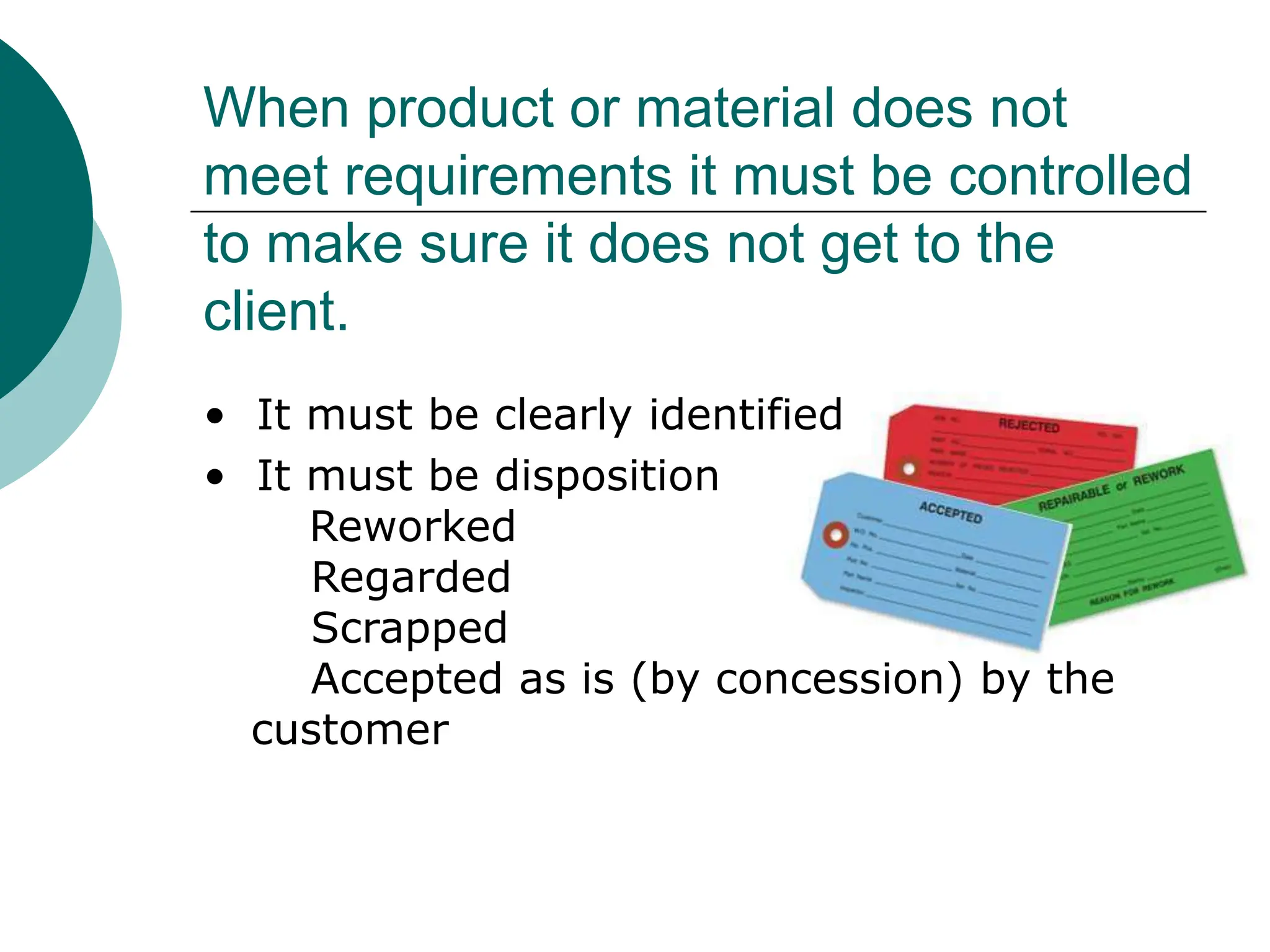
ISO 9001:2008 outlines the criteria for establishing an effective Quality Management System (QMS) that helps organizations manage processes, meet customer requirements, and achieve continual improvement. It emphasizes setting measurable quality goals, training employees, and controlling production processes to ensure product quality. Benefits of implementing ISO 9001 include increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced market opportunities.