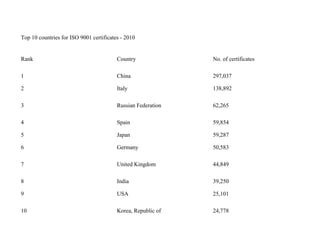
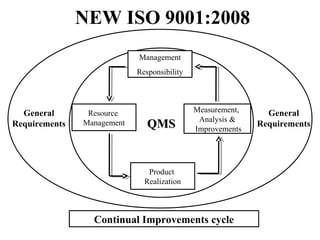
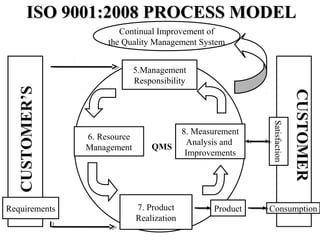
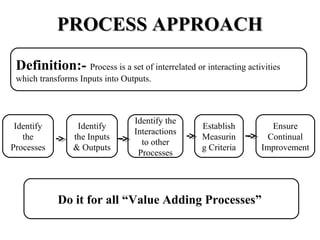
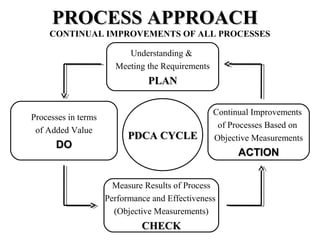
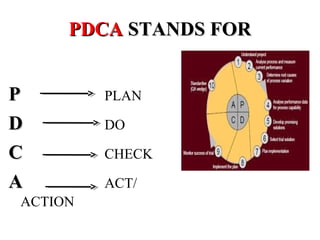
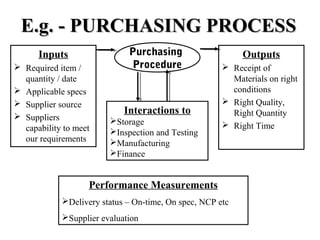
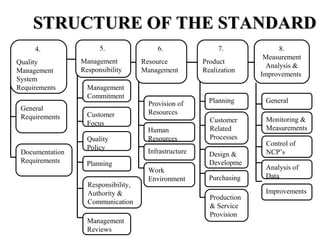
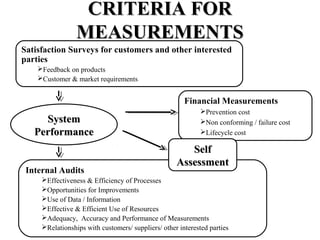
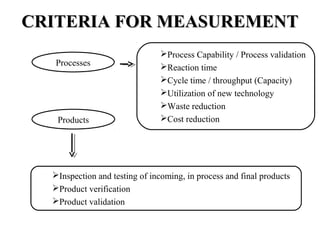
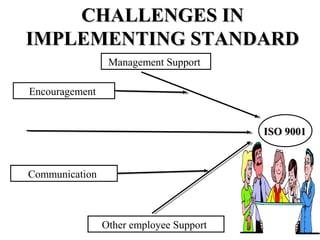
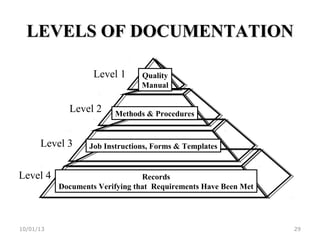
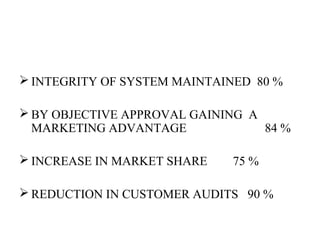
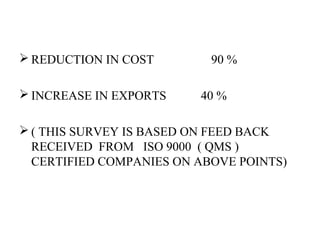
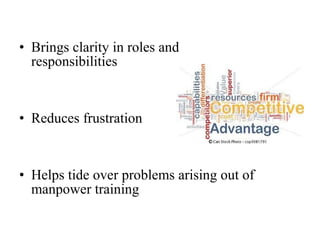
ISO 9001:2008 is an international standard for quality management systems. It provides requirements to ensure an organization consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. The standard is structured around Plan-Do-Check-Act cycles and emphasizes continual improvement. Certification to ISO 9001 can help organizations improve customer satisfaction, increase productivity and market share, and reduce costs.