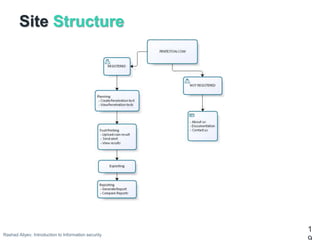
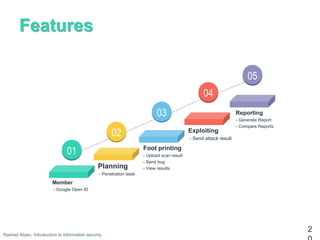
This document introduces information security topics. It discusses hackers and different types, vulnerabilities and how they work, footprinting and scanning techniques, and bug bounty programs. It also describes a penetration testing website that allows users to plan, perform exploits, generate reports, and view results. Useful links are provided for hands-on exercises in cross-site scripting, web application hacking, and cybersecurity competitions.