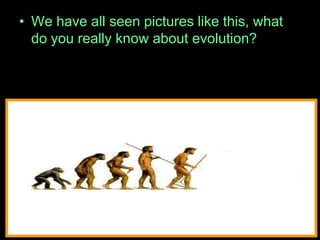
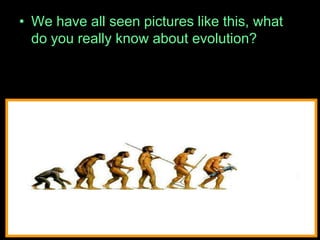
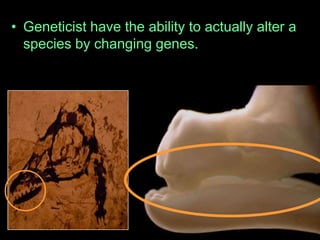
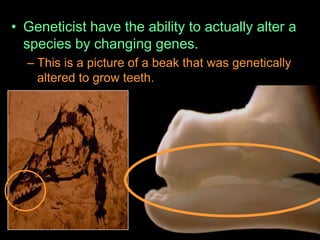
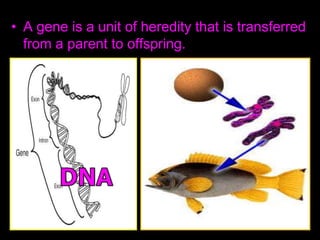
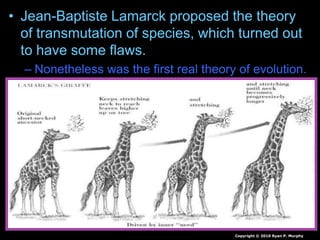
The document is a presentation about evolution and related topics. It discusses key figures in the development of evolutionary theory like Charles Darwin, Alfred Russel Wallace, and John Scopes. It also summarizes the Scopes Monkey Trial and how the theory of evolution was initially controversial but is now widely accepted in biology. The presentation provides overviews of natural selection, evidence of evolution, human evolution, and ecological succession.