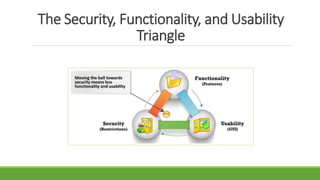
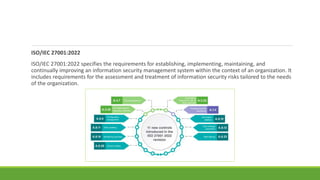
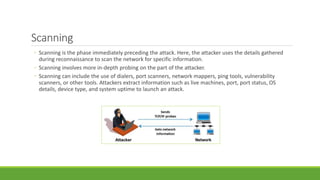
This document provides an overview of ethical hacking. It begins by defining information security and explaining the need for security. It then discusses what hacking is, different types of hackers (black hats, white hats, etc.), and hacker motives. It covers common attack vectors and the phases of a hacking attempt (reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, clearing tracks). Finally, it discusses what ethical hacking is, why it is necessary, skills required, and advantages/disadvantages. The document aims to give the reader a comprehensive introduction to the topics of hacking and ethical hacking.