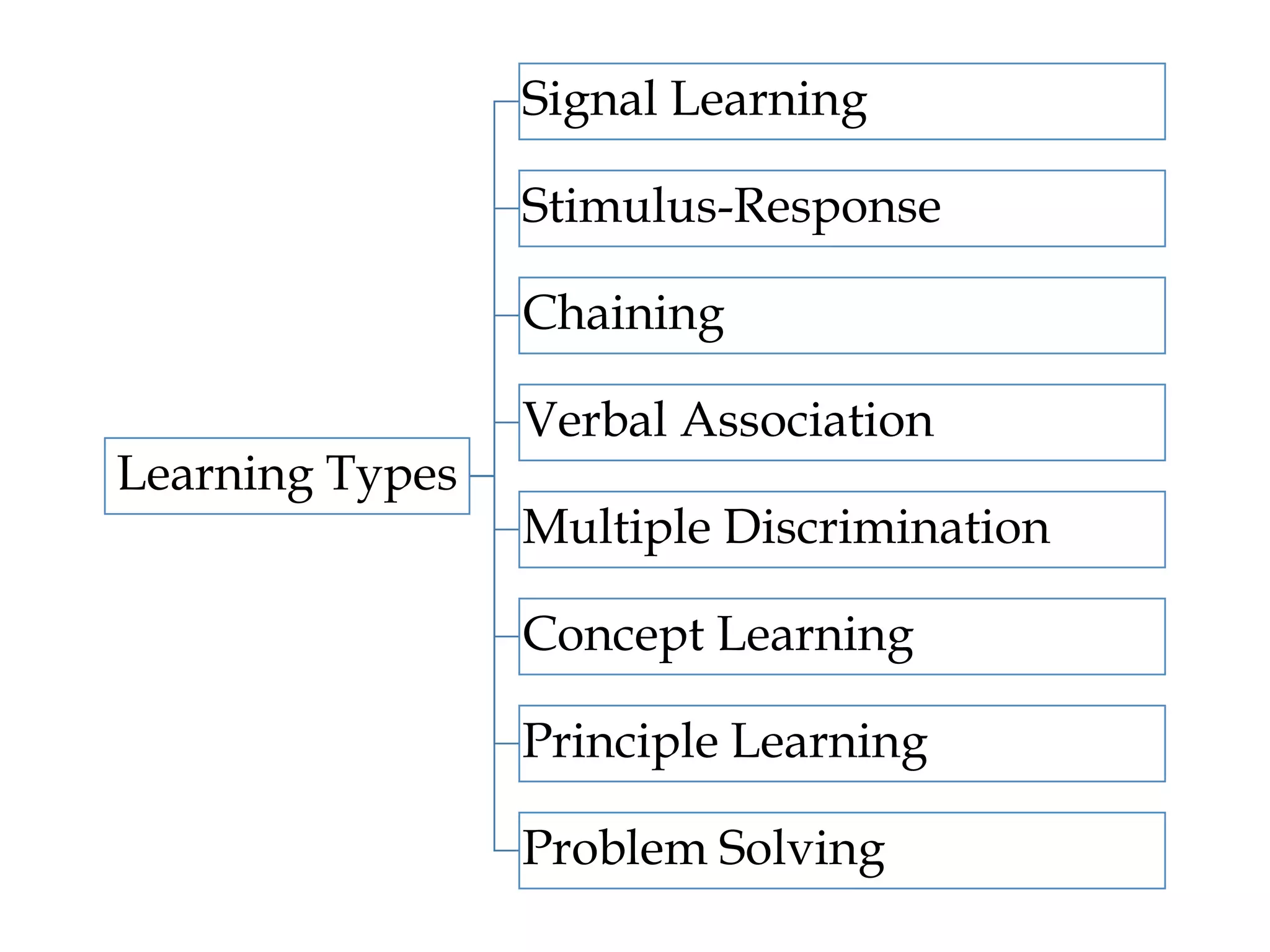
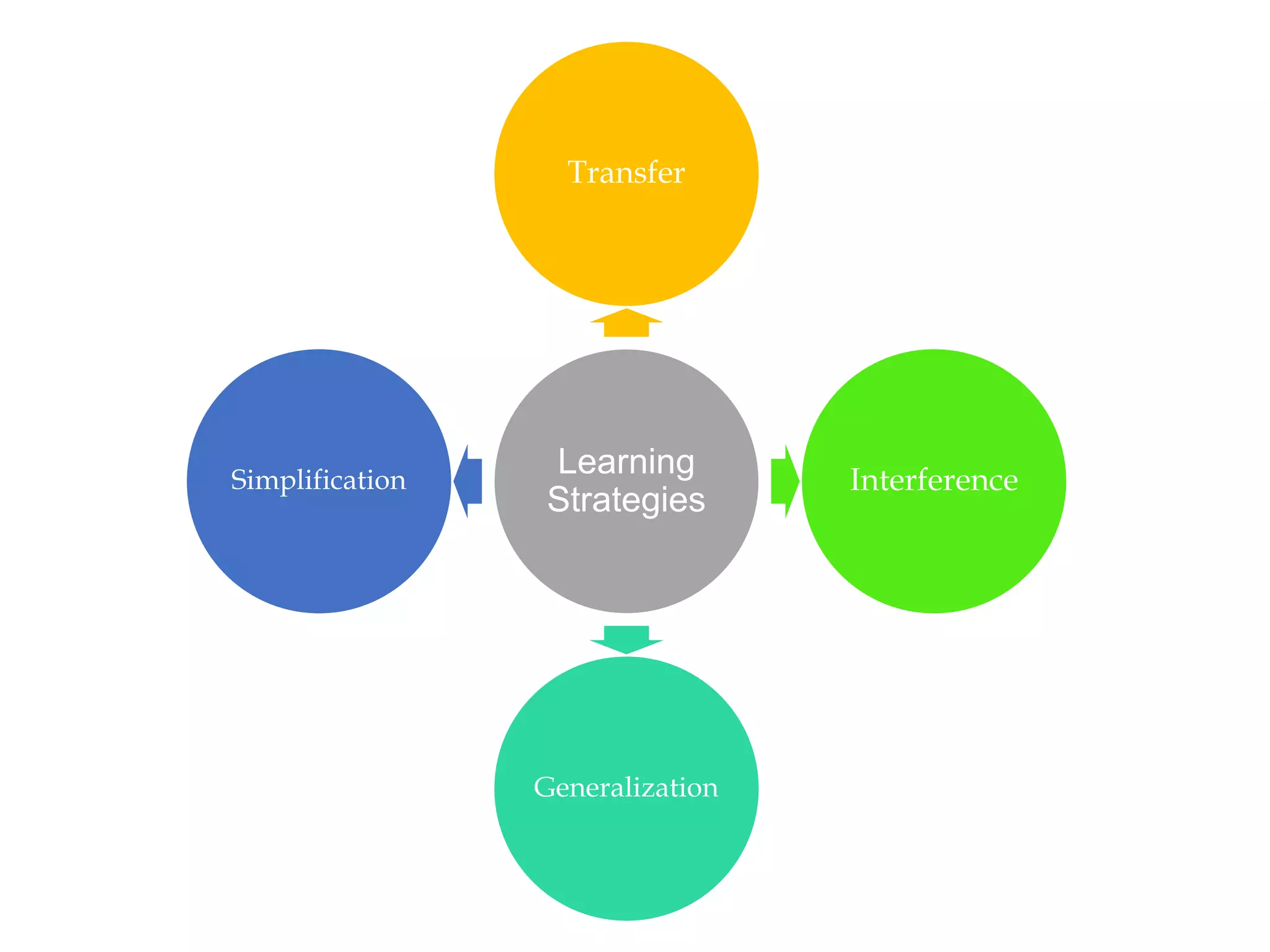
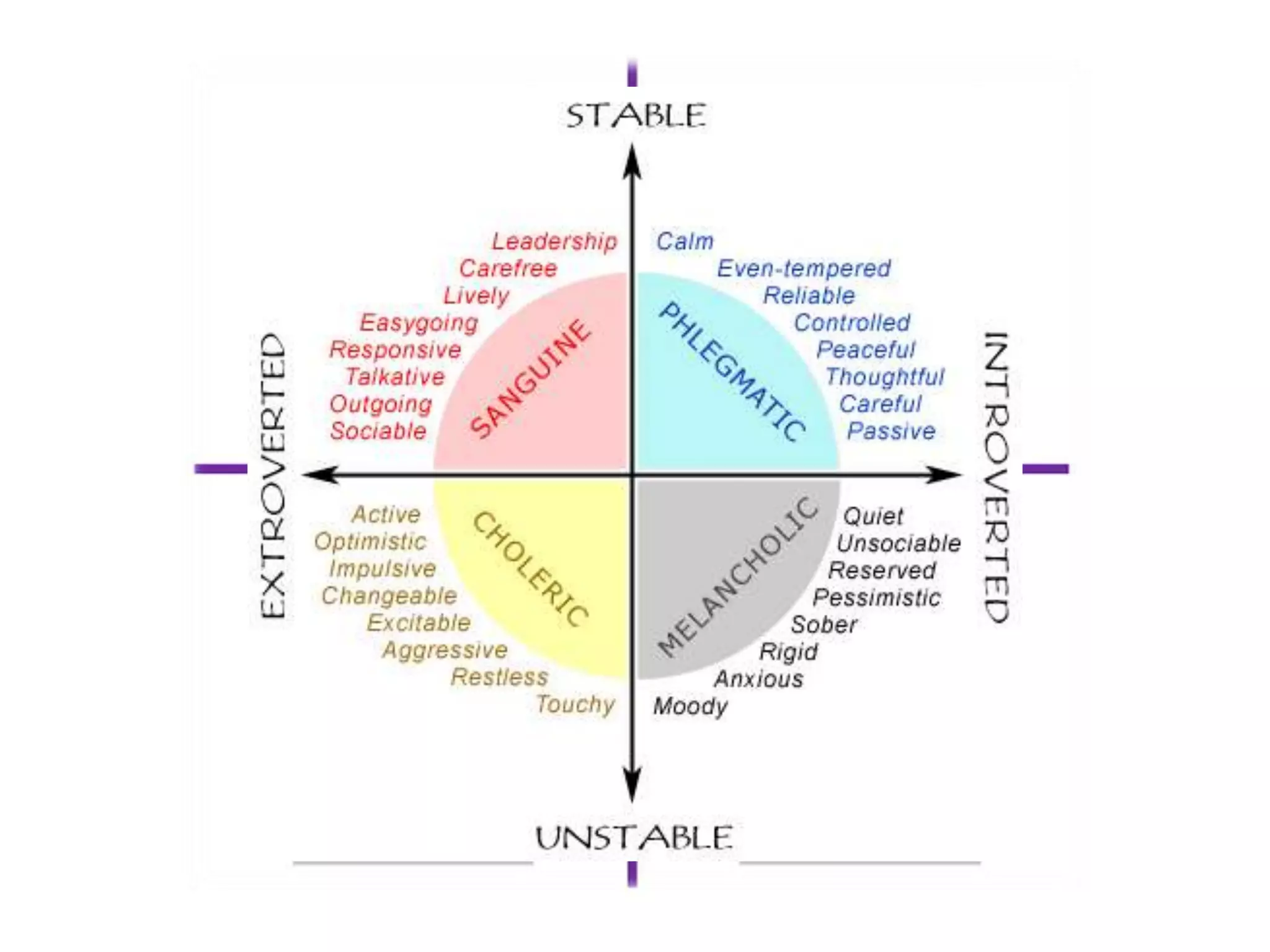
Edi Brata discusses language acquisition in three sessions:
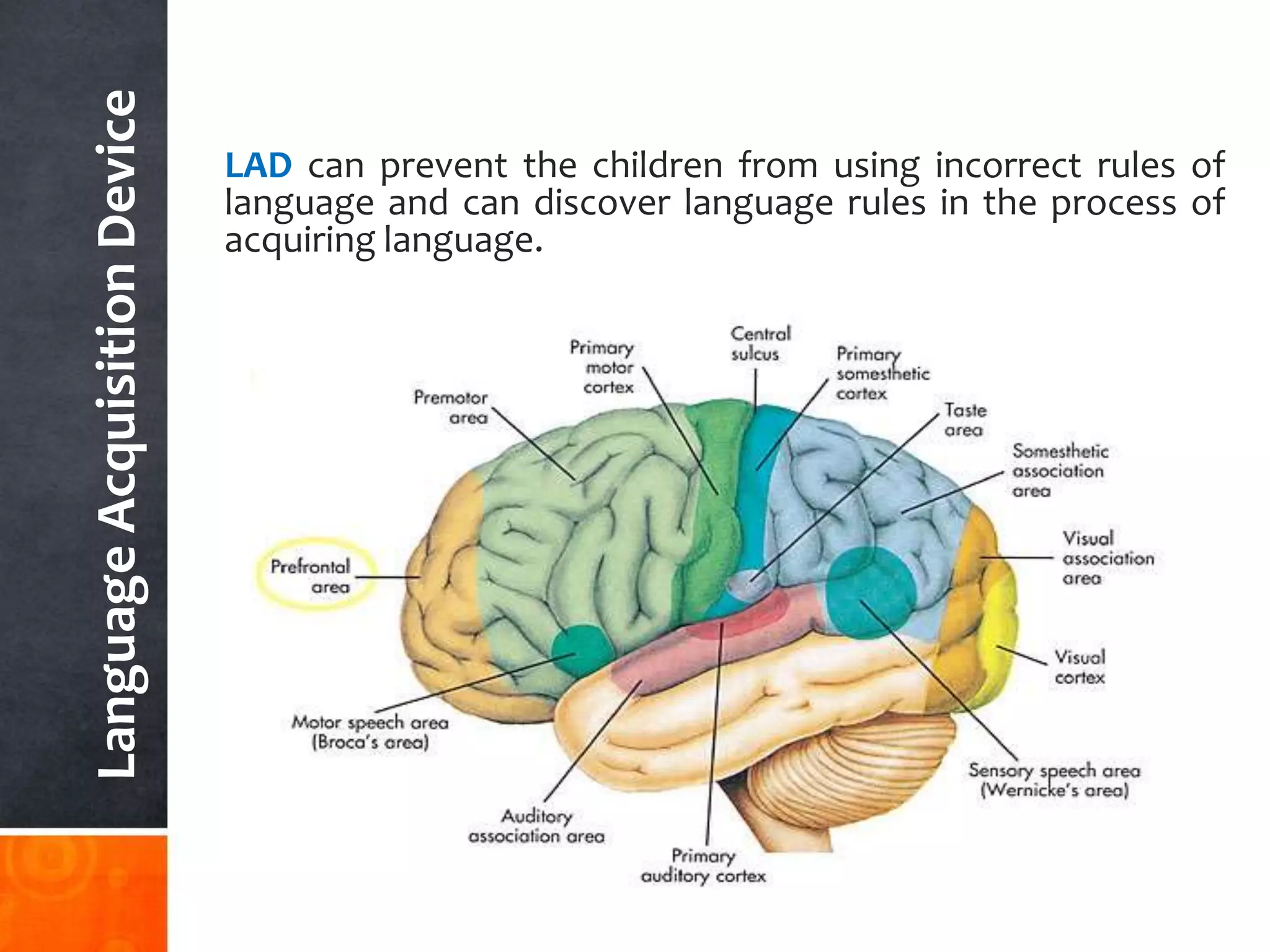
1) First language acquisition - Children acquire language naturally through exposure and without formal teaching. Nativist theories posit an innate language acquisition device.
2) Second language acquisition - Similar to first language but with native language interference. Requires sufficient exposure and practice using the new language.
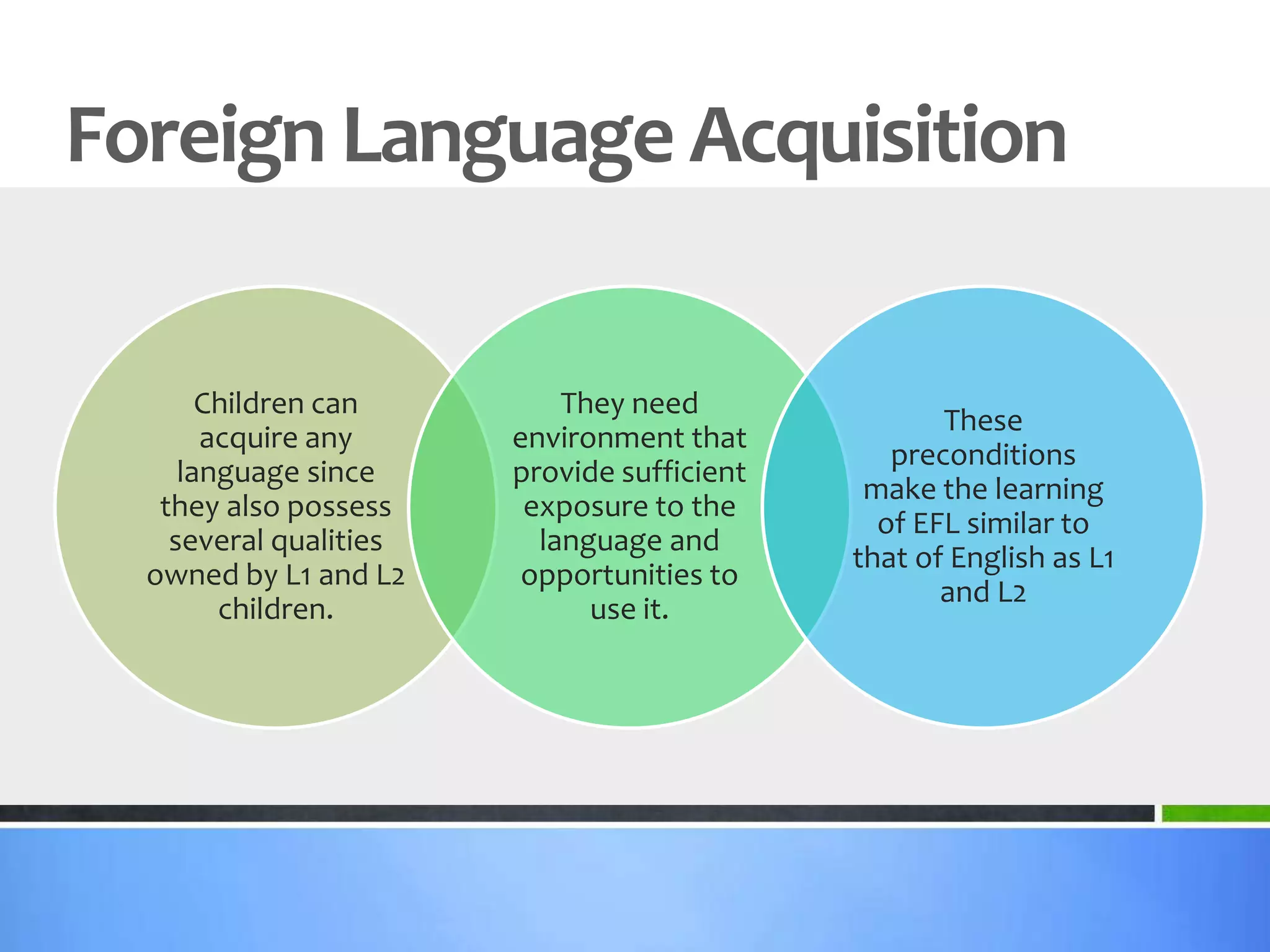
3) Foreign language acquisition - Children can acquire any language like L1 if the environment provides sufficient exposure and use, though adults face disadvantages like a lack of a critical period. Both children and adults learn via similar cognitive mechanisms.