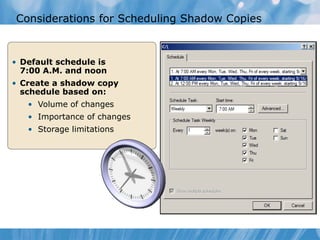
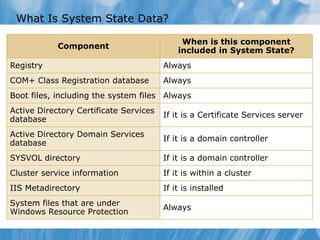
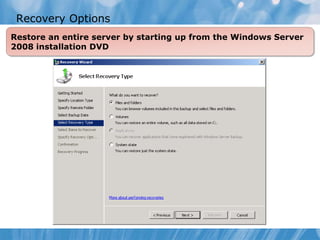
This document covers the recovery of network data and servers through shadow copies and Windows Server Backup. It includes how to configure shadow copies, restore data from them, and different types of backups available in Windows Server. The document also discusses user rights for backing up data and system state data components.