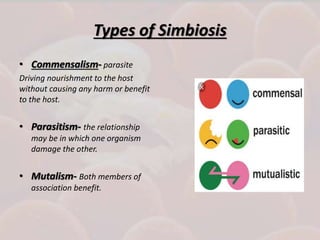
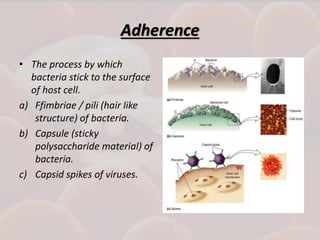
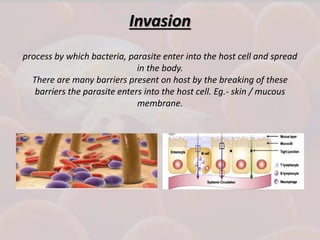
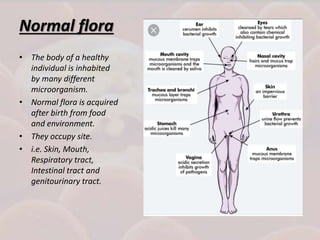
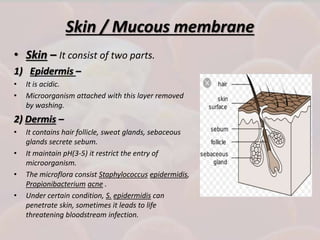
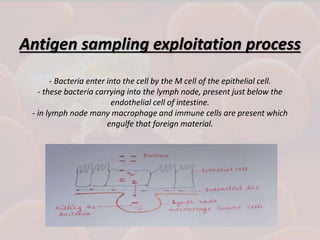
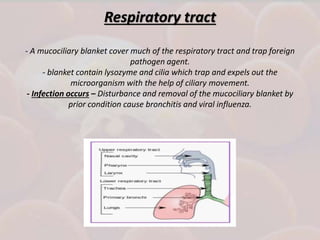
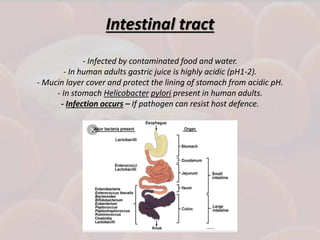
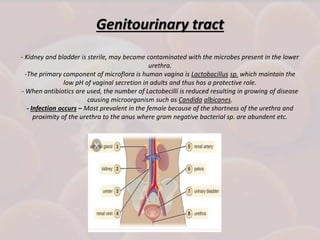
This document discusses host-parasite relationships and the entry of microorganisms into hosts. It defines key terms like host, parasite, pathogen, and explores different types of symbiotic relationships like commensalism, parasitism, and mutualism. Normal flora that benefit hosts are present in various sites like the skin, mouth, respiratory and intestinal tracts. Microorganisms can enter through these areas, especially if barriers are disrupted. Entry is also possible directly through uptake or antigen sampling in mucous membranes.