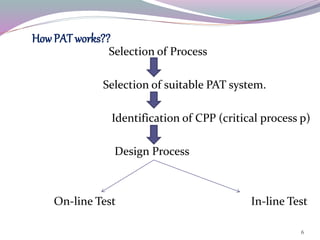
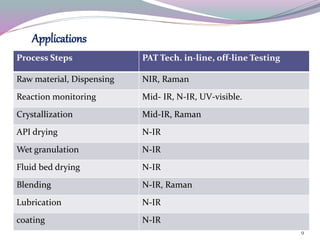
This document discusses Process Analytical Technology (PAT). It begins with an introduction to PAT, defining it as a system to design, analyze, and control manufacturing through timely measurements of critical quality attributes. It then discusses how PAT works by selecting a suitable PAT system and identifying critical process parameters. It highlights some key benefits of PAT such as improving process understanding and control, enhancing safety, and reducing variation. The document also provides examples of common PAT applications and discusses regulatory guidance around implementing PAT from agencies like the FDA.