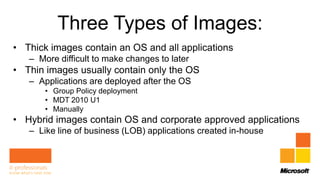
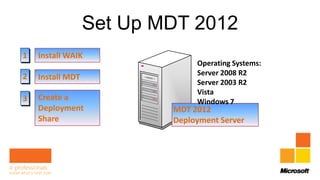
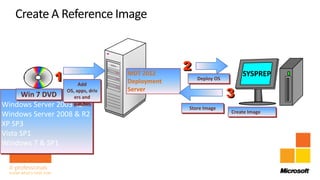
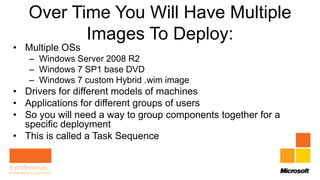
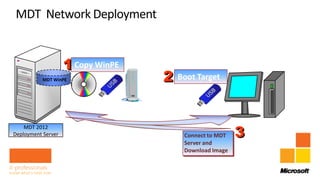
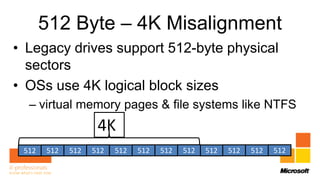
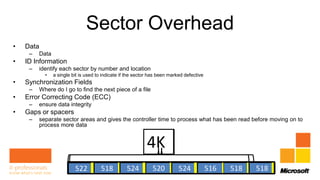
Rhonda Layfield gave an introduction to Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT) 2012. She discussed image formats like .wim and .vhd, deployment scenarios, setting up MDT, creating task sequences, and automating deployments. New features in MDT 2012 include support for UEFI, .vhd images, and cross-platform deployments. Rhonda also covered master images, updating deployments, and 512 byte sector alignment issues.