Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,905 times




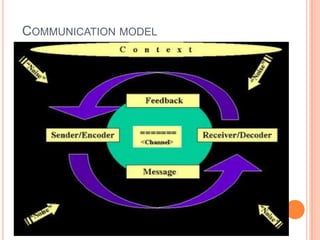









Oral communication describes any interaction that uses spoken words to convey a message. It has several advantages like being more time efficient and allowing for immediate feedback and clarification. However, it also has limitations such as messages not being retained for long and the inability to take back words once spoken. Effective oral communication requires clear pronunciation, brevity, precision, conviction and choosing appropriate words and register for the audience. It can be improved by reading, listening, and practicing speaking in different situations. Common types include face-to-face interactions, video conferencing, telephone calls, presentations, interviews and group discussions.












