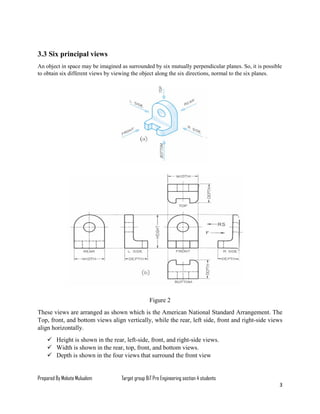
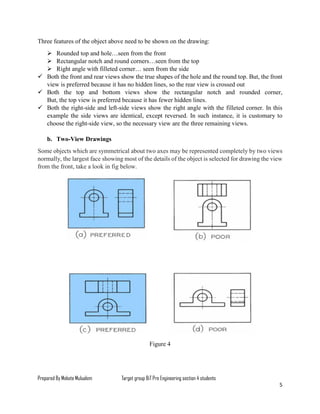
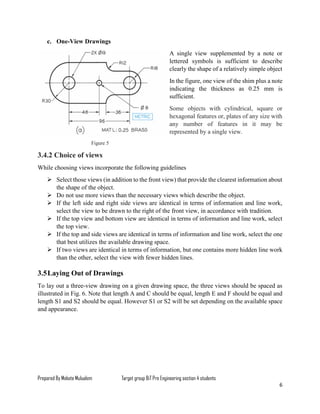
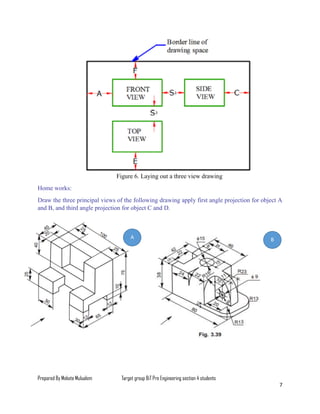
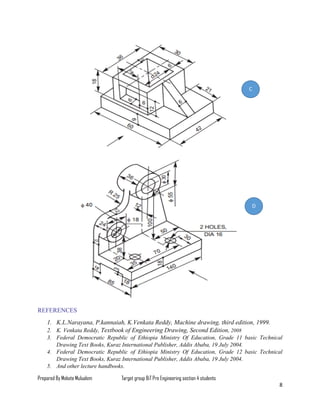
The document serves as a lesson on multi-view drawing for engineering students, detailing objectives such as preparing arranged views in first and third angle projections and identifying different surfaces. It explains the significance of multi-view projection in providing an accurate representation of objects through systematic arrangements of six principal views. Guidelines for selecting and laying out views in orthographic projections are also provided, supplemented by references for further reading.