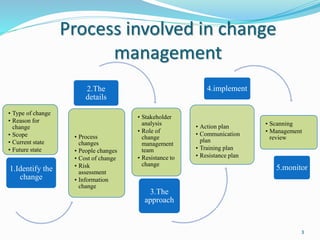
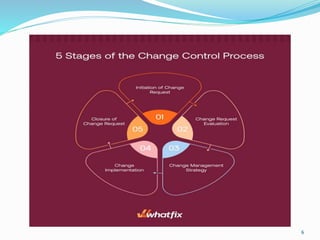
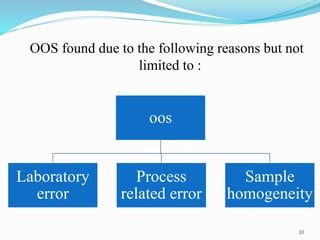
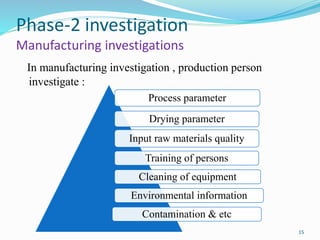
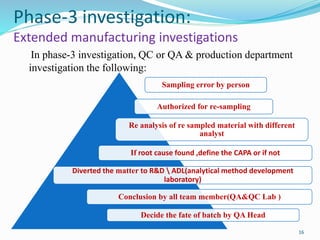
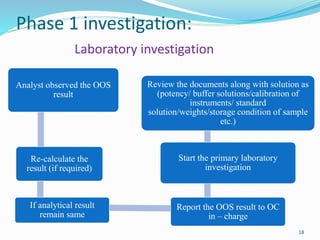
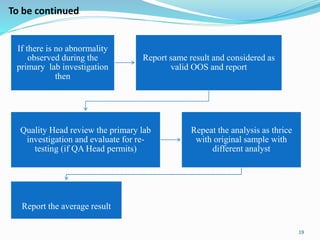
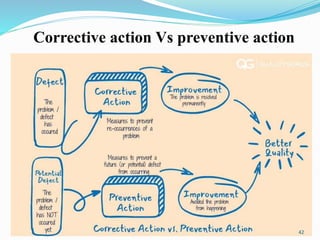
The document provides a comprehensive overview of change management, out-of-specification (OOS) handling, and complaint management within pharmaceutical quality assurance. It details processes for investigating changes, benefits of effective change management, definitions of OOS and out-of-trend results, and the necessary steps for managing complaints and conducting root cause analyses. Additionally, it covers the importance of corrective and preventive actions, product recalls, annual product reviews, and procedures for batch release and in-process quality control.