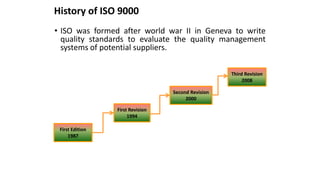
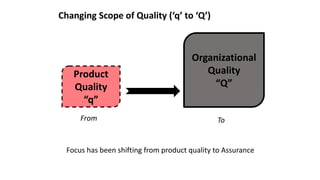
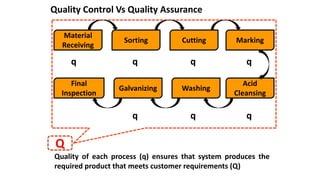
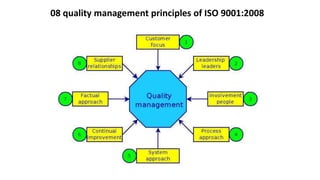
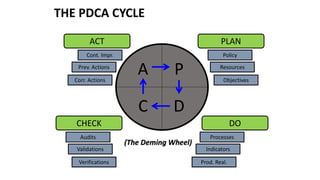
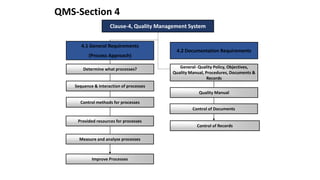
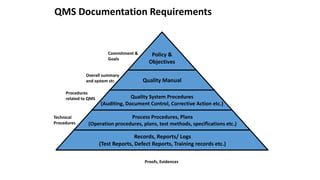
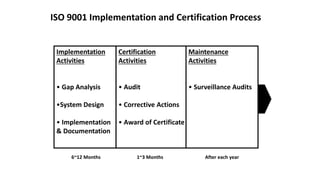
ISO 9001 is a standard for quality management systems that helps organizations ensure they meet customer and regulatory requirements. It contains requirements in areas like management responsibility, resource management, product realization, and measurement, analysis and improvement. Organizations can choose to certify their quality management system to the ISO 9001 standard to demonstrate they have an effective system in place. Benefits of certification include increased customer confidence, profits, and market share.