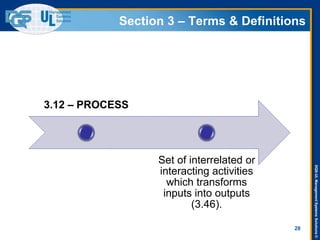
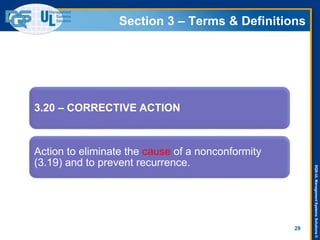
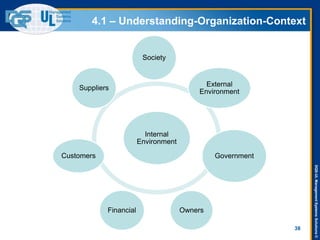
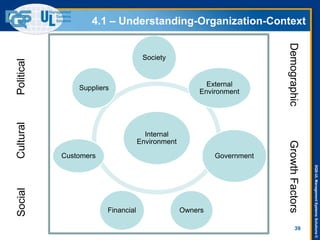
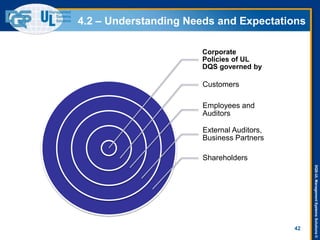
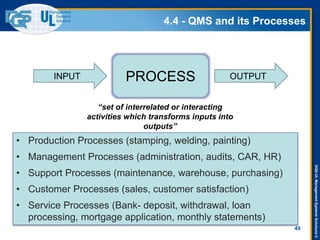
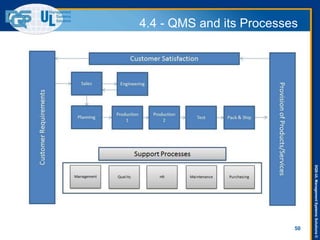
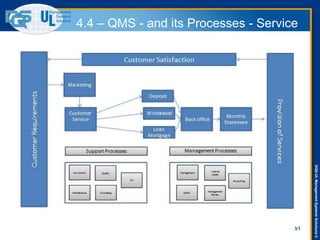
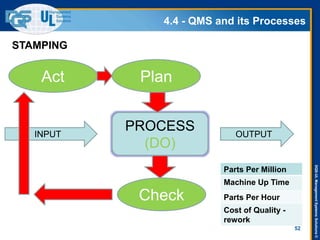
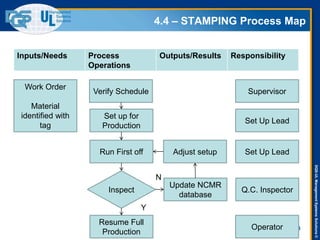
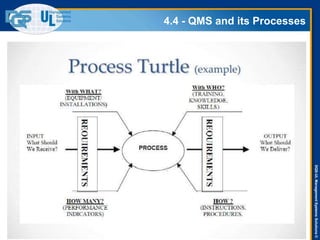
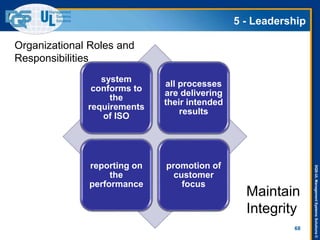
The document provides an overview of the ISO 9001:2015 standard, covering its scope, context of the organization, leadership, and the required documentation. It highlights key changes from previous editions, including the shift from an element-based approach to a process-oriented approach, with an emphasis on identifying and managing processes. The presentation also addresses questions from previous webinars related to implementation, risk management, and required documentation updates.