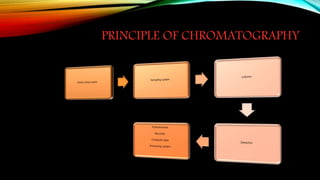
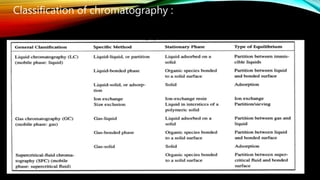
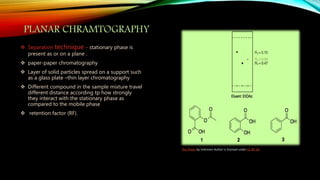
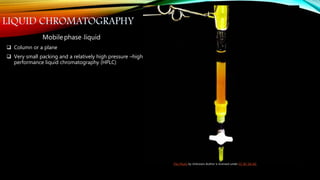
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures by distributing components between a stationary and mobile phase. It works on the principle that different compounds interact differently with the phases and therefore move through the system at different rates. There are various types of chromatography classified by mobile phase (gas or liquid) or interaction forces (adsorption, partition, ion exchange). Key components are the mobile phase, stationary phase, and supporting medium. Chromatography is widely used in fields like analytical chemistry, biochemistry, environmental analysis and forensic science.