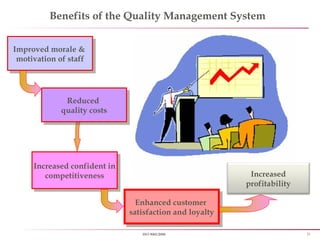
The document outlines the ISO 9001:2008 Quality Management System, detailing its history, aims, principles, and requirements. It emphasizes the importance of a process-based approach, employee involvement, and the benefits of certification for enhancing customer satisfaction and organizational effectiveness. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of continual improvement and established auditing processes to maintain compliance with the standard.






![7ISO 9001:2008
What is quality [1]
Degree of excellence/ Extent to which a product or a service satisfies
the customer expectation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iso90012008-151027170904-lva1-app6891/85/Iso-9001-2008-7-320.jpg)
![8ISO 9001:2008
What is quality [2]
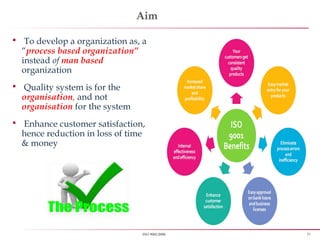
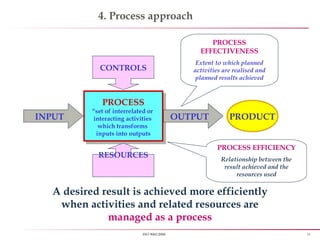
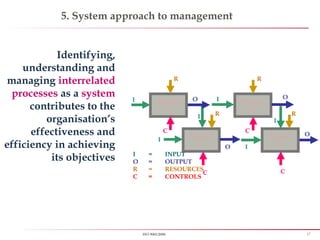
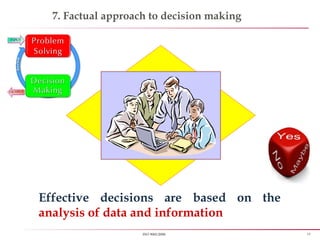
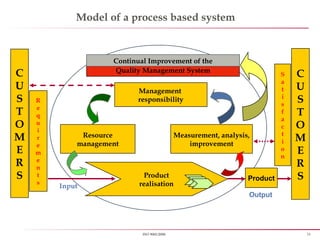
First rule of quality - An organization shall be a “Process based”,
instead of old tradition “Man based organization”
All process shall have a “Control measure”, hence ensuring low defect
and enhancing customer delight or satisfaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iso90012008-151027170904-lva1-app6891/85/Iso-9001-2008-8-320.jpg)