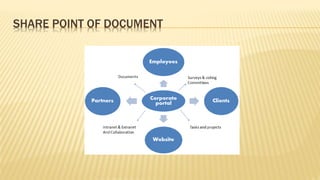
Pranjay Sadashiv Patil, a first year M.Pharm student, presented on documentation in pharmaceutical quality assurance. Documentation defines a system to minimize risks from misinterpretation or errors in oral communication. It includes specifications, test procedures, distribution records, and electronic data handling. Specifications provide parameters and limits for materials, equipment, and products. Test procedures must validate compliance to the end of shelf life. Controlled documents require approval and management of changes, while uncontrolled copies are for reference with a watermark.