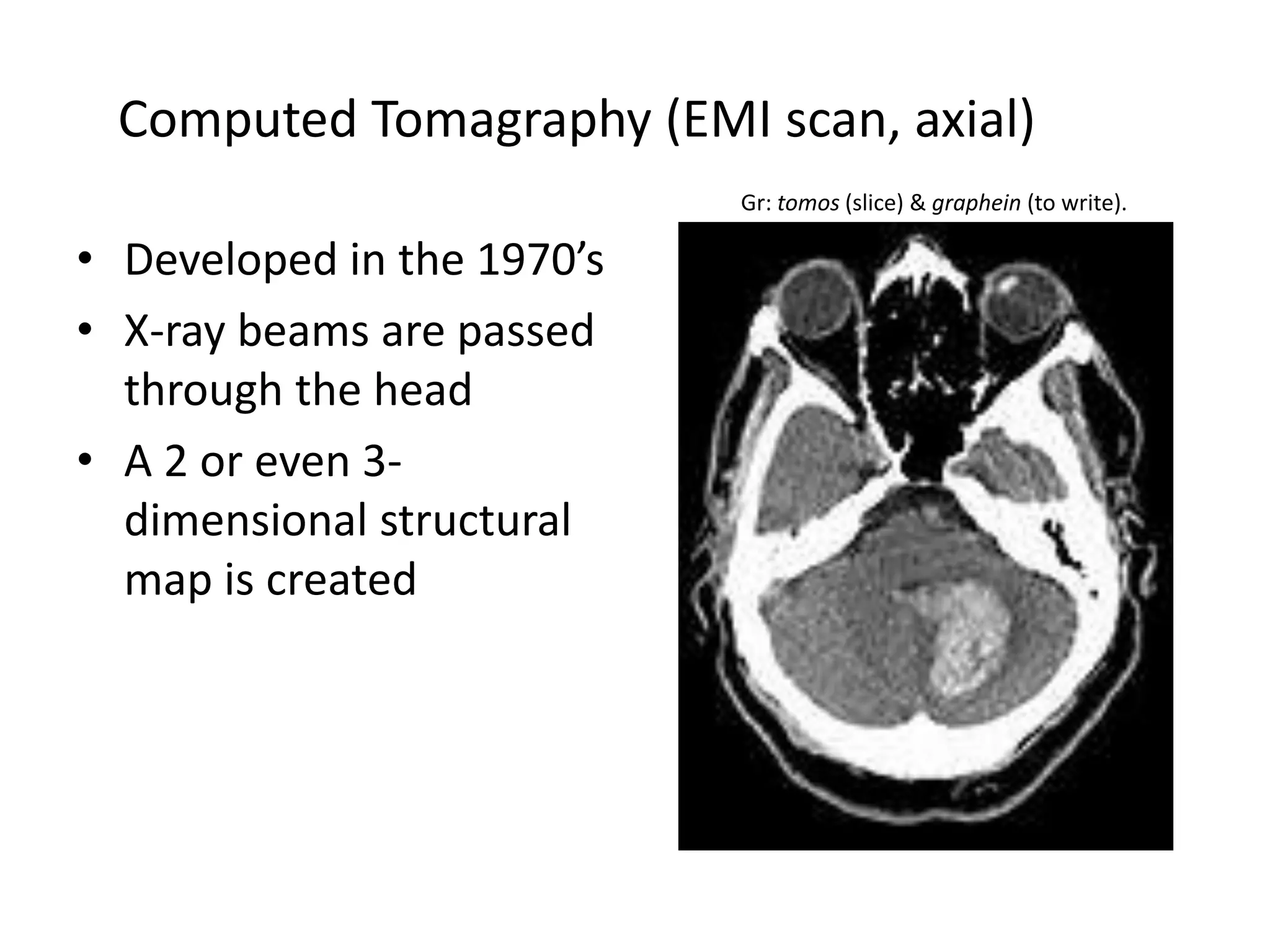
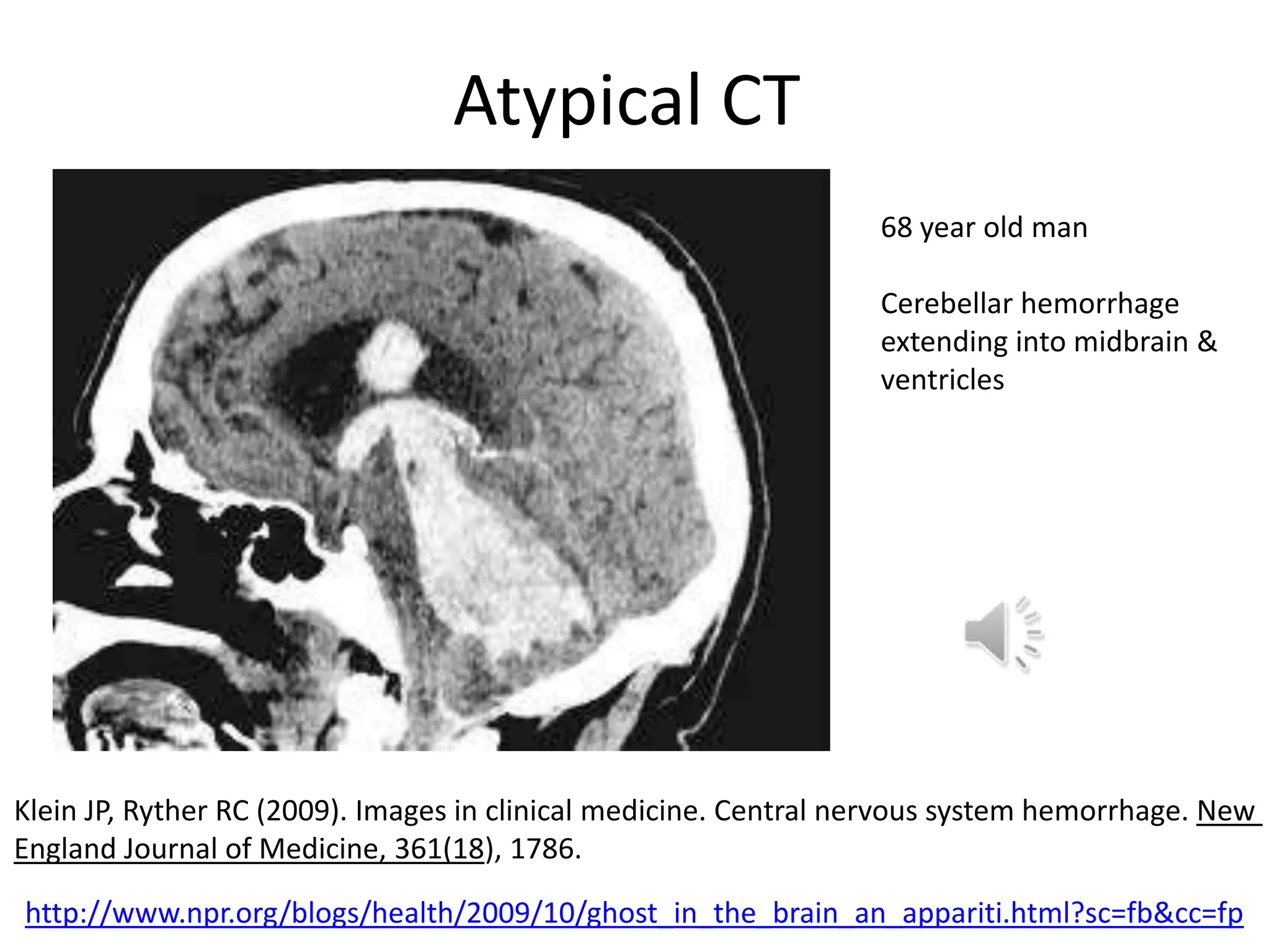
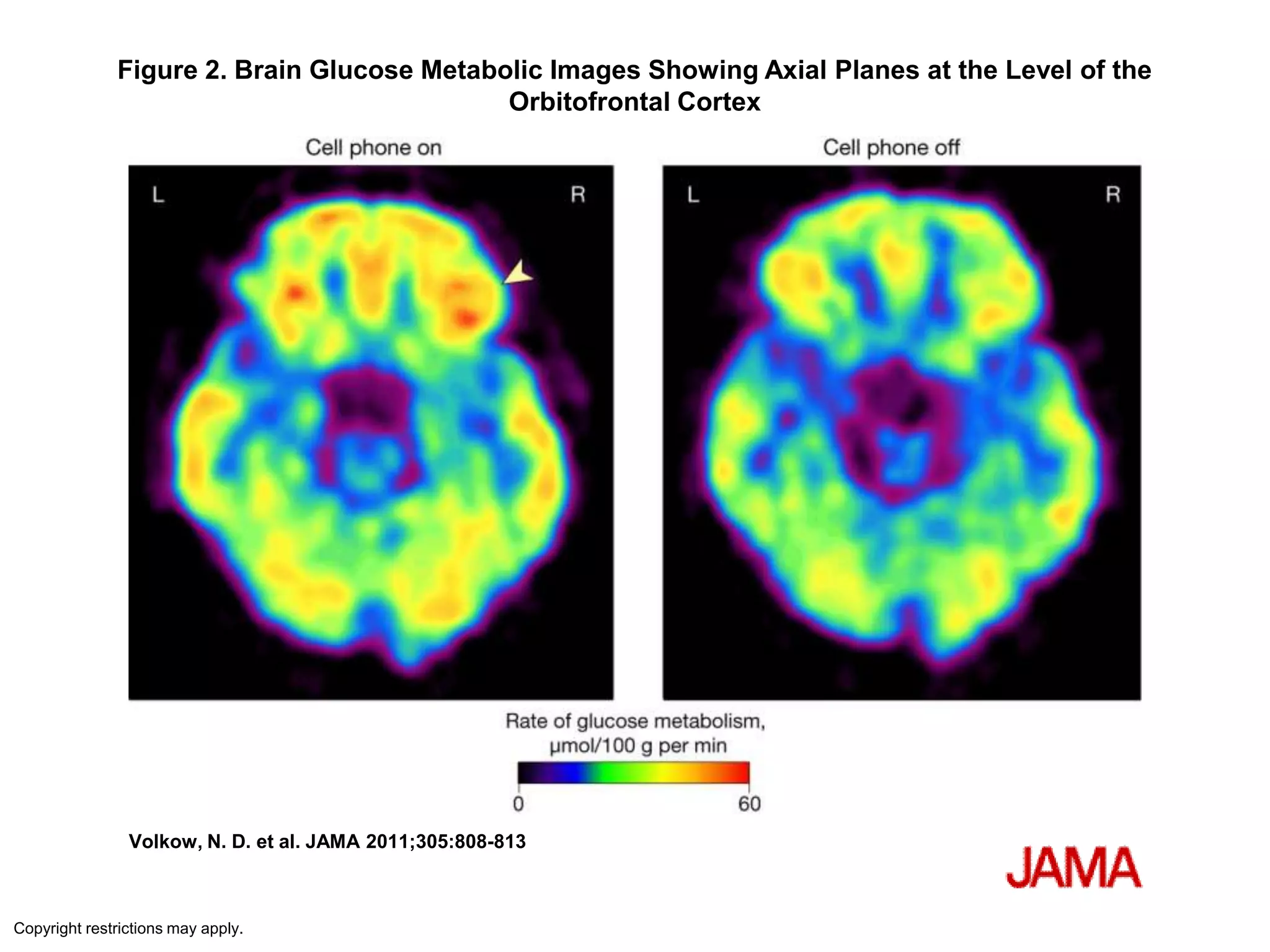
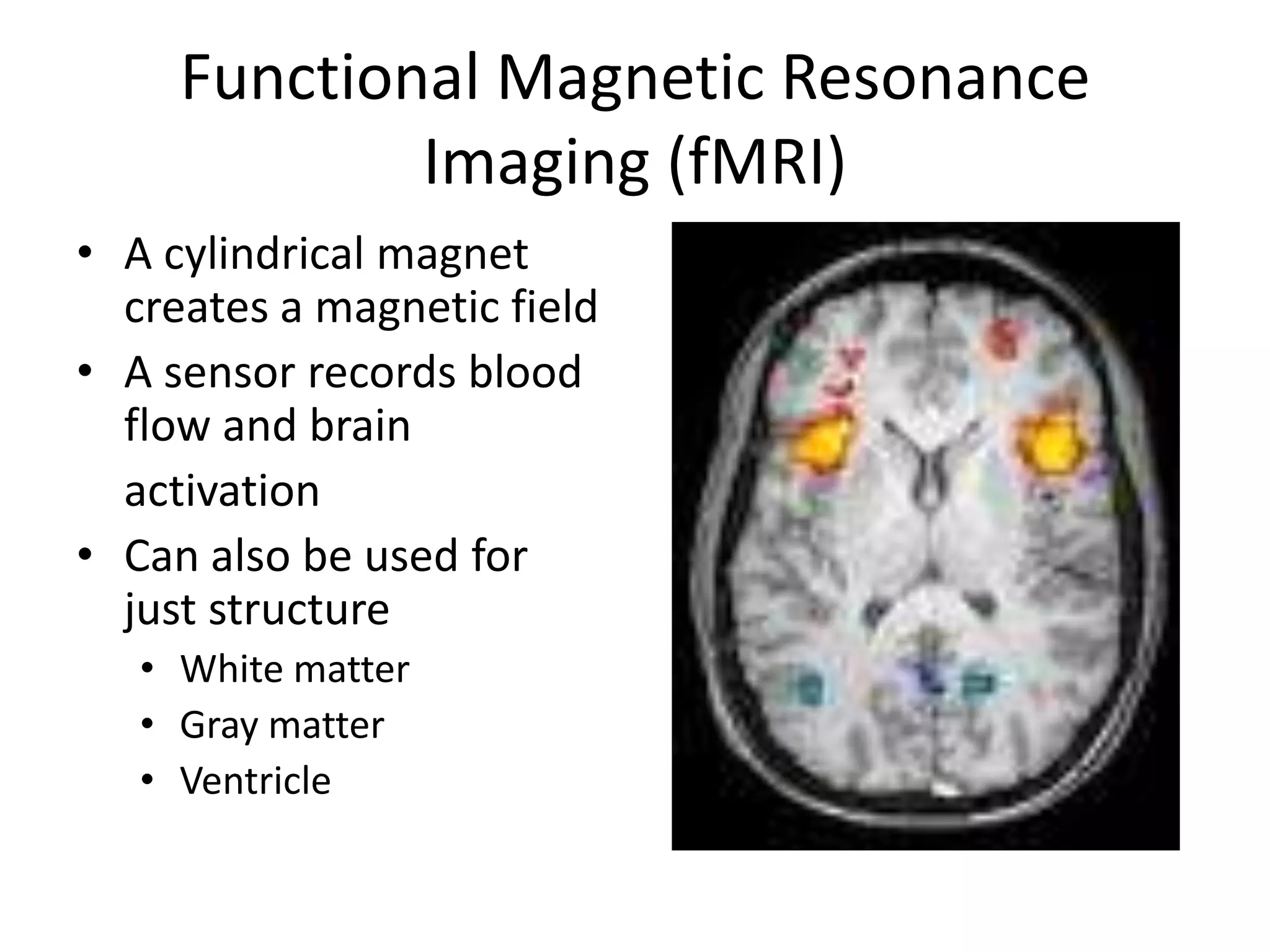
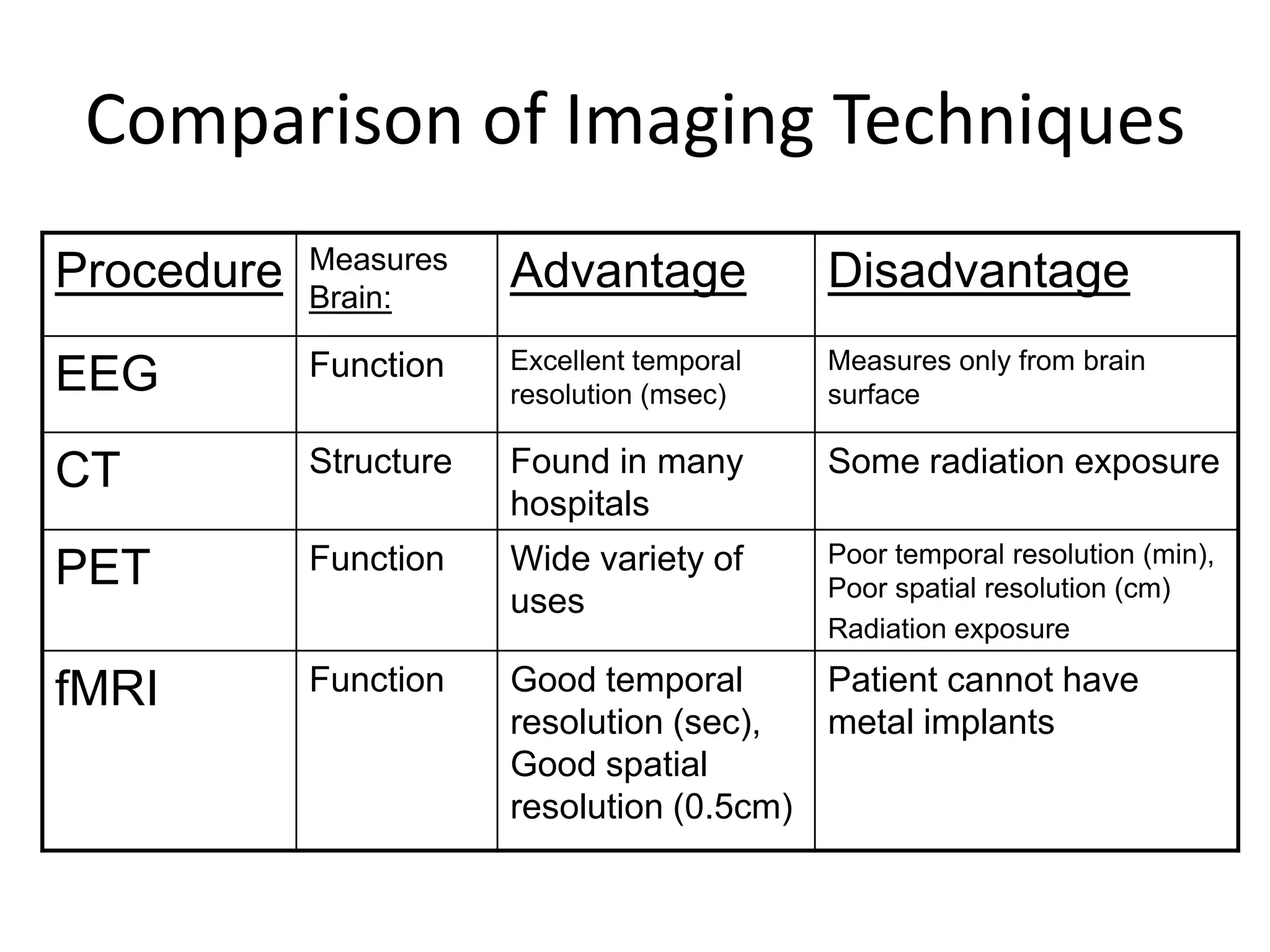
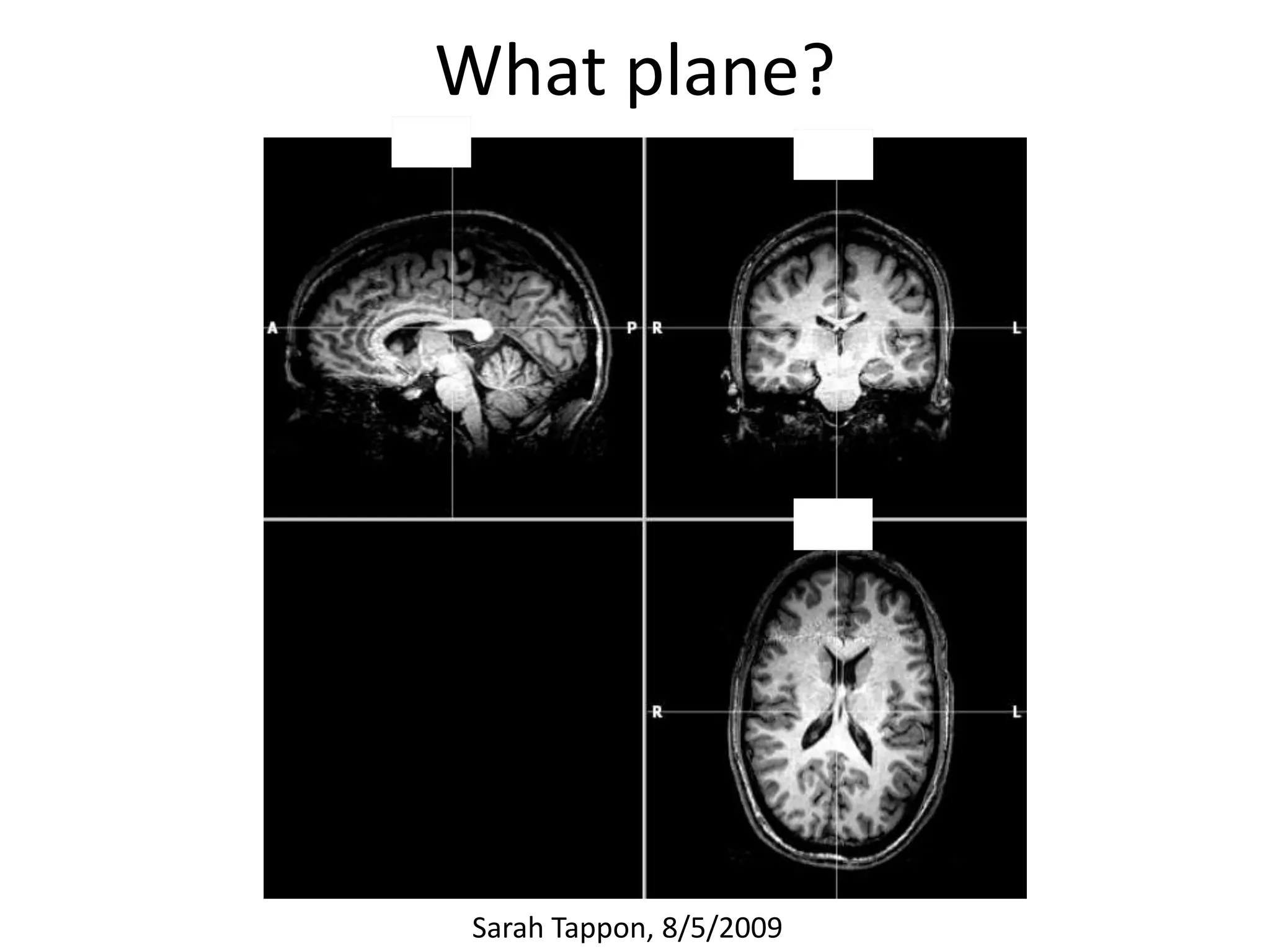
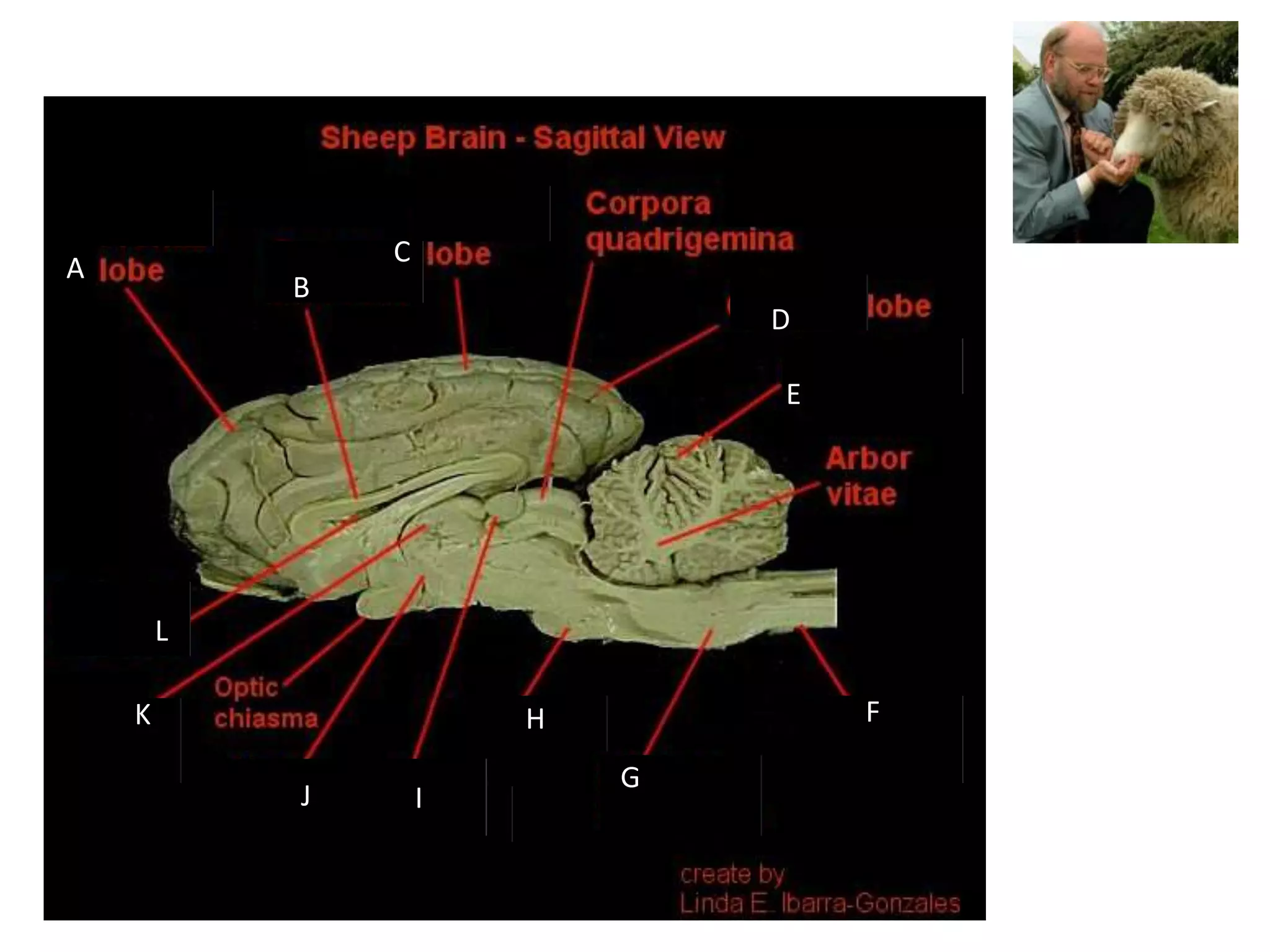
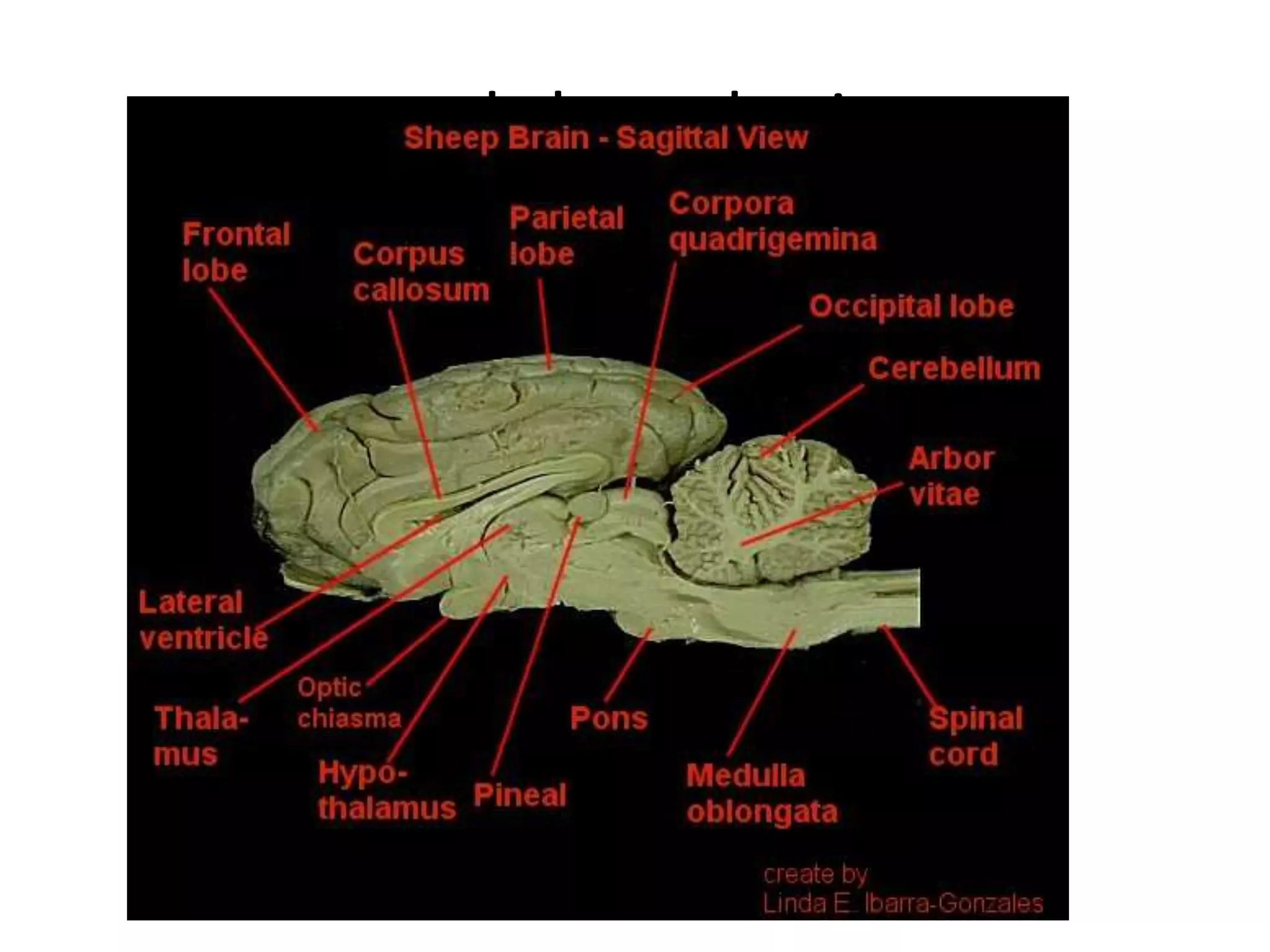
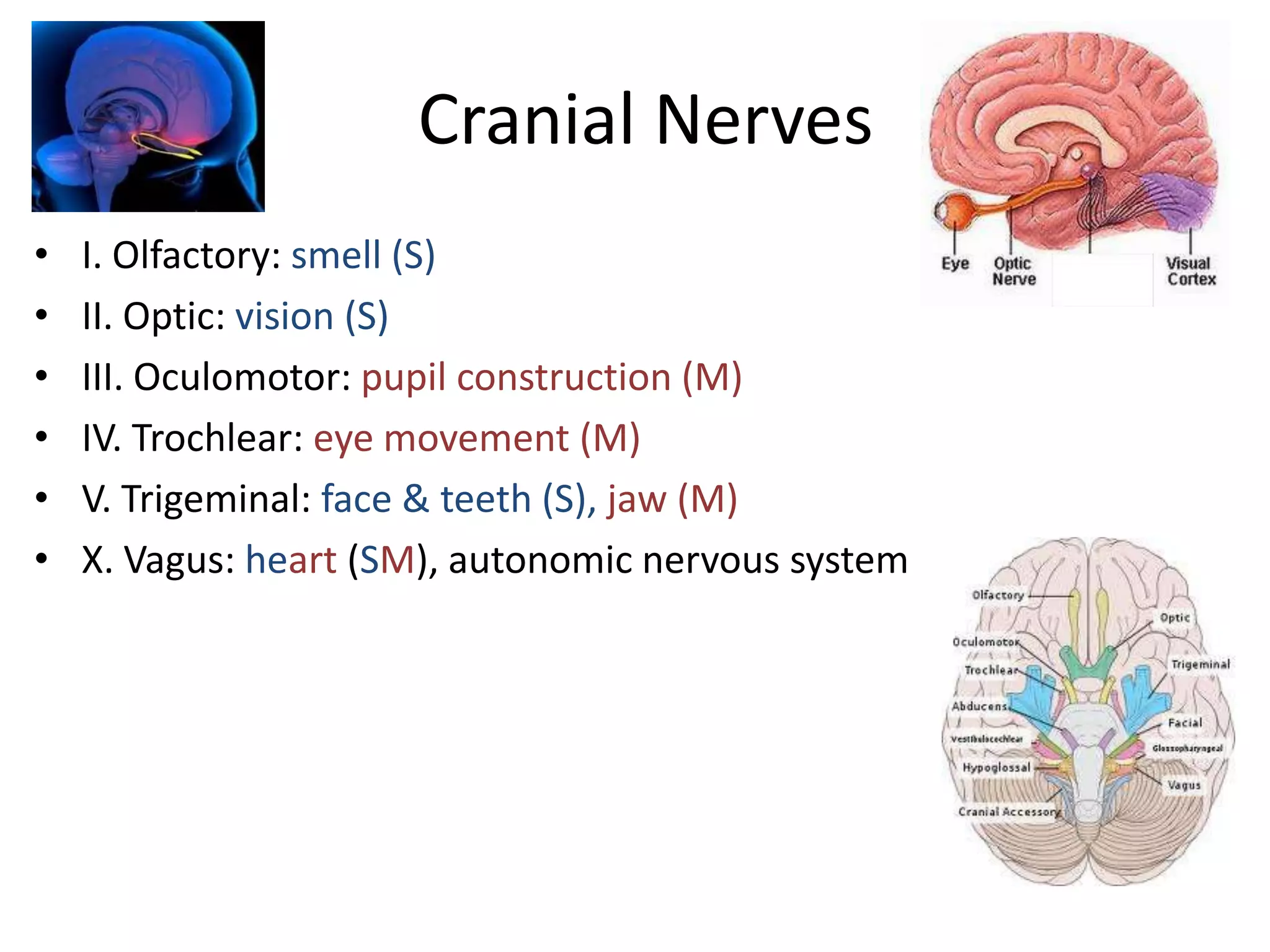
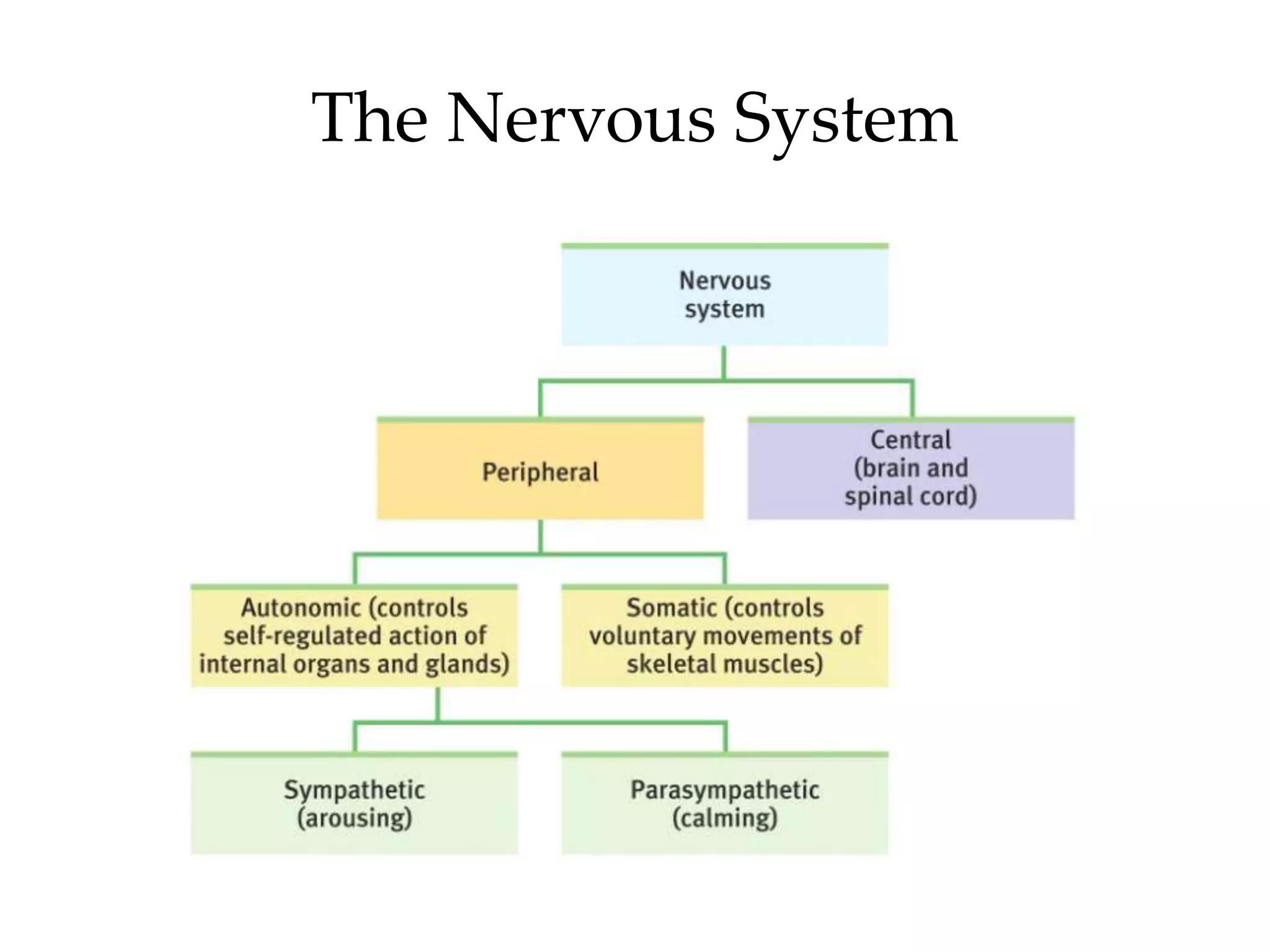
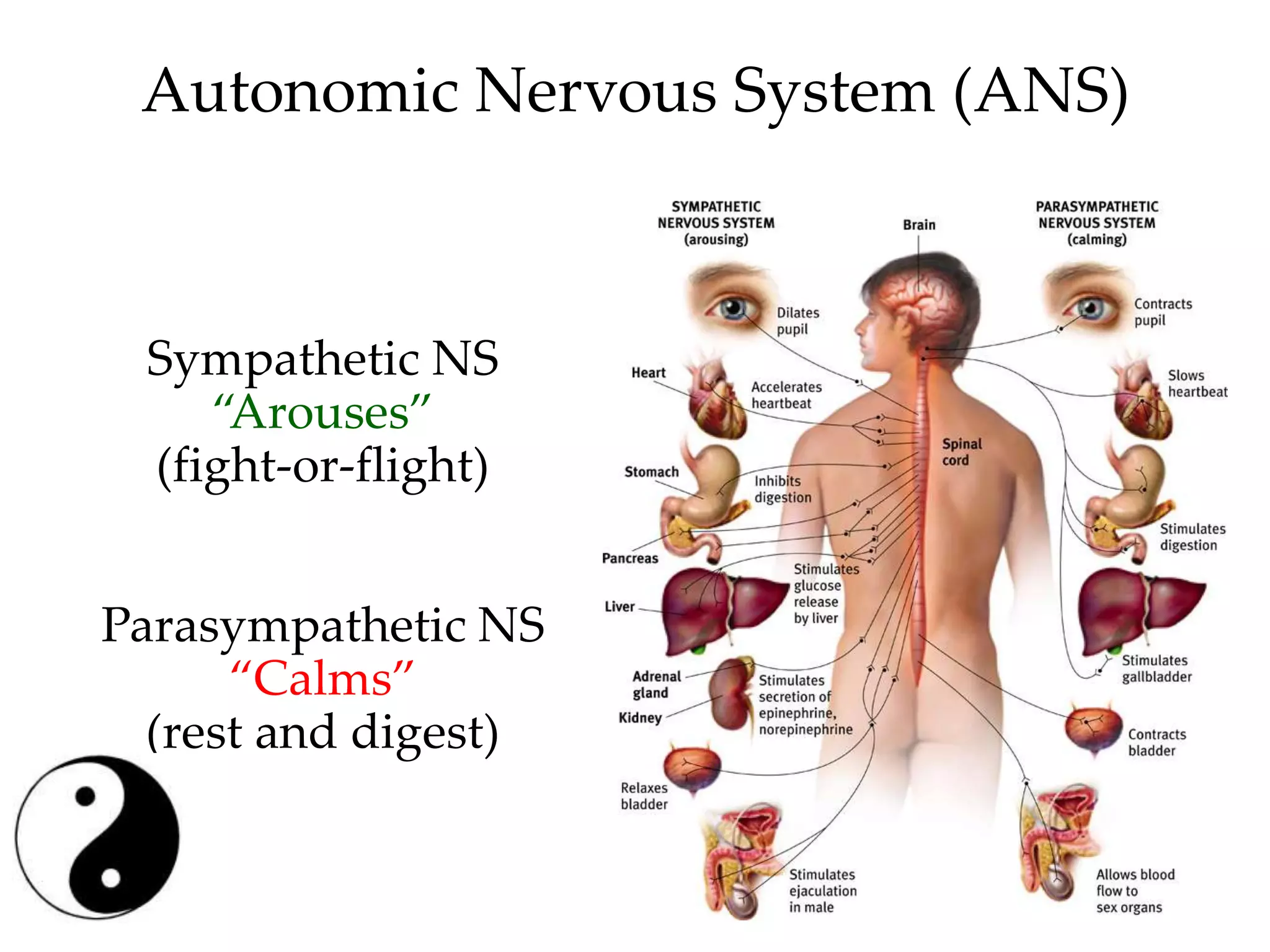
The document outlines key aspects of neuroanatomy and neurophysiology, including major brain areas such as sensory, motor, and emotional regions. It also describes various brain imaging techniques like EEG, CT, PET, and fMRI, detailing their advantages and disadvantages in studying brain function and structure. Additionally, it covers important structures and functions of the spinal cord and brain, emphasizing areas involved in cognition, memory, and emotional regulation.