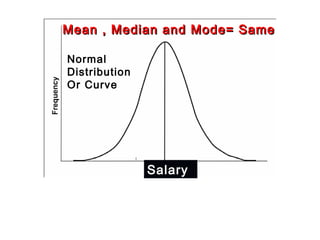
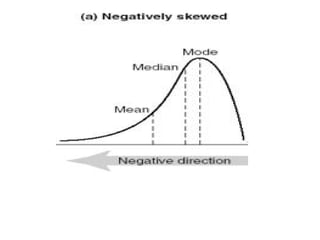
This document introduces common measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variation (range, variance, standard deviation, coefficient of variation) in biostatistics. It defines each measure and provides examples of calculating and interpreting them. The mean is the most common measure of central tendency but the median is more robust to outliers. The choice of central tendency measure depends on whether the data is skewed. The mode is used for measuring popularity. Measures of variation quantify how spread out the data values are.