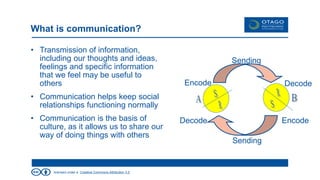
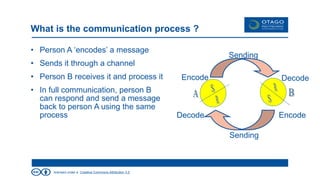
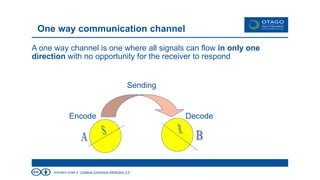
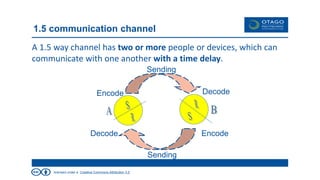
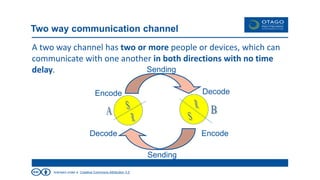
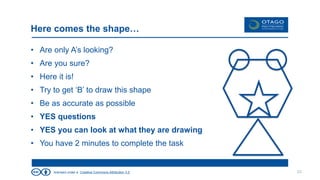
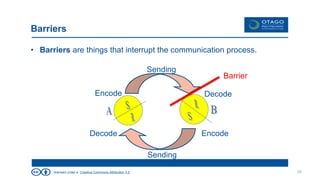
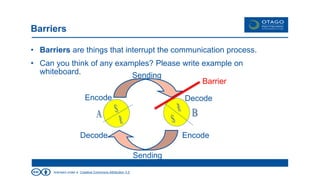
The document explores the theory of communication, detailing its processes, types, and channels, while highlighting the importance of non-verbal cues and the potential barriers that can disrupt effective communication. It categorizes communication into one-way, 1.5 way, and two-way channels, describing their characteristics and providing examples. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of choosing the right communication channel to enhance understanding and avoid misinterpretations.